Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
To address the complex challenges of ensuring safe and wholesome food production and distribution, the International Standards Organization has developed several structured frameworks of standards. These standards aim to manage risks, enhance efficiency, and uphold consumer trust.
The most widely recognized ISO standard for the food industry is the ISO 22000 Food Safety Management System (FSMS). This standard plays a significant role in guiding food businesses to achieve the highest level of safety, quality, and regulatory compliance.
WHAT WE'LL COVER:
ISO stands for the International Standards for Organization.
The organization is independent and nongovernmental, establishing standards for quality, safety, and efficiency.
The ISO sets steps for different organizations to demonstrate their capability and efficiency in controlling food safety hazards. Their standards are internationally recognized and provide a framework for organizations to ensure food safety.
Continue reading as we focus more on the significance of ISO 22000 and how our innovative Food Safety Management System can help you achieve certification compliance efficiently.

The ISO standards consist of a wide range of regulations that apply to particular industries.
Among the many different ISO standards, the ISO 9001 is the most applicable standard for any business. The standard highlights quality management principles and requirements for customer confidence and continuous improvement.
ISO 22000 is family of standards that's most compatible with businesses in the food industry. This standard identifies the requirements for a functional food safety management system in any food business.
ISO 22000:2018 is the ISO standard that outlines the requirements for a comprehensive food safety management system covering all areas of the entire food supply chain. This particular standard includes objectives, such as identifying relevant food safety hazards, establishing critical control measures, having an internal audit program, implementing one of the best food traceability systems, and more.
In addition to ISO 22000:2018, other notable ISO 22000 standards include:
The ISO 22000 food safety management system standards are designed to ensure the safety and quality of food products throughout the entire supply chain. Adhering to these standards will enhance your ability to consistently deliver products and services that meet both customer expectations as well as regulatory food safety requirements.
It's important to note that food safety standards and regulations can vary by region and country. Organizations operating in the food industry should stay up-to-date with relevant standards and regulations to ensure compliance and the delivery of safe food products to consumers.
Yes, the ISO 22000 standards are necessary. They're generally recognized to provide a solid foundation for international regulation and requirements for food safety. The organization's standards help optimize business operations and reduce barriers to conducting safe and quality international trade.
ISO management standards harmonize transactions between countries and different industries.
Specifically, the ISO 22000 standards help achieve the following objectives:
The benefits of ISO 22000 contribute to creating effective food safety management systems and equally safe and efficient food production systems across different nations and industries. They promote the best practices to ensure consumer safety, higher quality of products, and sustainability of the environment.
The objectives and benefits of the ISO 22000 standards align with FoodDocs'. With the help of our smart Food Safety Management System, establishing a monitoring program based on a comprehensive HACCP Plan is super easy. Powered by artificial intelligence, our system can automatically generate customizable monitoring tasks, complete with detailed instructions.

