Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
In every step of the food supply chain, a significant food safety hazard such as cross contamination can happen right under everyone's noses. Without adequate knowledge of proper food safety practices, cross-contamination can happen at the slightest touch.
A mere accident of putting down a raw chicken on a counter surface can significantly increase the risk of foodborne illnesses. Similarly, food handlers who don't regularly wash their hands can cause cross-contamination on a wide scale.
That's why individuals involved in food preparation must ask themselves: how do you avoid cross-contamination?
Key takeaways
Understanding cross-contamination is the first step to effectively prevent it in any food-related environment.
Cross-contamination can occur at any point in the food supply chain and is a significant cause of foodborne illnesses.
Proper food safety training is crucial to inform and educate food handlers on preventing cross-contamination.
Proper storage of foods and chemicals is essential to prevent cross-contamination between foods and other substances.
Strict food hygiene practices, such as regular hand washing and using clean uniforms, are effective in preventing the transfer of contaminants.
Regular cleaning schedules for kitchen surfaces and equipment help minimize the risk of cross-contamination.
Monitoring operations regularly ensures consistent application of food safety practices and helps maintain a high level of food safety.
Shopping practices can influence cross-contamination, and care should be taken to separate different types of foods and non-food items.
Preparation and cooking practices must ensure the separation of tools and ingredients to prevent cross-contamination and ensure food is cooked to safe internal temperatures.
Every year, a large portion of the cases of foodborne illnesses is caused by cross contamination of foodborne pathogens. Such cases occur because of the lack of food safety and hygiene training as well as a comprehensive food safety management system (FSMS).

Avoiding cross-contamination starts with knowing what it is. Cross-contamination is the movement of food safety hazards from one place to another, making food unsafe for consumption. This occurrence in the food supply chain accounts for a large portion of the foodborne illnesses that happen around the world. Find out more about how cross-contamination happens here.
Cross contamination is not limited to biological hazards only such as harmful bacteria and viruses. It can also occur to chemical and physical hazards. The best way to avoid cross-contamination is to implement a comprehensive food safety program.
Through such a program, the sources of food safety hazards can be identified and addressed through proper monitoring and the application of preventive actions.
There are many ways how you can avoid cross-contamination in your kitchen area. Some ways are very obvious that they are part of your daily routines but are just sometimes forgotten. Avoiding cross-contamination requires a key ingredient: consistency. One blunder of forgetting to apply food safety practices can significantly affect your operations.
More specifically, here are some of the most effective ways of how to avoid cross-contamination.
During training, the kitchen staff is oriented on what is cross-contamination, how it occurs, what factors contribute to it, and how can you avoid it from happening.
Food safety practices involve operations such as proper segregation of raw foods and those that will only be minimally processed during preparation. This also includes knowing how to use separate utensils such as knives and chopping boards when dealing with these two types of foods.
Knowing the principles behind cross-contamination does not only increase awareness among food handlers. It also allows them to appreciate its importance more. Food safety managers are responsible for providing this basic training for them. Without proper training, foodborne diseases and other related cases can occur and cost your business a lot.
Cross-contamination requires contact between the food being prepared and another object. Knowing how should food be stored to avoid cross-contamination is part of any food handler's safety training. Cross-contamination can come from food handlers who did not wash their hands, food contact surfaces, other foods, or other objects such as cleaning materials.
When working with chemicals, the best practice to avoid cross-contamination is to properly label and store them far from the food preparation area. This means separating dry from wet ingredients, as well as properly stacking them.
Storage of foods does not mean shoving all raw materials in a cabinet or the refrigerator. They need to be properly arranged in such a way that they will not get contaminated. Particularly in a refrigerator, ready-to-eat foods, minimally processed ingredients, and raw materials must be separately stored.
Foods that require thorough processing must be at the bottom shelf of the refrigerator so the juices from raw meats will not drip into foods that only require minimal processing. Use a fridge food safety layout poster to guide you on how to arrange foods inside a refrigerator.
Food hygiene refers to operations that aim to minimize the spread of bacteria through clean and safe operations. One of the most important tasks involved in food hygiene practices includes proper handwashing. This operation is perhaps one of the most effective ways of avoiding cross-contamination.
