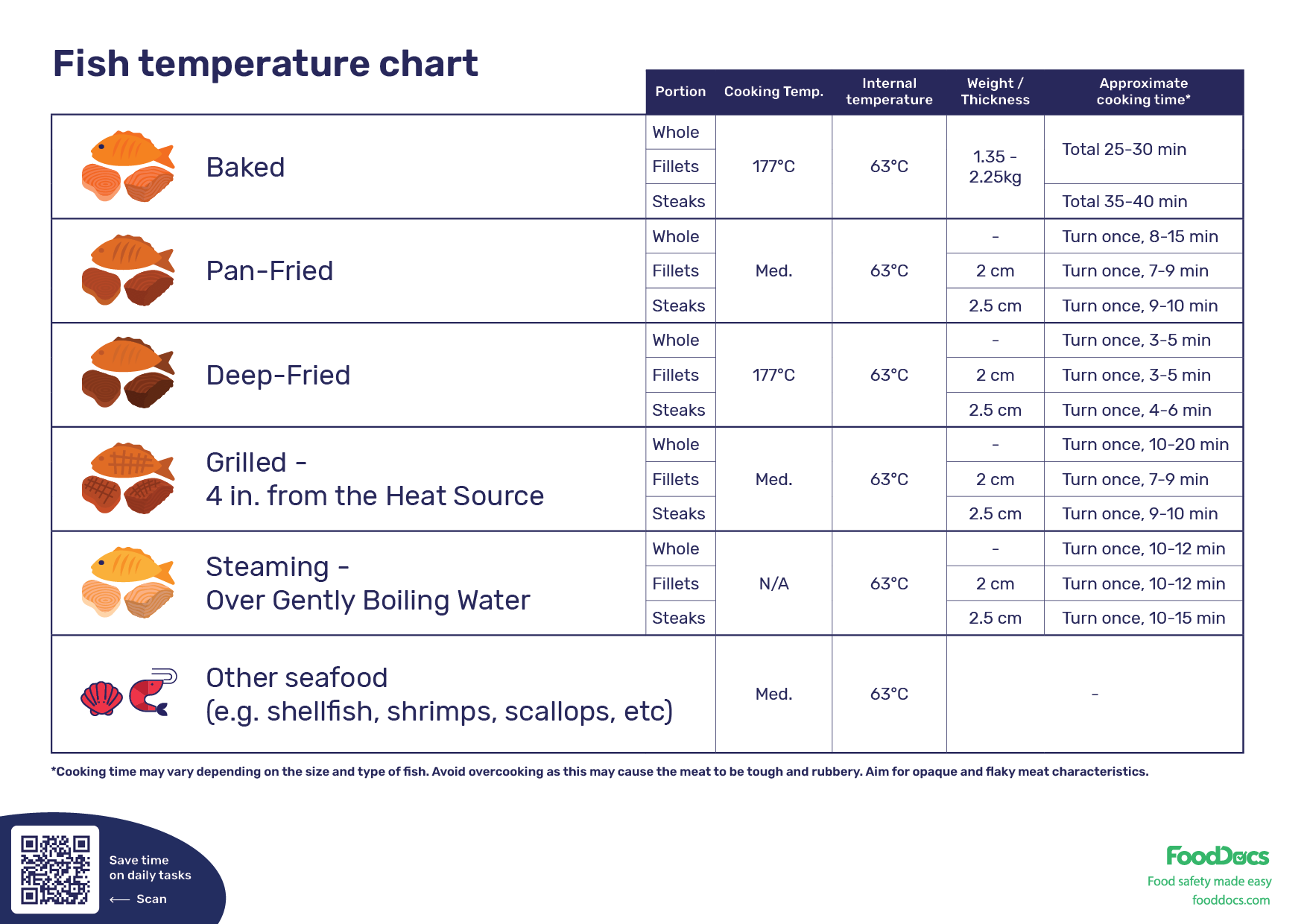
FISH TEMPERATURE CHART

This is how our Digital Food Safety platform saves 20% of your time on daily tasks:
- Get upcoming task notifications
- Add data into the app
- Check the status of tasks in real-time

When food safety was still handled on paper, I typically spent a couple of hours per day getting the papers and going around checking or completing tasks… Now I can sit down and it's just all there in one place. It takes me 5-10 minutes.
Ruth B.
