Free Food Safety Template Hub
Use more than 200 free resources of food safety checklists, posters, forms, logs, eBooks, and much more.
Download a Free Template Pack
based on your custom filters
Food Safety Templates Hub: Posters, Checklists, Logs, Signs, Smart Tools, and More
This food safety templates hub provides essential resources designed to help maintain the highest standards of food hygiene and compliance.
Whether you operate a small café, a large restaurant chain or a food production facility, our comprehensive suite of food safety posters, checklists, logs, eBooks, and customizable templates is extensive to meet your unique needs.
Food safety posters: visual reminders for best practices
Visual aids like our Kitchen Safety Poster and Hand Washing Poster are crucial in reinforcing proper food handling practices and hygiene practices. Display these posters at strategic points in the kitchen and dining areas of your food establishment to remind staff of essential procedures like handwashing, correct food storage, and cross-contamination prevention, which are pivotal in preventing food contamination.
Our Fridge Layout Poster and Food Cooling Poster are specifically popular for helping staff understand the correct storage and cooling processes, essential for maintaining proper temperature and critical for food safety in any food service operation. These signs with symbols provide quick, clear food safety tips and reinforce standard food safety procedures.
Customizable food safety templates: streamline your safety processes
Our customizable templates are essential tools for comprehensive food safety management, allowing you to manage food safety protocols effectively. For example, the Food Safety and Sanitation Template and the SSOP (Standard Sanitation Operating Procedures) Template enable you to tailor your cleanliness standards to meet food safety requirements and regulatory needs.
The Restaurant Opening Checklist and Closing Checklist Templates are crucial in ensuring that all aspects of your operation are reviewed and ready for business each day, aligning with health department guidelines and risk-based preventive controls.
Comprehensive food safety checklists: your daily compliance partners
Use our Restaurant Cleaning Checklist to maintain a clean and safe environment daily. The Health Inspection Checklist is designed to align with local health codes to prepare for unexpected visits, supporting regular inspections and adherence to food safety tasks.
Our Temperature Log Sheet and Pest Management Plan Checklist are pivotal in monitoring critical areas that affect food safety, like correct temperature settings and potential risks in food handling. These tools help create a routine that staff can follow, enhancing food safety training efforts and maintaining public health standards.
Food safety signs and printables: essential tools for a safe environment
Our Food Allergy Warning Signs and Allergen Posters are vital for ensuring customer safety, effectively communicating potential hazards, and food safety risks associated with allergens. These resources are invaluable in environments with high customer turnover and diverse dietary needs.
Additionally, the Proper Food Storage Chart and Temperature Danger Zone Chart serve as quick references for safe temperature and proper food storage practices, crucial for preventing food poisoning and food contamination.
Food safety logs: essential tools for accurate record keeping
Maintaining detailed food safety logs is a crucial component of any effective food safety management system. Logs such as the Temperature Log Sheet and Thermometer Calibration Log provide a systematic way to record critical data, which is essential for monitoring safe food products and ensuring the safety of cooked foods and perishable foods.
These logs are indispensable for tracking cooking, holding, and storage temperatures, enabling quick responses to food safety issues and risk of contamination. They also provide valuable data during health inspections and are critical in tracing the source of any issues, protecting your business against liability.
Food safety charts: visual guides for quick reference
Food safety charts, like the Food Temperature Chart and Proper Food Storage Chart, offer visual reminders of critical control points in food handling and storage. These charts can be strategically placed in food preparation and storage areas to provide staff with at-a-glance information that supports best practices in food safety.
Displaying these charts in key areas of your kitchen ensures that all staff can easily reference them during their daily tasks, such as using a food thermometer to check internal cooking temperatures for types of food like hamburger patties or fresh produce.
Smart tools for more efficient food safety management
Some of our free digital resources such as the smart tool Recipe Card Generator and Food Cost Calculator, help save you time but also reduce errors in kitchen management. This is thanks to the fact that you can edit as well as add/or remove rows.
This built-in customizability is important because it enables you to fill, for example, a product specification template neatly in a PDF format instead of potentially illegible paper copies that risk getting damaged or lost.
5 Benefits of using these food safety resources in your food business
1. Enhanced compliance and reduced risk
Using our comprehensive food safety resources ensures that your business complies with local and international food safety regulations, including those from the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA).