ISO 22000 compliance means following the guidelines and applying them to your food business.
The International Standards Organization suggests a general 4-step procedure when complying with any of their programs, and are all essential for any ISO standard compliance.
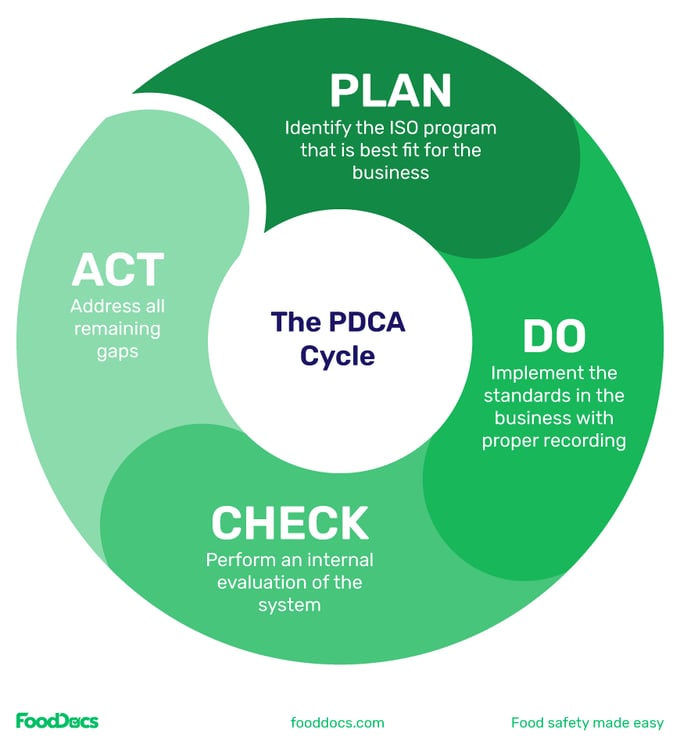
After following the steps above, you're ready to start the official process of ISO 22000 certification with an accredited third-party certification body.
The ISO 22000 certification formally confirms a food organization's efforts to establish a food safety management system compliant with the ISO 22000 standards.
The certification program aims to identify the comprehensiveness of an organization's food safety system. It also evaluates the organization's food safety practices, procedures, and documentation.
The ISO food safety certification program also ensures that a company's food safety system is seamlessly integrated with the principles of the Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points (HACCP) system.
The certification program involves an auditing system where the food company will undergo a thorough evaluation. The ISO 22000 certification will be awarded to a food business that has proven its commitment to food safety and preparedness for safety and business risks.
![]()
To achieve the ISO 22000 certification, the organization outlined clear guidelines and requirements for food safety for businesses. These basic requirements help organizations identify hazards, control them, protect consumers, and continuously improve safety and efficiency.
Fulfill all the ISO 22000 requirements with the help of FoodDocs' smart Food Safety Management System. Our smart software covers all the steps in building your food safety system and plans for ISO 22000 certification.
Powered by artificial intelligence, our innovative software can help automatically generate a comprehensive food safety system with monitoring tasks, a traceability system, auditing materials, and intelligent tools for food safety compliance.
In addition to establishing a complete food safety management system, our software can help you build your HACCP. With our built-in HACCP plan template builder, you can get a customizable template based on your specific business operations. This feature can help you complete all ISO 22000 certification requirements.
Getting ISO 22000 certified is lengthy and requires a lot of attention. So preparation is key for a smooth certification process.
We narrowed down the essential procedures for any food business to get ISO certification in 10 easy steps:
 How to apply ISO standards and get ISO 22000 certified poster
How to apply ISO standards and get ISO 22000 certified poster
Obtaining ISO 22000 certification involves implementing a food safety management system within the organization and undergoing a comprehensive evaluation by an accredited auditor.
Achieving an ISO 22000 certification can be a strong competitive advantage. It implies that the business has covered the essential areas for food safety and customer protection as evaluated by a certified auditor.
The speed at which food businesses can obtain an ISO 22000 certification depends on their size, the complexity of their operations, whether they're starting from scratch or adapting a paper-based FSMS, and more. But generally, this multi-step process can take six months to a year at minimum.
After the long preparation and certification process, the business will be awarded an ISO 22000 certificate as proof of its commitment to food safety. The program also promotes continual improvement by conducting periodic surveillance audits to ensure the business consistently follows ISO 22000 requirements.

The process of ISO 22000 certification may be long, but there are ways to speed up the process without sacrificing the quality of the requirements. Use FoodDocs' AI-powered Food Safety Management System with a built-in HACCP builder. With the help of our smart software, essential monitoring tasks can be established based on identified hazards and critical control points from your gap analysis.
Food businesses can get a comprehensive food safety system in just 15 minutes with the help of our smart software. Using our solutions, you can create automatically generated monitoring tasks and checklists that can further be customized to fit ISO standards. These tasks can be used to record information and analyze gaps in the business. Findings can be immediately addressed and realigned with ISO standards.
In addition, each task is equipped with educative materials that can be used to train food handlers according to the ISO standards.
Businesses can also get smart auditing tools that can be used to evaluate their operation's compliance with ISO standards.
ISO compliance and certification are significantly related terms but refer to different concepts and levels of adhering to ISO standards.
Compliance refers to the organization's commitment and adherence to the requirements, principles, and guidelines of the ISO 22000 standards. This means a compliant organization uses the ISO guidelines in their practices and food safety systems.
While documentation is part of compliance, this concept does not involve external auditing from third-party accreditors.
ISO certification is the formal process of undergoing a comprehensive evaluation by an independent third-party certification body. Certification involves a series of audits, reviews, and assessments conducted by qualified auditors from the certification body.
If the organization successfully demonstrates compliance with the standard's requirements, they are awarded an ISO certificate.
Complying with the ISO 22000 requirements can take months of preparation and several hours of documenting the food safety system.
Use FoodDocs' smart Food Safety Management System with a built-in HACCP plan builder to efficiently comply with all the ISO 22000 certification requirements.
Our innovative software can fulfill all ISO certification steps and continuously improve food safety systems for food businesses.
One of the main objectives of ISO 22000 is to establish a system with adequate control over the food safety of a food business's food safety team. Get the essential tools, such as customizable monitoring tasks, for recording compliance from our software.
 Customizable Temperature Log from FoodDocs software
Customizable Temperature Log from FoodDocs software
All generated monitoring tasks can be further tailored to fit unique operations. Improve each monitoring task according to the ISO 22000 guidelines. Add fields, tasks, and parameters that need monitoring to ensure that the Food Safety System captures the essential information required by the ISO certification program.
Make monitoring tasks more comprehensive by applying suggestions from the ISO certification auditor. Quickly edit monitoring tasks and incorporate their points for improvement to show commitment to food safety.
Show the business's comprehensive approach to food safety by providing the food safety team with clear and educative instructions for food safety training. Another essential objective of achieving ISO 22000 certification is for the team to show mastery of applicable food safety rules and knowledge of food hygiene.
All monitoring tasks and checklists generated by our system come with step-by-step instructions on performing and monitoring the task. These instructions are expertly attached to each monitoring task to serve as a guide for food handlers.
 Monitoring tasks with step-by-step instructions from FoodDocs software
Monitoring tasks with step-by-step instructions from FoodDocs software
Managers can use these instructions for food safety training and onboarding new food handlers. Our system also accommodates customizations of instructions as it allows admins to upload their version of the instructions as videos or images.
Use our system to prepare the team for the actual ISO certification process. Upload or audit checklists to our system or create new ones from scratch and conduct in-house evaluations through any mobile device.
Identify areas that need more attention and address all potential gaps in the food processes before the ISO certification audit. Use our intelligent tools to review the system as needed and ensure everything is in place.
Incorporate findings from the gap analysis into established auditing checklists and evaluate whether the team has resolved the issues effectively.
A critical requirement of the ISO 22000 certification program is for the food business to have a way to monitor their product's movement across the entire food chain.
Our smart Food Safety Management System fulfills both monitoring task needs and traceability requirements. Use our Smart Traceability System to log and access information about product and ingredient batches efficiently.
With the help of our Traceability System, historical data about production batches can be easily accessed, especially for food recalls. Make production management more effective with the help of this feature. Use our Advanced Search options to find precise documents about a particular product quickly.

