Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Every food business must have a Food Safety Management System. Do you know how to establish one?
Every food business must have a systematic approach to controlling food safety hazards.
To implement that approach, you first need to know what a Food Safety Management System (FSMS) is, the purpose of an FSMS, and the necessary steps to create an effective one.
A Food Safety Management System (FSMS) is a structured, documented framework that food businesses use to identify, control, monitor, and verify food safety hazards across all stages of food production, handling, and distribution.
An FSMS is a legal requirement for almost all food businesses, as food safety is a key concern in the food industry. A compliant FSMS covers monitoring receiving processes up until the distribution of finished products.
Food Safety Management Systems vary depending on the nature of a food establishment. Routine safe practices and appropriate monitoring procedures will vary depending on the potentially present food safety hazards in a food business.
Here are a few examples of how this nuance may present itself:
All operations related to the management of food safety procedures of a business must be documented as proof that the business has established a line of defense.
This documentation must be regularly visited and reviewed to ensure that the system is still efficient and effective. In case of improvements, the collected information can be used for every decision needed.
The terms food safety system and food safety management system are often used interchangeably, but they do not mean the same thing.
A food safety system refers to the overall approach a business takes to keeping food safe. This may include safe handling practices, hygiene rules, staff training, and hazard controls.
A Food Safety Management System (FSMS) is the formal management framework that brings these activities together into a controlled, documented, and auditable system. An FSMS defines:
In practice, food safety systems describe what is done, while a food safety management system explains how those activities are planned, managed, reviewed, and improved over time.
The purpose of a food safety management system is to ensure that all food safety operations are working effectively while reducing the risk of causing foodborne illnesses.
The elements of food safety management systems aim to manage potential food hazards in any food business and ensure safe food products for human consumption are released to the market.
A proper FSMS also guides food handlers on how to properly conduct essential food safety procedures and maintain a high level of food hygiene. It lays out concrete and standard operating procedures of food handling practices, including information on how and when to perform them.
A positive result of implementing food safety management systems is that it helps to increase consumer education and awareness. If you communicate your food safety practices transparently (which we suggest businesses do), customers will trust and choose you more.
Food safety is a global priority, after all, with various regulatory bodies ensuring that food businesses adhere to strict safety standards. There are key regulatory authorities that you're likely familiar with such as the United States' FDA and USDA, and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA).
There's also the Codex Alimentarius, which sets international food standards and plays a crucial role in establishing the guidelines and requirements for Food Safety Management Systems (FSMS).
Once you determine which FSMS is relevant to your business or you're trying to gain certification from, understanding that regulatory framework will help your business align its practices with global standards, ensuring food safety compliance and enhancing consumer trust.
Managing these hazards is critical to keep a food business running. Fulfilling management tasks means building a comprehensive food safety management system that will protect public health from harmful food handling practices and prevent the occurrence of a foodborne illness outbreak. The requirement is a food industry standard and is considered the highest effort for any food business to ensure food safety.
Learn the basics and importance of building a strong food safety management system from this article.
WHAT WE'LL COVER:
A Food Safety Management System is required—or strongly expected—for most food businesses, although the exact legal requirements vary by country and business type.
In general, an FSMS applies to:
Food safety management system requirements are defined at a national or regional level, but many are aligned through international guidance.
Because requirements differ by jurisdiction, food businesses must ensure their FSMS aligns with local regulatory expectations while maintaining consistency with recognized international principles.
Achieving food safety is not a guessing game. Proper food safety management systems are composed of objective standards and principles that must be apparent to achieve food safety.
These steps describe the management-level structure required to design, implement, and maintain a food safety management system. While specific controls vary by business type, the underlying management principles remain consistent.
As a system, an FSMS is composed of different parties and key personnel from the food industry.
It takes the participation of the food service manager, food workers, suppliers, and customers to build a working food safety management system.
Here are some of the essential components of a working food safety management system:
The success of your FSMS hinges upon the understanding of your operation's needs. For example, how complex are your current processes, the nature of the food items you produce, the level of risk and potential hazards.
Knowing the type of equipment your operations require, which team members are involved, and where in the product flow they're involved are all things you need to bring to the table first when starting to create a food safety management system.
And then the objective: are you just trying to set up a HACCP system, for example, before opening your business? Or are you striving to achieve a certification for all your locations from a globally recognized food safety organization?
When you're equipped with the information above, FoodDocs' FSMS software makes the rest of the process easy.
This team will be responsible for all the documentation and food-handling tasks. All food safety team members must have sufficient knowledge of food safety practices and the consequences of non-compliance with regulations.
The team will help maintain a safe working environment in any food business. As such, they must have proper training in observing the major food practices. Food handlers must have a proper understanding of accountability regarding food safety compliance and how to follow the FSMS.
Within the food safety team, at least one food worker must be certified through an accredited certification body to have adequate food safety knowledge. In some cases, all food handlers are required to have proof of proficiency.
Upon setup, the FoodDocs Team feature allows you add team members, assign roles, upload relevant food safety training or certification documents, and more! Once your team is set up, you can even assign role-based tasks which allows staff to get daily notifications in the FoodDocs app for their specific tasks.