Tools like the HACCP Plan Template and Health Inspection Checklist prepare your operation to meet stringent standards and pass inspections, reducing the risk of violations and potential fines. This proactive approach protects your business from legal issues and reputational damage.
2. Improved efficiency and consistency
Our customizable templates and checklists, such as the Opening and Closing Checklist and Restaurant Cleaning Checklist, streamline daily operations regular basis. When you standardize procedures, these tools ensure consistency in your service and safety protocols, improving efficiency and helping maintain the quality of food items across the food industry.
3. Increased staff accountability and training
Visual aids like the Kitchen Safety Poster and Hand Washing Poster serve as constant reminders for your staff, reinforcing proper practices and enhancing effective training efforts. The Cutting Board Color Chart and Meat Cooking Chart are practical tools that assist in training new employees, ensuring everyone follows the same food handling standards. These resources foster a culture of safety and accountability among your team.
4. Enhanced customer trust and satisfaction
Implement visual food safety measures such as displaying Food Allergy Warning Signs and using the Allergen Poster on menus to communicate your commitment to food safety. This transparency builds trust and reassures customers about the quality and safety of the food served, enhancing your business’s reputation.
5. Cost savings and waste reduction
Effective use of our food safety resources like the Food Expiration Dates Guidelines Chart and Vacuum-Sealed Food Shelf Life Chart helps manage inventory more efficiently and reduce food waste. The Food Cost Calculator and Recipe Card Generator aid in portion control and budgeting, minimizing costs. You'll likely achieve significant cost savings when you reduce waste and optimize food usage.
8 Practical tips for incorporating food safety resources to enhance food safety culture
1. Integrate into employee onboarding and training
Start by embedding food safety resources like the Hand Washing Poster, Meat Cooking Chart, and Food Allergy Warning Signs into your onboarding and training programs. Use these materials as visual aids during training sessions to emphasize the importance of food safety from day one.
Regularly schedule refresher courses that incorporate these resources to keep food safety top of mind and ensure that teams can effectively adopt new standards or procedures.
2. Develop role-specific guides
Create role-specific guides using our templates and checklists, such as the Kitchen Safety Poster for cooks and the Restaurant Cleaning Checklist for janitorial staff. Tailor these guides to address the unique responsibilities of each role within your food business.
This customization helps employees understand their direct impact on food safety and how they can contribute to maintaining high standards.
3. Foster open communication
Encourage an open environment where staff feel comfortable discussing food safety issues. Use resources like the Allergy Matrix and Food Traceability Templates as discussion starters in team meetings to review procedures and encourage suggestions for improvement.
Gather feedback on the usability and effectiveness of the food safety resources you implement, and be responsive to suggestions for changes or additional tools.
4. Recognize and reward compliance
Implement a recognition program to reward employees who consistently adhere to food safety practices, such as correctly using the Temperature Log Sheet or updating the Food Cost Calculator accurately.
Publicly acknowledging these positive behaviors not only boosts morale but also reinforces the importance of everyone's role in upholding food safety standards.
5. Use technology for engagement
Leverage digital tools like the Food Safety Plan Template and Digital Temperature Logs to engage staff with interactive elements. For example, integrating quizzes or interactive checklists within digital platforms can make the learning process more engaging.
Technology can also provide real-time updates and reminders to staff about critical tasks, further embedding food safety into daily operations.
6. Manage change effectively
When introducing new resources, such as a new version of the HACCP Plan Template or a revised Restaurant Equipment List, manage the change process carefully. Provide clear explanations for the change, and offer training to ensure all team members understand how to use the new resources.
Consider a phased rollout where you introduce changes gradually, allowing staff to adjust and provide feedback on their experience.
7. Create a safety committee
Establish a food safety committee that includes members from various levels of your organization. This committee should meet regularly to review safety performance, discuss issues highlighted by using resources like the Health Inspection Checklist and Pest Control Checklist, and plan for ongoing safety initiatives.
Having a dedicated team focused on food safety ensures continuous attention to improving standards and practices across the business.
8. Document and analyze incidents
Use incident reports and tools like the Food Recall Template and Hazard Analysis Template to document and analyze any safety incidents. Regular analysis helps identify trends or areas for improvement, and sharing these findings with your team can help prevent future incidents.