Food handlers touch almost everything around the kitchen. Without washing their hands, they can spread pathogens easily from one place to another. Not to mention that humans are natural carriers of a large variety of pathogens that can be transmitted to foods.
Handwashing effectively removes these pathogens and protects foods from cross-contamination. Other food hygiene practices include regularly trimming nails, properly wearing protective uniforms, and not wearing soiled clothes to work.
Similar to the principle of handwashing, kitchen surfaces as well as other areas of your kitchen must be kept tidy and sanitized. Floors, walls, windows, and ceilings, can become sources of contamination when left unclean. The buildup of dirt can unintentionally transfer to foods and therefore must be kept to a minimum.
Cleaning must be thorough, effective, and consistent. Proper concentrations of the correct cleaning agents must be used. Included in this operation is properly tidying up after, This means storing cleaning agents away from the preparation area where it can contaminate the foods being prepared.
As we have mentioned, consistency is key in preventing cross-contamination from occurring. Food handlers must maintain a high level of commitment to performing food safety operations even when no one is looking. To ensure this, food businesses must implement a working FSMS.
At FoodDocs, we have automated this operation to make things easier for you. Our digital Food Safety Management System product can automatically generate a complete monitoring system that is based on your daily operations. You won't even have to worry about forgetting a task because our system implements a smart notification system for this particular reason.

If you thought that cross contamination can only occur inside a kitchen, you thought wrong. The mere placement of your grocery items inside your shopping cart can cause cross contamination. Additionally, the sequence of adding ingredients to your cart can also affect this. To avoid cross contamination when shopping, follow these pointers:
During common food preparation, foods are most at risk of becoming contaminated especially with poor food safety practices. The operations mentioned above are general and can be applied throughout the whole food chain. Here are some specific tasks which you can do to avoid cross contamination during food preparation:
When cooking, cross-contamination can still occur. Especially when target internal temperatures are not reached, the objective of cooking foods may not be entirely effective in preventing food poisoning. Follow these steps to avoid contaminating foods being cooked:
Cleaning agents can contaminate foods when they are not rinsed well. Additionally, they can spill into foods being prepared when not properly stored. Chemical contamination due to cleaning agents can cause significant health problems to consumers. They can cause burning, food poisoning, and other serious issues when consumed.
To prevent cross-contamination while cleaning, food service workers must:
As mentioned, foods can get contaminated even if they are just sitting inside a refrigerator. This can occur by improperly stacking them and mixing them raw with cooked ingredients. Follow these pointers to avoid causing cross-contamination:
The risk of cross-contamination does not end when the food is cooked. Products can still become cross-contaminated even when served. Precautions and correct procedures for serving are required.
Common food allergens are recognized as hazards for consumers with food allergies. They can significantly cause health problems to vulnerable groups of people which can sometimes be life-threatening. Allergens can travel from one source to another through their dust particles or cross-contamination. Avoid contaminating other dishes with allergens by following these pointers:
The best way to avoid cross-contamination is to implement a comprehensive food safety management system (FSMS). This program includes all known food safety practices that contribute to avoiding cross-contamination. Food hygiene and safety are all part of an FSMS and keeping them always monitored and followed as well. An effective FSMS is one that covers all monitoring procedures for your daily operations in your food business.
Cross-contamination has a serious consequence on public health and the status of your food business. It can spread illnesses that can manifest through diarrhea, abdominal cramps, vomiting, and nausea. In other cases, cross-contamination of physical hazards can cause injuries such as wounds, scratches, and even injury.
More serious cases of cross-contamination can lead to hospitalization, or worse, death. These side effects can be addressed by properly identifying the source of the contamination and administering the proper health care to affected consumers. Groups that belong to the high-risk population such as pregnant women, children below 5 years old, and the elderly are more likely to become severely affected by the effects of cross-contamination.
With our digital Food Safety Management System, food safety tasks will be done without fail as food handlers will be constantly reminded when to do them and be given smart instructions in case of noncompliance. Shifting to our digital platform would only take an average of 15 minutes. You can do it even while in line at the grocery store.