Fulfill the most significant part of the ISO 22000 certification program with the help of our built-in HACCP plan template builder. Our software can automatically generate a comprehensive digital HACCP plan template that can be further improved through customization.

Our system will generate the HACCP plan template based on the provided information. Fulfill one of the major requirements of the ISO certification in an average of 1 hour with the help of our built-in HACCP builder.
In addition, teams can add any suggestions from the accrediting body easily, as the digital HACCP plan is fully customizable.
Allow our intuitive Food Safety Management System to help your food business achieve your ISO 22000 certification more efficiently. In just 15 minutes, you can get a HACCP-based Food Safety System compliant with the ISO 22000 standards.
Book a free one-on-one demo with our food safety and software experts to walk you through our smart software. Our expert members can show you how our software can help your business achieve ISO 22000 certification efficiently.
To help you understand more about ISO 22000 certification, here are a few of the most common questions people ask:
The ISO 22000 standard covers a broader context than the HACCP system. ISO incorporates the principles of HACCP into food safety management systems and requires higher standards for the overall improvement of food safety. Contrary to just the HACCP system, the ISO 22000 standards include traceability, monitoring, consumer satisfaction, and production management.
Choosing between the two systems depends on the level of scope needed for a food safety management system.
ISO compliance requirements depend on the program under the organization. For food businesses, organizations must establish and maintain a food safety management system that adheres to the requirements outlined in the relevant ISO standard, such as ISO 22000.
This includes implementing processes to identify food safety hazards, establishing food safety control measures, conducting regular audits, ensuring employee training, maintaining documentation, and continuously improving the system.
On the one hand, Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points (HACCP) is basically a systematic approach that aims to identify and control food safety hazards in the food supply chain. On the other hand, ISO 22000 implements the same HACCP principles to establish a food safety system alongside other elements such as communication, management commitment, and continual improvement.
FSSC 22000 (Food Safety System Certification 22000) and ISO 22000 are related but distinct standards. The FSSC 22000 is a certification scheme recognized by the GFSI that is based on the ISO 22000 requirements.
The ISO 22000 standards focus on establishing a food safety system that focuses on the HACCP principles and can be applied to almost all food businesses. Although the FSSC scheme has more requirements, it has a more limited application. The FSSC is generally only applicable to industries including food ingredients, packaging, feed production, and handling high-risk animal products.
FSSC 22000 offers a more industry-focused approach by addressing sector-specific prerequisites, such as prerequisites for food packaging manufacturing and food producers.
ISO 9001 and ISO 22000 are international standards that cover different areas. ISO 9001 covers product quality management for different industries and not just food businesses. The standard aims to enhance the overall business process.
The ISO 22000 standards, on the other hand, focus specifically on establishing effective food safety management, ensuring safe production and handling of foods, and customer satisfaction.
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...