There are several different prerequisite programs in the food industry. Their main objective is to satisfy the minimum environmental conditions of a clean working space.
These programs include mandatory basic food hygiene practices to maintain clean and safe food preparation conditions. The operations under the prerequisite programs must be consistently delivered and performed.
Although essential to food safety compliance, these operations normally do not require comprehensive monitoring logs but daily checklists and food safety posters as visual aids.
During the automated HACCP Plan process, based on your business profile (and answers to a few key questions), FoodDocs generates the most applicable prerequisite program documents for your food business.
Our system will generate PRPs complete with the following information:
This component contains the core of the food safety management system. Depending on the food safety legislation in a location, the orientation of the hazard control plan may vary. The Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) program is perhaps the most well-known system.
The HACCP program contains systematic and detailed procedures to control identified and analyzed food safety hazards. It also contains important monitoring procedures to ensure that food safety compliance and hazard controls are always maintained.
If you need to set up a HACCP Plan, you can get it in less than an hour, thanks to our AI-powered HACCP Builder. The plan can be downloaded and also covers Critical Control Points, Standard Operating Procedures, a Flow Chart, and more.
After identifying and evaluating potential hazards, the next step is to establish control measures. These measures aim to prevent, eliminate, or reduce the hazards to acceptable levels and are typically applied at critical control points in the process. For instance, a control measure for preventing bacterial contamination could involve cooking at a specific temperature for a certain duration.
Corrective actions for any deviation on each critical control point. These corrective actions are intuitively set to automatically pop up from our mobile application as choices whenever a breach of standards occurs. This feature can easily guide food employees with which corrective action to perform.
At FoodDocs, we can help you take out the tedious process of identifying these corrective actions for all of your critical control points. Our built-in software HACCP plan builder can help you complete all 7 principles of HACCP in about one hour by automatically generating a comprehensive HACCP plan based on your business operations.
This means that you will automatically get comprehensive and intuitively suggested corrective actions for any potential breach in your operations.
All hazard control procedures must be properly recorded to ensure that foods undergo safe processing. The results must be documented in monitoring logs designed to capture specific data on food safety tasks.
Monitoring logs are used to record the hazard control procedures' results and prove that the FSMS is effectively functioning. Documented food safety records must be retained for at least two years in case food safety concerns arise from released food products.
Some of the most important and commonly used monitoring logs may include the following:
Find free templates of the most important food safety monitoring logs from our free food safety templates library.
The FoodDocs Monitoring system makes it easy to fill and verify tasks. It also gives you a high-level and hyper-detailed view of your operation's overall food safety health.
As you validate your FSMS with FoodDocs' food safety management software, you'll use its Monitoring tools to ensure that your hazard controls and, more importantly, corrective actions are working exactly as designed.
During the smart implementation process, we automatically set up your monitoring and traceability mobile app, which saves your team time on monitoring and traceability tasks, allowing them to complete logs in seconds. Team members will receive smart notifications with instructions from the app, so they’ll never miss another task!
All while reducing time spent on paperwork and processes by 20%.
As part of an FSMS, some businesses may require a recall and traceability system to address public health concerns. Food business must be prepared for any customer complaints.
The component consists of established procedures to control hazardous or unsafe food released to the market. Having an FSMS helps food business owners handle recalls and incidents better, as recommended by food safety agencies like the FDA.
A complete FSMS with extensive monitoring logs allows food businesses to track down which parts of the market where the affected products are distributed.
FoodDocs' FSMS allows visibility over the distribution of food products. Our smart FSMS features an intuitive Traceability System that helps quality managers keep track of their resources and products in real time.
Using the Traceability system, you'll be able to sort the logs by product name, batch, expiry date, or created by date quickly and easily pull up necessary food recall data.
Effective food safety management systems are all about documentation. Details and information about the hazard control system are essential. Every critical procedure must be properly recorded.
Establishment documentation can be used to verify whether the FSMS needs to be improved or if it is still working efficiently. Documents such as food safety certificates, safety inspection reports, traceability logs, and training documents must all be properly collected and stored as part of the FSMS.
Prerequisite programs, standard operating procedures, certificates, food recall communication... the list goes on. And it's a list that easily translates to hundreds of pages of paper or more.
That is, if you use a paper-based FSMS. FoodDocs neatly and safely secures any documentation you have and gives you full capacity to customize folders as needed.
That way, when it's time for an internal audit or annual inspection, you can confidently and quickly update or produce the food safety documents in question.
Intensive and sufficient training on food handling practices and food hygiene are integral parts of an FSMS. Food safety training highlights how to properly perform food safety tasks, the frequency of performing them, how to monitor each task and their particular importance.
It's far too easy for food safety training to simply become a box that people check, but it's a valuable investment of time. Remember: your business's food safety culture is only as good as people who put it into practice.
Add our free food safety quiz to your food safety management training, and use it to test and train employees on food safety topics.
As more and more team members complete food safety trainings and gain new certifications, keeping track of physical sheets of papers or even emails (both of which can get lost) becomes tedious.
