Jul 14, 2025
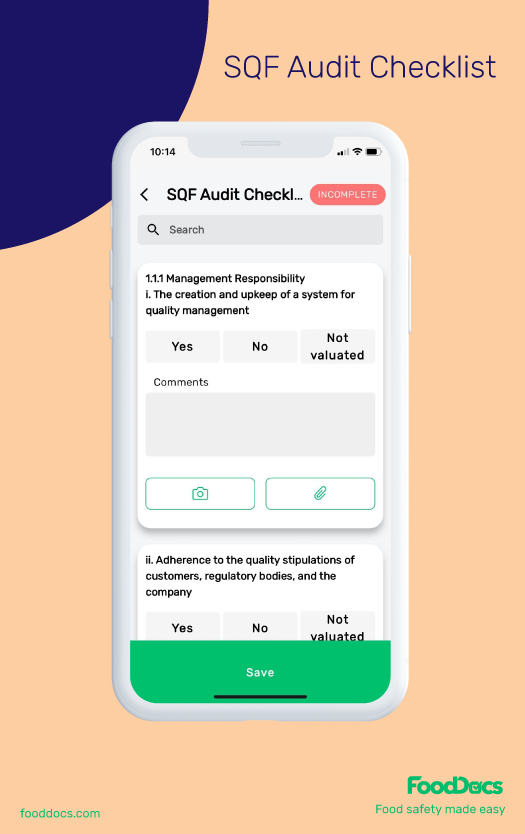
SQF AUDIT CHECKLIST FREE DOWNLOAD



Preparing download...

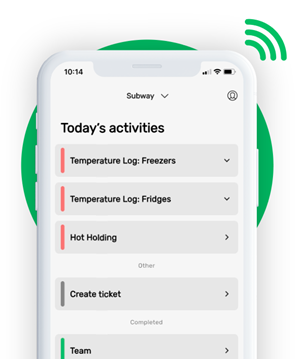
This is how our Digital Food Safety platform saves 20% of your time on daily tasks:
- Get upcoming task notifications
- Add data into the app
- Check the status of tasks in real-time

When food safety was still handled on paper, I typically spent a couple of hours per day getting the papers and going around checking or completing tasks… Now I can sit down and it's just all there in one place. It takes me 5-10 minutes.
Ruth B.
Store Manager
Digitize your internal SQF audit checklist and Simplify your SQF compliance journey with FoodDocs
You can recreate and further customize this SQF audit checklist in FoodDocs' Food Safety Management Software!
Once you have an account set up, you can head over to the Audits feature, and create one from our templates or start a "New audit template" from scratch based on the SQF standards.
Start your 14-day free trial today! No credit card required.