Store Manager
How to use a Fish Temperature Chart?
Follow these steps to use our Fish Temperature Chart:
- Download the chart from above by entering your correct email address and pressing "download."
- Find the downloaded full-quality file from your downloads folder and print it.
- Attach the chart to the wall of your kitchen and/or other working areas. We suggest a place where food handlers can see it during cooking.
- Briefly explain the use of the chart and summarize the importance of cooking fish properly to your employees.
- Stay up to date with our new free templates, tools, and posters from our template hub and through the newsletter that we will send you once a month to introduce our new content.
In this post, find out how our Fish Temperature Chart and a handy meat thermometer can help you ensure you cook fish at the correct temperature. In addition, learn how you can switch to our digital platform and start monitoring your food safety tasks with our smart Food Safety Management System that's designed carefully for the food service industry.
Key points covered:
- Fish meat is more sensitive to heat compared to other meats due to shorter muscle fibers, cooking faster and requiring precise temperature control.
- Fish should ideally be cooked to an internal temperature of 145°F (63°C) and can be safely frozen for later consumption.
- Fish and seafood are more likely to cause foodborne illnesses due to the risk of undercooking.
- Consuming undercooked fish increases the risk of foodborne illnesses caused by pathogens like Salmonella and Listeria.
- A fish temperature chart is essential for ensuring the safe internal cooking temperature of various types of fish (like saltwater fish).
- A fish temperature chart focuses on safety, providing proper cooking temperatures to eliminate foodborne pathogens.
- The chart is particularly important when serving high-risk groups like pregnant women, children, and the elderly.
- The chart helps minimize foodborne illnesses, ensures proper cooking, acts as a reminder for food handlers, and is a cost-saving tool for businesses.
- Food safety suggestions include using fresh fish, practicing proper hygiene, and using a calibrated thermometer to reach the desired internal temperature.
- FoodDocs offers a smart food safety management system to monitor cooking temperatures and ensure compliance. It offers customizable monitoring logs, a traceability system, a food safety dashboard, and notifications.
Optimal Cooking: Using a Fish Temperature Chart for a Perfect Fish Dish
A fish temperature chart is a visual guide that contains the correct internal cooking temperature for fish.
There are many things to consider when cooking fish meat. It is more sensitive to heat than other types of meats, cooks faster, and can go wrong with just a few degrees off of the target temperature.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) highlights that fish and other seafood are the most likely foods to cause foodborne illnesses. That's because chefs are more likely to undercook delicacies like lobster meat, shrimp, and mussels. As such, cooking fish raw meat safely is a critical task for every food handler in your food business. This is where a fish temperature chart comes in, which prevents guessing when it comes to the ideal temperature range for fish.
What is a fish internal temp chart?
A fish temperature chart is a visual guide that displays the correct internal fish cooking temp. The internal temperature mentioned in a fish cooking temperature chart is based on achieving the highest level of safety. There are other fish internal temperatures that can be used for quality purposes, but a fish cook temp chart is more concerned with safety.
It’s important to have a fish temperature chart on hand because fish and other seafood are common proteins that are often served undercooked. The chart includes Atlantic salmon, raw tuna, lake trout, and northern pike. You may also be familiar with firm sashimi, sushi, ceviche, and other dishes that use fresh seafood as the main ingredient. Plus, fresh meat steaks from fish, such as the Ahi tuna, can even be served rare with the control of temperature set at 115°F (46°C) instead of the general standard, which is 145°F (63°C) for proper doneness.
A fish temperature chart becomes even more important if you have high-risk groups (e.g., pregnant women, children, and the elderly) eating at your establishment. For these people, consuming raw and undercooked foods can significantly increase the food safety risk from harmful bacteria like Salmonella, E. coli, Streptococcus, and Campylobacter.
The good news is that, unlike toxins that cause food poisoning, these pathogens can be eliminated with proper fish cooking temp. Just remember to always use an internal temperature chart as a guide for interpreting the internal temperature of your dish. You can use a digital thermometer for an accurate reading.
Who needs an internal temperature for fish chart?
A fish temperature chart is a useful guide for all food service establishments (such as restaurants, food trucks, cafeterias, and fish stores) that want to make their food amazing. In addition to acting as a reminder for the correct internal temperature, it can help food handlers estimate the correct cooking time to reach the target temperature. Of course, the cooking process in correlation to time varies depending on other factors such as the size and type of fish cut (but a temperature chart serves as an important guiding principle).
