Have you ever built something without instructions?
Just like a furniture manual, LEGO set or a house blueprint, product specification in the food industry enables consistent, high-quality, and safe products for the public.
Key points covered:
- In food manufacturing, food specification acts as a blueprint that helps all parties understand the exact requirements for creating products.
- Businesses implement detailed specifications in food manufacturing is to standardize production, maintain quality, and ensure safety.
- Food product specification determines: ingredients, nutritional information, physical properties, chemical composition, packaging requirements, shelf life, storage conditions, and safety standards.
- If a producer fails to meet a specification, the buyer can point to the objective standard the manufacturer missed, serving as the basis for rejecting non-conforming goods.
- The seven steps of writing a product specification are: defining the product, listing ingredients, specifying quality standards, detailing package and label requirements, setting storage and handling requirements, including test procedures, and regulatory compliance.
- You can also include tolerances for imperfections (e.g., acceptable number of defects per batch).
- Factors like product marketing or promotional strategies are not necessary details to include in food product specification sheets.
- FoodDocs' Traceability software helps to track your ingredients and food items through all stages of production.
What is product specification?
A product specification is a detailed document that outlines the necessary standards, ingredients, and quality parameters for a food product. In food manufacturing, comprehensive specifications act as blueprints for everyone from production teams to ingredient suppliers to understand the exact requirements.
Specifications can cover everything from physical characteristics to chemical properties, ensuring product consistency and compliance with regulatory standards. (More on that below.)
What is the purpose of specifications in food manufacturing?
The purpose of product specifications in food manufacturing is to standardize production, maintain quality, and ensure safety. Clear specifications allow manufacturers to produce consistent products, manage supplier relationships more effectively, and avoid costly recalls due to non-compliance.
These specifications also help guarantee that the final food product meets legal requirements set by government agencies such as the FDA or USDA, and satisfies consumer demands and expectations.

What does a food product specification determine?
Food product specification determines:
Ingredients
A food product specification outlines each ingredient used, ensuring that production adheres to strict recipes. This includes specifying the source, quality grade, and whether any substitutions are permissible.
For allergen management, it's crucial to clearly identify common allergens such as nuts, dairy, or gluten. By listing ingredients in detail, the manufacturer can maintain consistency and comply with regulatory requirements, such as food labeling laws.
Nutritional information
Nutritional profiles are a legal requirement in most markets, dictating what must appear on food product labels. The specification document should include detailed calculations for calories, fats, proteins, and carbohydrates, as well as micronutrients like vitamins and minerals.
Accurate information on nutritional labels not only helps maintain transparency with consumers but also aligns the product with dietary guidelines or certifications, such as "low-fat" or "high-fiber."
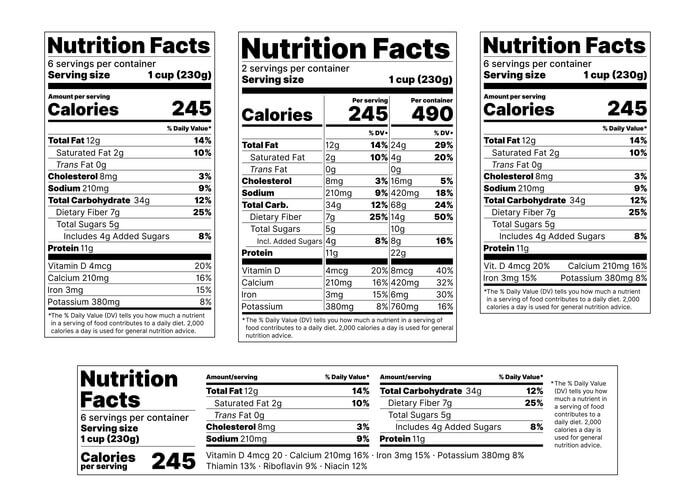
Physical properties
Characteristics like texture, color, size, and shape are vital for customer expectations. For instance, the exact consistency of a sauce or the dimensions of a frozen food product must be specified to ensure uniformity across production batches.
This reduces consumer dissatisfaction and prevents variability, which could lead to product rejection by retailers or customers.
Chemical composition
For some products, chemical standards are just as important as the physical ones. Parameters such as pH, moisture content, acidity, or sugar levels must be tightly controlled to meet safety compliance standards and extend shelf life.
Failure to adhere to these chemical properties can lead to spoilage, health risks, or regulatory non-compliance, especially when dealing with perishable or high-risk foods.
Packaging requirements
The packaging not only protects the food but also impacts shelf life, distribution, and presentation. The specification should address the type of material (plastic, glass, etc.), dimensions, and any specific needs such as tamper-evident seals or vacuum sealed packaging.
Key requirements may also include sustainability practices, such as recyclable or biodegradable materials, which are increasingly important for companies committed to environmental responsibility.
Shelf life and storage conditions
Stating the required shelf life helps retailers manage stock more effectively and minimizes waste. The product specs should provide essential details about the optimal storage environment (e.g., refrigeration, freezing, or ambient storage) to ensure quality preservation.
You should also specify the temperature range for each phase of the product’s lifecycle, including transport, storage, and point-of-sale handling.