This practice not only improves safety outcomes but also demonstrates a commitment to learning and improvement within your food safety culture.
As you integrate these practical tips, your food business will enhance its food safety culture, making food safety a clear priority and shared value among all team members. This approach not only helps in complying with regulations but also builds a foundation for a sustainable and responsible business.
Download our free resources or sign up for a 14-day free trial and see how easy it is to set up your digital Food Safety Management System!
Make food safety easy with FoodDocs
Food Safety and Quality Managers, as well as their teams, use our food safety compliance software to meet regulatory standards.
Since business operations can vary so widely, FoodDocs is a fully customizable software solution that can meet their specific needs. Plus, you can easily digitize your food safety processes and ensure compliance in just 15 minutes.
Move from piles of paperwork to a single digital tool for managing compliance
- Get a food Safety Solution with a smart monitoring app, fast HACCP builder, and all-in-one traceability system
- Monitor any kind of food safety process with a real-time dashboard
- Easily comply with HACCP, SQF, FSMA, ISO 22000, BRC standards, and more
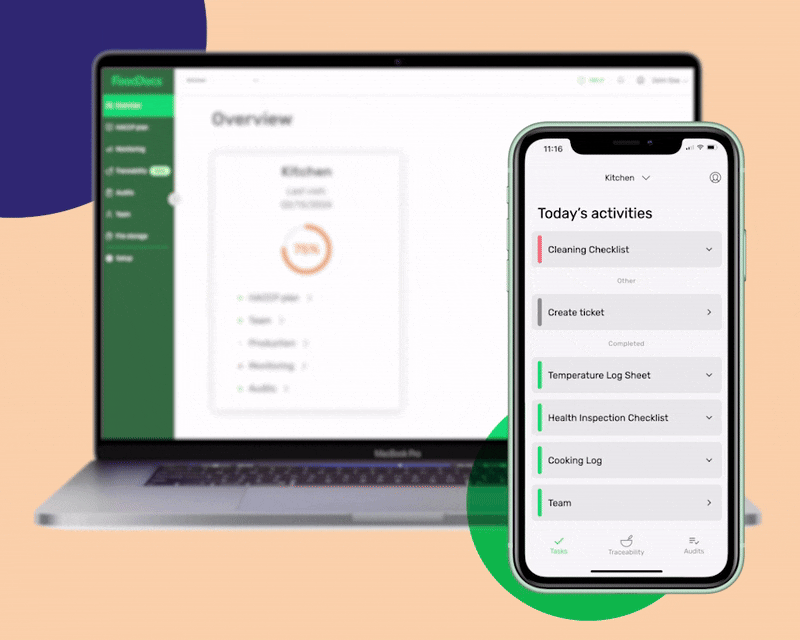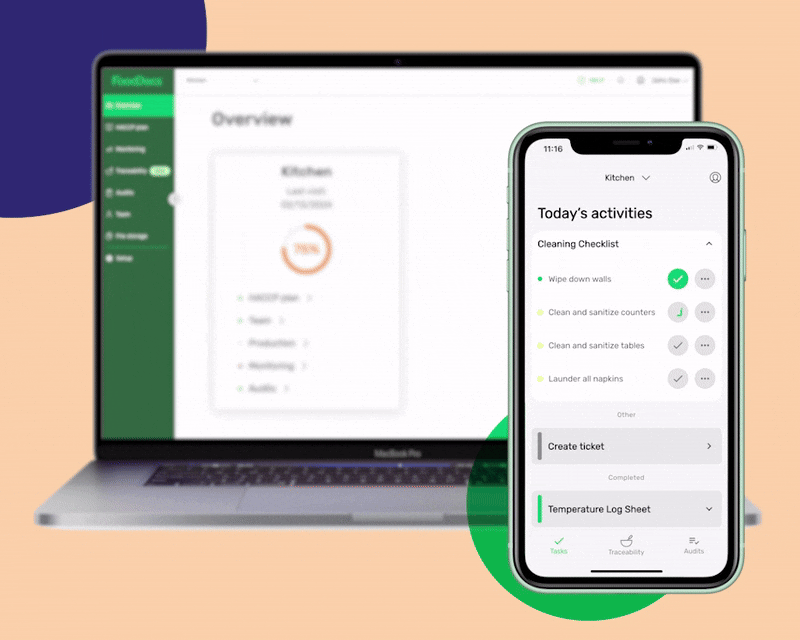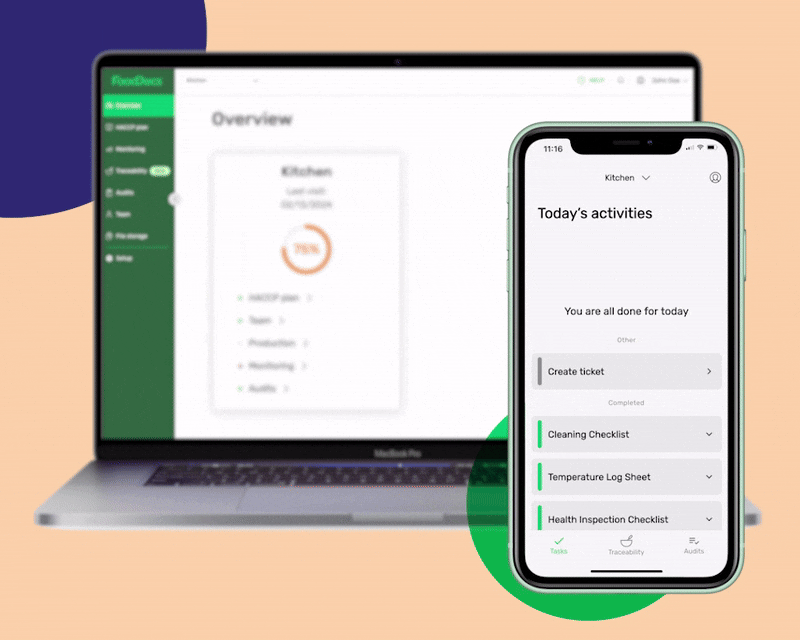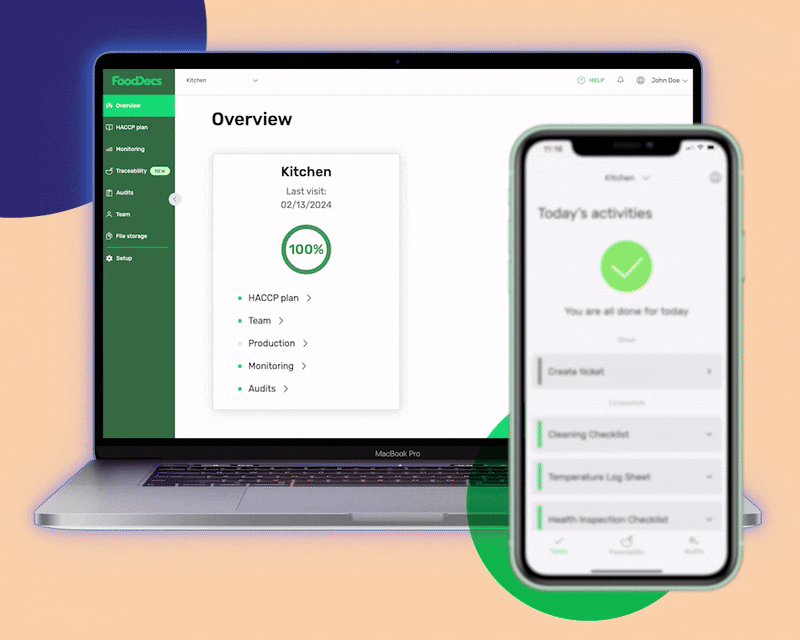
Customize the digital solution to your exact business operations
- Use our ready-made checklist templates to get started fast
- Build your detailed tasks with as much detail as you need
- Assign each task to team members based on their roles
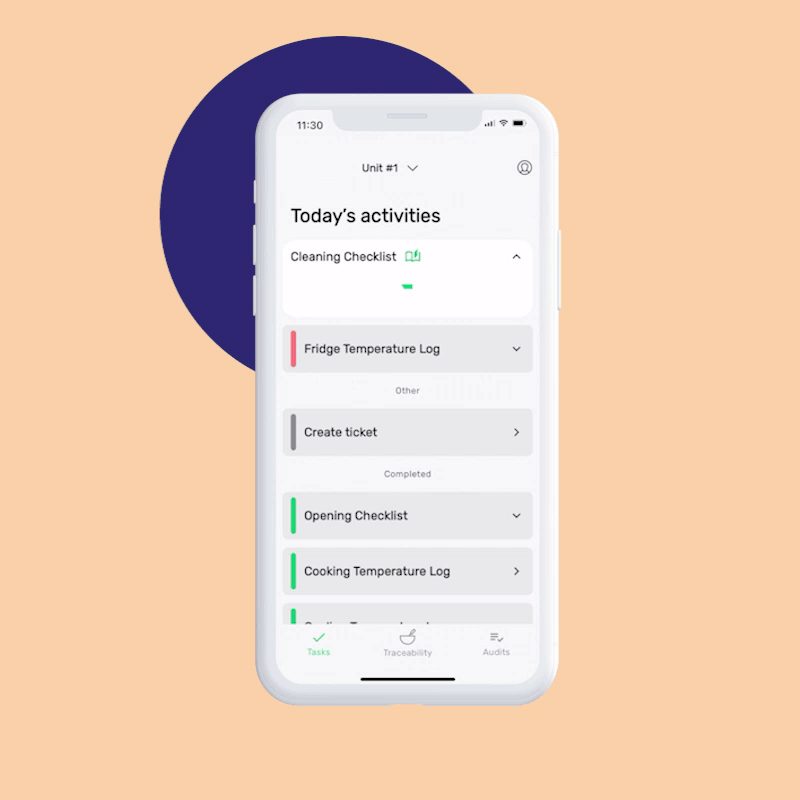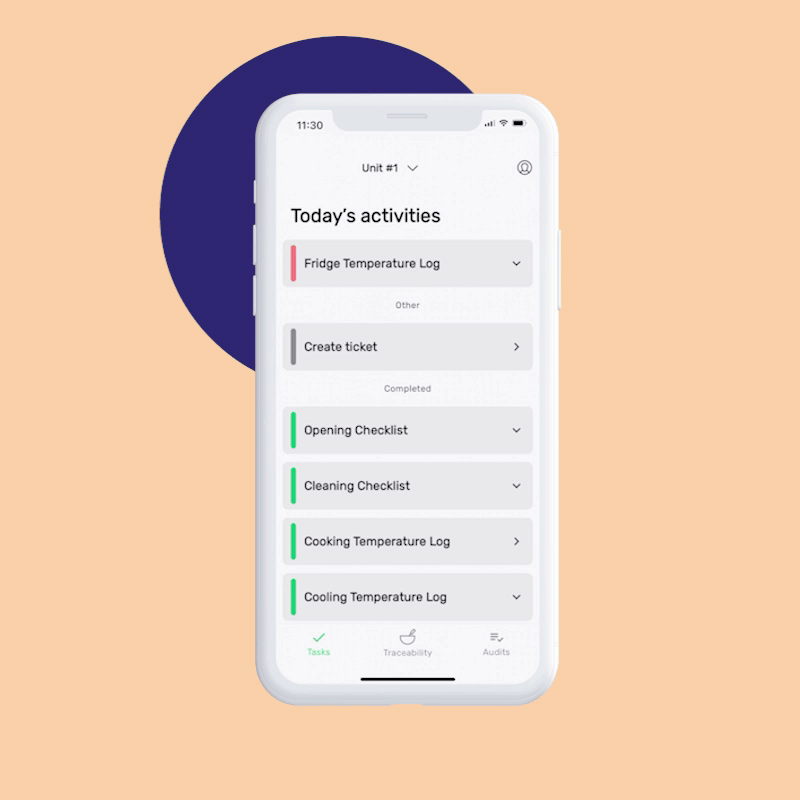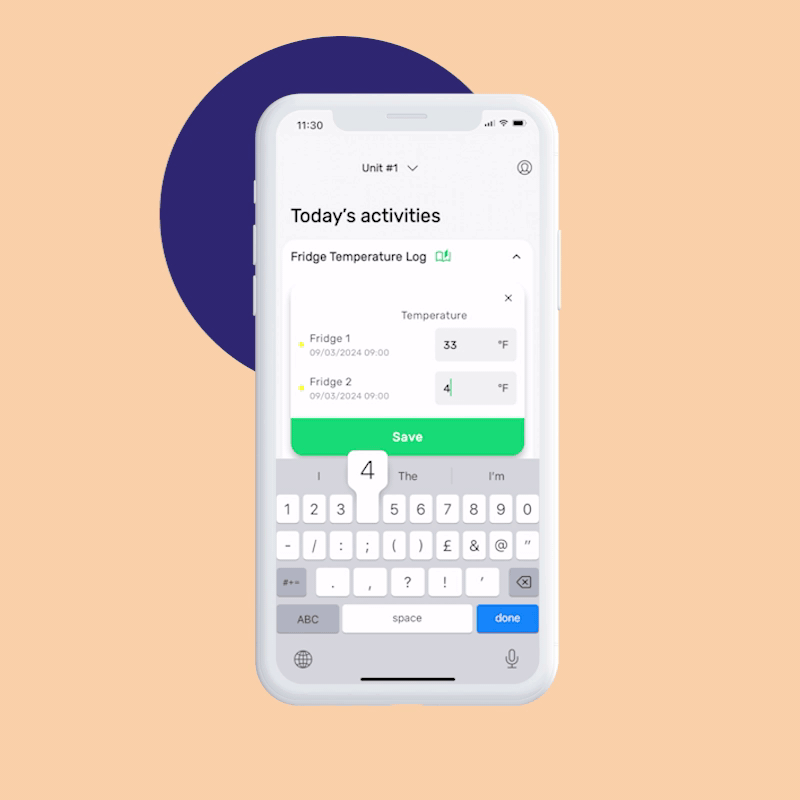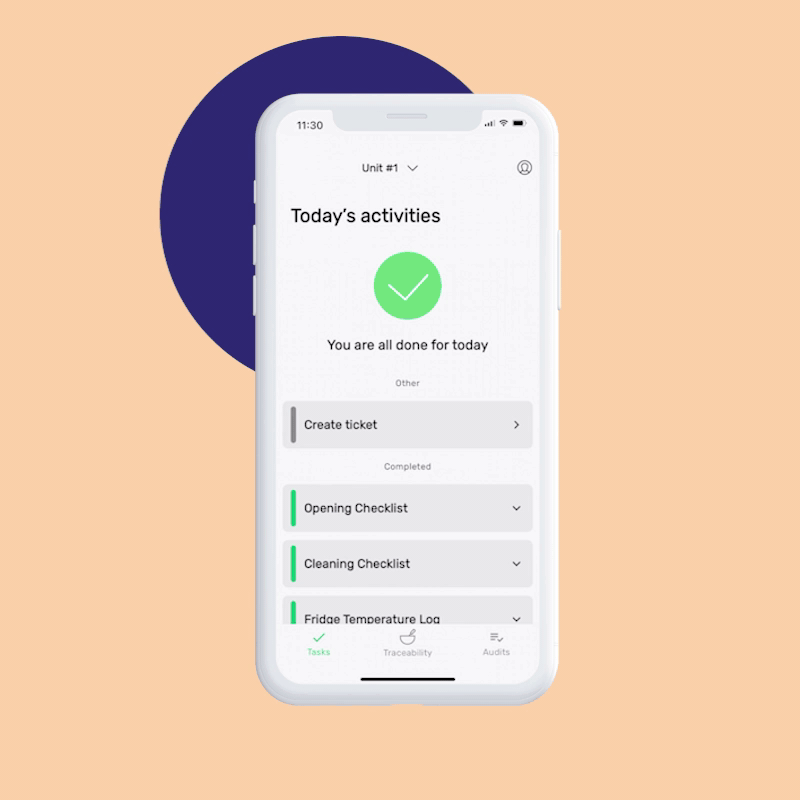
Reduce time spent on paperwork and processes by 20%
- Automate the setup process in just 15 minutes
- Never miss a task with mobile app notifications
- Save one working day each week on supervision with a real-time overview
Get a Free Template Pack

This is how our Digital Food Safety platform saves 20% of your time on daily tasks:
- Get upcoming task notifications
- Add data into the app
- Check the status of tasks in real-time

When food safety was still handled on paper, I typically spent a couple of hours per day getting the papers and going around checking or completing tasks… Now I can sit down and it's just all there in one place. It takes me 5-10 minutes.
Ruth B.
Store Manager