What are the benefits of using a fish temperature chart?
In general, a fish temperature chart helps minimize foodborne illnesses that result from consuming undercooked food. It offers the following benefits:
- Reminder. Most food service establishments serve multiple types of protein. All of these meats have different target internal temperatures. This can confuse food handlers, especially those who are new to their jobs. A cooked fish temperature chart can serve as a helpful reminder to ensure that fish and seafood dishes are properly prepared and cooked.
- Ensure food safety and taste. Because the risk of causing foodborne illnesses is high when consuming undercooked or raw seafood, cooking it to up to 145°F (63°C) is very important. At this temperature, most foodborne illness-causing pathogens are eliminated (while maintaining the taste of the dish). Beyond this temperature, pathogens may be eliminated, but the fish meat can become tough and dry.
- Cost-saving. Foodborne illnesses and related injuries can cause quite a commotion. Food businesses involved in an outbreak can lose profits from bad publicity, which may lead to a negative stigma attached to your business for a while. That’s because customers tend to stop eating at a food business that got involved in a food safety issue. To prevent this from happening, make sure to always cook foods to a safe temperature by consulting the fish temperature chart.
- Food safety training. As part of a food handler's food safety training, they are required to familiarize themselves with most, if not all, cooking internal temperatures. A fish temperature chart can allow them to master how to cook fish and other seafood. This training allows them to maintain food safety in the kitchen and promote accountability in case of a mistake.
If your food business offers both thoroughly cooked and undercooked seafood dishes, precise cooking and a constant temperature must be practiced for distinction. Customers would expect your team to serve appropriately cooked fish when they request it. This is why a food temperature chart is so useful. Also, in the case of undercooked fish, your food business must be well-equipped with a consumer advisory as notice to your consumers.
Suggestions for cooking fish safely
Here are some suggestions your food handlers should follow when cooking fish:
- Ensure that the fish you are using is fresh.
- Practice proper hygiene when handling fish.
- Use dedicated cutting boards and utensils when preparing fish.
- Make sure that the heat source is hot enough to reach the desired fish internal temp.
- Cook fish to an internal temperature of 145°F (63°C).
- Ensure that the thermometer you are using is properly calibrated.
- Avoid eating undercooked fish, as this increases the risk of causing foodborne illnesses.
- Always place raw and undercooked fish below ready-to-eat foods inside the refrigerator to avoid cross-contamination.
- Cook fresh fish within 1 to 2 days after refrigeration to ensure safety.
- Refrigerate cooked fish for a maximum of 3 to 4 days.
You can guide your employees on properly cooking fish using our Fish Cooking Chart. You can also complement this tool by using our Fridge Organization Chart to guide food handlers on properly storing cooked and raw fish in the refrigerator.
For a more intuitive solution, use our smart Food Safety Management System at FoodDocs. Using digital food safety software, food handlers can log cooking temperatures as they process the fish, and you can ensure food safety compliance from a single dashboard. More on this later!
How to use a Fish Temperature Chart?
Follow these steps to use of our Fish Temperature Chart:
- Download the chart from above by entering your correct email address and pressing "download."
- Find the downloaded full-quality file from your downloads folder and print it.
- Attach the chart to the wall of your kitchen and/or other working areas. We suggest a place where food handlers can see it during cooking.
- Briefly explain the idea of the chart and summarize the importance of cooking fish properly to your employees.
- Stay up to date with our new free templates, tools, and posters from our template hub and through the newsletter that we will send you once a month to introduce our new content.
At what temperature is fish done?
Fish is ideally cooked to an internal temperature of 145°F (63°C) using any cooking method. At this temperature, the fish meat is fully cooked and any pathogenic microorganisms are killed.
The recommended temperature also maintains the quality of the cooked fish. Beyond 145°F (63°C), the fish meat can become tough and rubbery or lose moisture.
Remember to use a properly calibrated thermometer to ensure that the target internal temperature for fish is achieved. Visually, a properly cooked fish is milky white in color and not transparent. The meat should be flaky and not tough when cut with a fork.
Monitoring fish cooking temperature control with FoodDocs
Fish is an everyday food and we all have a favorite fish. If you run a restaurant, it’s going to be one of the hottest items on your menu. This means your food handlers will spend a lot of time cooking fish and the margin for error will be low.