Our system's process starts by answering a few basic questions about your food business. After this, our system will automatically generate a complete digital FSMS that is based on your daily operations. You can even customize the documents that we automatically create to further fit your operations. You can add unique tasks to your food business and create digital monitoring forms.
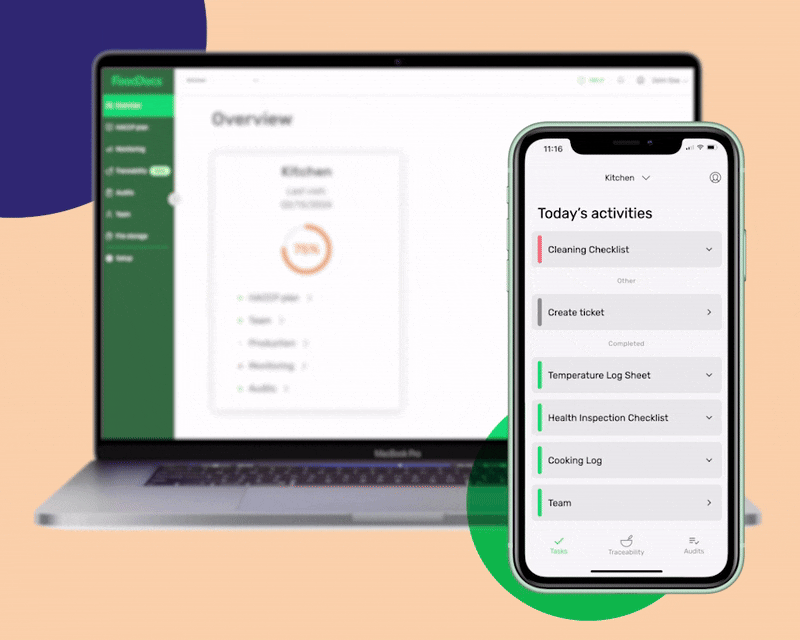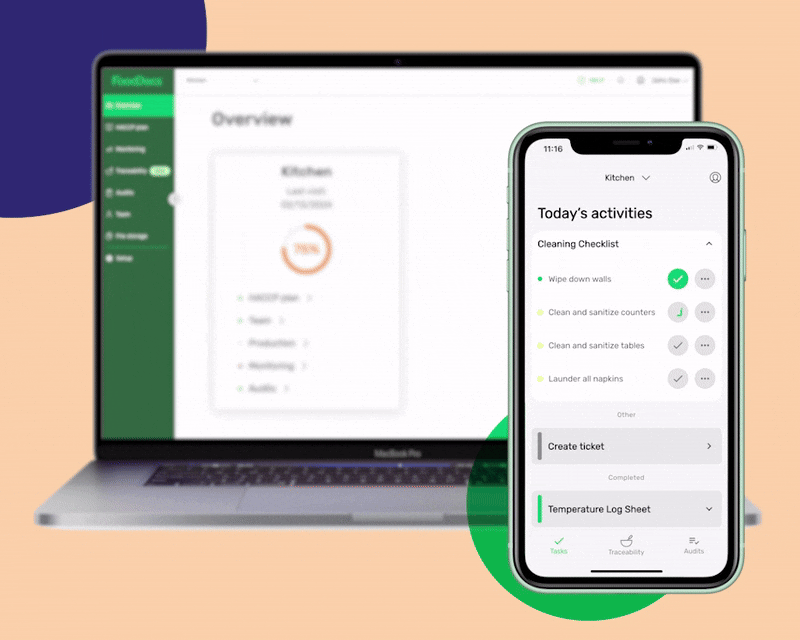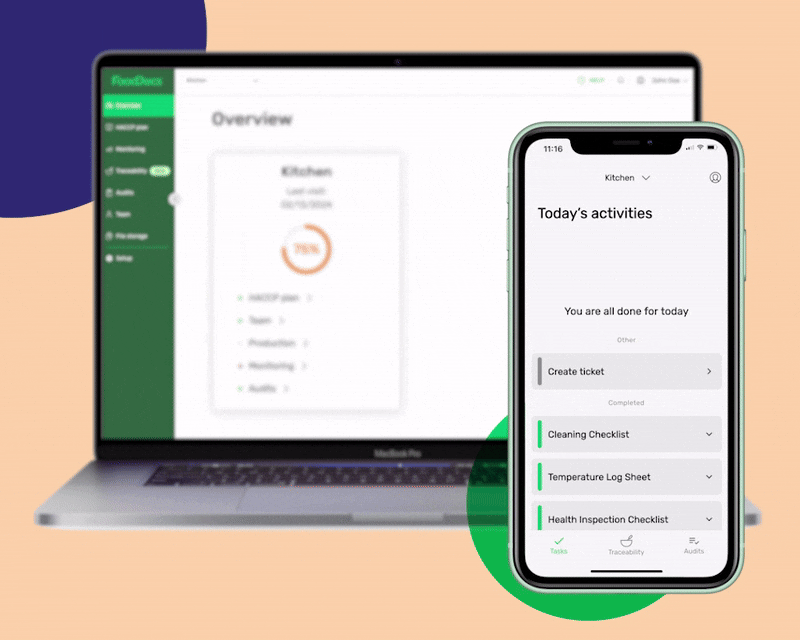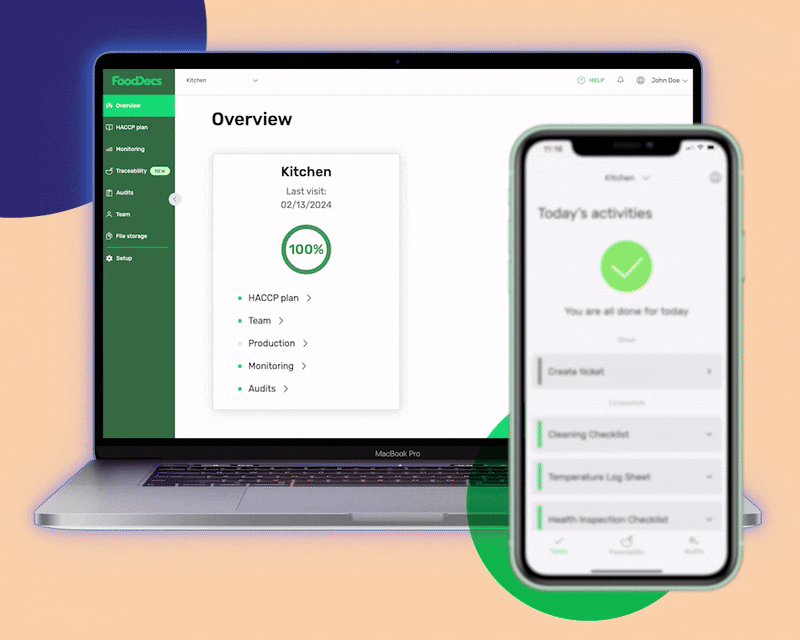
In addition to these features, our digital FSMS can provide you with these highlights:
With our digital FSMS, you can stay compliant with the most significant food safety laws and regulations locally and internationally. Make sure that all sources of cross contamination are addressed and that the assigned food safety tasks to avoid the spread of foodborne illnesses are controlled. Sign up now for your free, 14-day trial to get a feel of how our system works.
Here are a few questions and quick answers to help you understand more about how do you avoid cross-contamination:
Cross-contamination can be avoided through proper and strict food safety practices such as washing hands, separating raw and cooked foods, and regularly cleaning the kitchen area and food contact surfaces.
During storage, keep ready-to-eat foods away from raw materials. This type of food does not need any further processing and will be immediately consumed once served. As such, there would be no other kill step to remove the contamination.
By using separate tools such as spoons in between tasting, you can minimize the risk of cross-contamination by avoiding the introduction of pathogens from a food handler's mouth and hands to the food being cooked.
To avoid cross-contamination, remember to (1) wash your hands regularly, (2) separate cooked foods from raw materials, (3) clean food contact surfaces, and (4) use different utensils when preparing food.
There are several things that you can do to avoid cross-contamination during preparation. Some of the most effective operations include practicing food hygiene such as washing hands with soap, separating foods during storage depending on their categories, and using separate tools to prepare foods.
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...