Safety standards
A high-quality product specification ensures that the food meets regulatory standards for safety and hygiene. This could involve compliance with international safety standards, such as HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) or specific national requirements (e.g., USDA, FDA, EU regulations).
Safety standards protect both the consumer and the manufacturer by ensuring the product is free of contaminants, and by outlining the required tests for microbiological hazards, toxins, or foreign materials.
How to write a product specification (in 7 steps)
Writing a detailed, seven-step product specification involves careful planning and collaboration across departments like Research and Development (R&D), quality assurance, and regulatory compliance.
Getting product spec documents right is important because, according to The Food Law Firm:
Manufacturing a product “to spec” holds legal significance, signifying that the manufacturer has fulfilled its agreement, obligating the buyer to purchase the goods. Conversely, if a producer fails to meet a specification, the buyer can point to the objective standard the manufacturer missed, serving as the basis for rejecting non-conforming goods. Specifications define precisely where a breach occurred, and no breach of contract dispute can proceed without a clear deviation from an objective spec.
Here’s how you can write an effective product specification:
1. Define the product
Begin by offering a clear, concise description of the product, which should include its intended use and any unique selling points. This section also serves to differentiate the product from competitors, ensuring stakeholders understand the product’s niche in the market.
For example, define whether it’s a ready-to-eat item, a raw ingredient, or a meal kit component.
2. List ingredients
Break down each ingredient used in the product and specify the type of product, its origin, and quality grade. It's essential to list both primary and secondary ingredients, along with the exact proportions required for production.
For allergen control, clearly mark any known allergens, cross-contact risks, and any ingredients that require special handling, such as organic or fair trade-certified products. This level of detail helps reduce the risk of recalls due to undeclared allergens or ingredient substitutions.
3. Specify quality standards
Establish criteria for the product’s quality attributes, including acceptable ranges for texture, color, and flavor. This step often involves setting sensory analysis guidelines that outline what the product should taste, look, or feel like, ensuring consistent production.
You might also include tolerances for imperfections (e.g., acceptable number of defects per batch). Quality standards act as a quality control measure that can be tested regularly.
4. Detail packaging and labeling requirements
Provide specifications for the packaging materials, including dimensions, durability, and compliance with food safety regulations. Packaging must be appropriate for the product’s intended distribution environment (e.g., vacuum sealing for shelf stability or moisture barriers for frozen goods).
Labeling needs to cover legal requirements, such as nutrition facts, ingredient lists, and allergens. You should also specify any voluntary labeling, like organic certification, non-GMO certification or fair trade seals, which can enhance the product's marketability.
5. Set storage and handling requirements
Clearly define the conditions necessary to preserve the product’s quality throughout its shelf life. This includes temperature controls (e.g., frozen, refrigerated, or ambient storage) and humidity levels.
For products with sensitive components, specify the maximum time they can spend outside controlled environments. This section is crucial for minimizing spoilage and ensuring that retailers and consumers store the product safely.
6. Include testing procedures
To maintain quality and safety, your specification should outline the necessary testing protocols. This may include microbial testing, sensory evaluations, or chemical analysis to ensure the product meets established standards.
Testing procedures also help with food traceability, allowing manufacturers to track and address quality control issues quickly. Detail who is responsible for developing a testing plan, carrying it out, and how often tests should be performed.

7. Regulatory compliance
Compliance with food safety regulations is critical in avoiding legal issues and recalls. Ensure that the product specification includes references to any applicable standards, such as the FDA food code or EU food labeling regulations.
Include any certifications the product must meet (e.g., gluten-free, organic), and ensure that these align with current legal definitions. Regularly review and update this section to stay compliant with evolving regulations.
Product specification example for food
Let’s take a simple example of a tomato sauce product specification:
- Product name: Classic Tomato Sauce
- Ingredients: Tomatoes, olive oil, garlic, salt, and basil.
- Physical properties: Thick, red sauce with a smooth texture.
- Chemical properties: pH of 4.3–4.5, moisture content below 68%.
- Packaging: 500ml glass jars with a tamper-evident seal.
- Shelf life: 12 months at room temperature in a dry, dark place.
- Storage: Store at 64-77°F (18-25°C); once opened, refrigerate.
Food product specification sheet
An effective product specification sheet provides a detailed overview of the minimum requirements necessary to produce a safe and compliant product. This document should be shared across departments to ensure uniformity during the product development process as well as in testing and distribution.
To streamline the process, you can use our free, editable product specification template, which has an image upload section for visual representation and simplifies data entry while ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Or download the printable product specification sheet and fill it out with pen and paper.
Download the Food product specification sheet

Thank you for downloading Food product specification sheet!
Want to get a customizable HACCP template?
Or set up your food safety system in 15 minutes?
START FREE TRIAL
Use FoodDocs to support your product specification and traceability needs
FoodDocs' food safety management software makes compliance easy. The Traceability System helps to track your ingredients and food items through all stages of production.
Its features allows you to:
- Create traceability logs within seconds: Complete a traceability log and attach a monitoring task to that traceability log right away. This feature helps you ensure high-quality food safety and protects you in case of food recalls.
.gif?width=680&height=450&name=Traceability_log%20(1).gif)
- Access detailed recall data easily: Find a product’s historical data for your local authority or auditor quickly, or in case of a recall or customer complaint. You can search by product, batches, ingredient, or expiry date.
- Automated shelf-life date tracking and smart reminders: Our app fills in shelf-life dates on the traceability log automatically, according to previously inserted data. All you need to do is confirm the logs (or update them if the data has changed).
- Organize your recipe and product specifications: Ensure accuracy across all food products you make by adding detailed instructions to help train your team.

- Calculate recipe ingredients automatically: Plan your production by calculating the ingredients while completing the traceability log to save time and avoid human error. Just select the batch you’ll use for preparing dishes and fill in the amount.

Frequently asked questions about product specification