You serve one undercooked piece of fish that leads to a foodborne illness and the reputation of your entire food business will be at stake. Not to mention the extremely costly litigation that can follow food poisoning incidents.
Of course, you could use a digital food thermometer to manually check each of the seafood dishes you serve. But that’s going to eat up all of your time — time that could be spent on more meaningful tasks, such as adding new items to your menu and creating a killer digital marketing strategy.
The solution? FoodDocs, a smart food safety management system. Our developers have spent countless hours to ensure FoodDocs has all the features you need to serve safe food without wasting time.

With our food safety system, you get:
1. Automatically generated monitoring logs
2. Detailed instructions to help you train food workers
3. Smart notifications to alert you to important food safety issues
4. All-in-one traceability system to help you keep a track of your ingredients
5. A real-time food safety overview so you're always on top of your operations
Automatically generated monitoring logs
FoodDocs lets you automatically generate monitoring logs customized for your food business operations. Logs that will be especially life-saving for seafood restaurants include:
- Cooking temperature log
This log ensures your team cooks fish at the proper temperature. You can add a temp range and ask your food workers to measure and record seafood temperature in FoodDocs. If the recorded temperature is out of range, FoodDocs will display corrective actions that your team must take. You can set these corrective actions according to the food safety best practices.
- Receiving chilled goods log
- Fridge temperature log
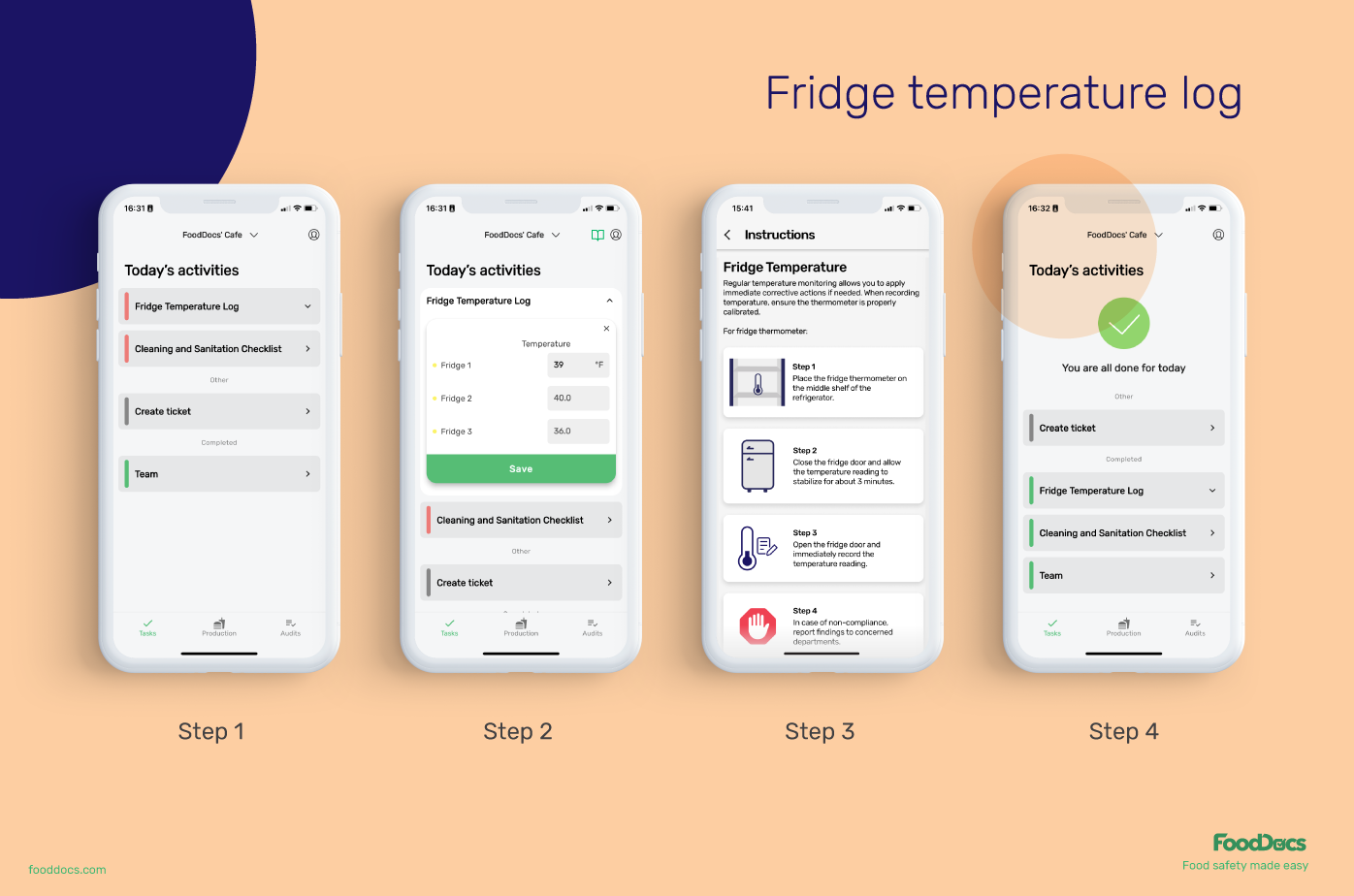
- Employee hygiene checklist
Detailed instructions
It doesn’t stop here. We’ve ensured these logs are highly useful for businesses by adding the following features detailed instructions. All generated monitoring logs come with these instructions on how to perform the tasks. You can use this to train food handlers and ensure that every task is done correctly, taking your food safety to the next level.
Smart notifications
A smart notification system will remind your team of any food safety operation that is incomplete. Using our mobile application, our system will send intuitive notifications to the assigned food safety staff. This will ensure those pathogens never slip through your checks and make their way to the customers’ tables!
Wait, it gets even better. And this is the best part. You don’t have to be tech-savvy to use our food safety management system. We’ve designed this software for food business owners (not rocket scientists) and it takes just 15 minutes to set it up. Curious to learn how? Book a demo now!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
To help you understand more about how to cook fish and other seafood properly, here are five commonly asked questions about the topic:
How to tell if fish is cooked?
If fish meat turns milky white and becomes less transparent, it is cooked. The texture of cooked fish is usually flaky (not rubbery).
The best way to confirm that the fish is cooked is to ensure it reaches a cooked temp of 145°F (63°C).
Can you freeze cooked fish?
Yes. Freezing is an effective way to preserve cooked fish for later consumption or cooking. Fat-rich fish, such as tuna or salmon, can last for up to three months in the freezer, whereas leaner fish can last for up to six months.
Food handlers must remember that this estimated shelf-life can be achieved only if the cooked fish is properly prepared. Also, use the two-stage cooling method before putting the cooked fish in an airtight container.
What are the consequences of eating uncooked fish?
Failure to reach the proper cooked temp for fish increases the risk of causing foodborne illness. Fish is a known carrier of foodborne pathogens, such as Salmonella, Listeria, and Vibrio.
These pathogens can lead to vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. As a food business, it is your responsibility to ensure that your dishes reach the recommended cooked fish temp and harmful pathogens are eliminated.
What temperature should fish be cooked to?
Fish and other seafood should be cooked to an internal temperature of 145°F (63°C). At this cooked temperature, fish meat develops an opaque, white color up to the center and flaky meat characteristics. You can test fish for doneness by sticking the tip of a knife through the thickest part of the fish steak. Overcooking will cause the fish meat to become rubbery and dry and your customers will be left with what's called "firm fish".
Is salmon safe at 120 degrees?
Undercooking salmon can increase the risk of foodborne illnesses, especially for vulnerable groups of people. Cooking salmon to the category temperature of 120°F (49°C) using your choice of cooking process gives it medium-rare doneness where more moisture is retained up to the innermost portion. Depending on the fat content of the salmon, this fish can be cooked longer and is less prone to drying. It can be processed by baking, steaming, or the grilling process.
What is the suggested fish internal temp?
Fish and other seafood -- such as crab meat -- are suggested to be cooked to an internal temperature of 145°F (63°C). This temperature ensures food safety while maintaining the quality of fish meat.
Can you eat fish at 120 degrees?
Some types of fish, including salmon, are often cooked at internal cooking temperatures around 120°F (48.8°C). This temperature recommendation is true, especially for leaner fish. Despite this, federal agencies, such as the USDA, recommend fish to be cooked at 145°F (63°C).
Does fish have to be cooked to 165?
No. Fish normally has less fat than other types of meat, so heat can travel more efficiently to its core. This is why the recommended temperature of fish is 145°F (63°C).