FoodDocs' Team feature not only makes customizing team members' roles and monitoring tasks easy. It safely stores those documents all in one place, with their expiry dates, so you can always ensure up-to-date food safety across the board.
Your food safety management system is — or at least should be — a living and breathing thing. In some cases, updates on food safety standards are imposed on your business (as is the case for many needing to get compliant with FSMA 204 requirements).
However, one of the best things you can do to instil employee and customer confidence is proactively review how you stack up against your own defined FSMS. Does your business adhere to its own standards on food safety? Or does it just "talk the talk"?
This could simply look like an internal food safety audit according to the standards you're trying to achieve (or maintain) every couple of quarters, for example.
FoodDocs accounts for and fulfills every component mentioned above. Every component prepares the food safety management team on how to handle food safety hazards and how to address cases of food safety issues.
Establishing an FSMS is a continuous process. This means that the system must be regularly updated based on food safety audit reports or amendments to the location's most essential food safety regulations.
Get a flexible food safety system at FoodDocs. All monitoring logs and checklists generated by our intuitive Food Safety Management System can be further customized to fit unique operations. Business owners can also easily apply comments from food safety auditors and immediately comply with their directions.
Start a 14-day free trial and see how easy it is to create your digital Food Safety Management System!
A food safety and quality management system ensures the safety and quality of food throughout the entire food production and supply chain for safe consumption. The system protects the public from foodborne illnesses and other related injuries.
Below are the most important aspects of a food safety management system:
The predefined operations in an FSMS help control particularly identified food safety hazards. When the FSMS is followed accordingly, a food business can become more credible in the eyes of the public from compliance with food safety policies and regulations.
Failure to comply with food safety regulatory requirements increases the risk of causing foodborne diseases or food poisoning. Because food safety risk factors are inevitable in the food industry, food businesses must use a complete FSMS to address any risk of food safety issues.
While the main objective of an FSMS is to maintain food safety, it also ensures quality products. A food safety monitoring system also considers changes in the physical and chemical characteristics of the food product.
Any change, whether visible or seen only through analytical testing, can affect safety as much as food quality standards. An FSMS promotes uniformity over the products and helps ensure that the food items are of good quality.
The operations monitored by an FSMS are often based on the product specification, which also relates to the product's quality.
An FSMS can help food businesses save on costs, improve consumer acceptance, and increase sales and profits.
In terms of cost, an FSMS can reduce the amount of food waste generated by a food business. Standardizing the operations for safety can help improve the efficiency and effectiveness of preventive controls and overall food production. The lack of a comprehensive FSMS can lead to causing a foodborne illness outbreak, which costs around $95.2 billion yearly for low- to mid-income countries.
Implementing an FSMS helps food businesses comply with food safety regulations and standards set by local authorities and international organizations.
The establishment of a food safety system itself is a requirement by food safety agencies in countries such as the US, UK, Canada, and Australia.
By establishing standardized procedures and practices, an FSMS streamlines operations, improves food waste management, and optimizes resource utilization.
A comprehensive FSMS can help food operators ensure that they cover all safety precautions during the production stage. This program also reduces the likelihood of unnecessary delays and food safety issues.
An FSMS promotes a culture of continual improvement by regularly reviewing processes, updating practices, and incorporating customer feedback for better food safety outcomes.
Operations can be efficiently improved once streamlined by a comprehensive FSMS. Verifications can be done through the gathered documents, and the multi-disciplinary food safety team can make more informed decisions.
With an FSMS, food businesses are less likely to conduct food recalls because operations are always monitored. The sources of problems are detected before the products are even served.
In case of a food recall, food safety records can help address the problems faster. Recall procedures can become more efficient as all needed information are organized and neatly compiled.
As the quality and safety of products improve with an effective FSMS, the business reputation and customer loyalty can improve. This aspect can help promote the business as an institution that values the safety of the consumers. Loss of customers can potentially occur when food contamination risks are uncontrolled.
Particularly for restaurants, a study concluded that a single foodborne illness outbreak had been estimated to cost around:
Another study in the journal Foods titled "Consumer Trust in Food and the Food System: A Critical Review" which analyzed producers, processors, and retailers stated:
Our review showed that the identified factors influence consumer trust in two distinct ways: either at the product level through labelling, or indirectly through actors of the food system. Providing direct assurance on the safety and quality of food items through food attribute claims, certifications, country and region of origin, and food traceability information, builds consumer confidence and trust.
Food safety and quality management system go beyond just the safety of food. The importance of having an effective and functioning FSMS cannot be neglected for the food business to succeed.
This is exactly what we envision at FoodDocs - for food safety to be accessible to all food businesses and help them flourish. Using our digital Food Safety Management System, operators can ensure the safety of foods and that all tasks are done correctly and consistently on time.
Our digital solution includes smart tools, such as an automated setup and smart notification system. Ensure that all food safety tasks are done on time by allowing our system to send intuitive notifications to food business operators through our food safety app.
The ISO 22000 food safety management standard, for example, specifically applies to all food producers, regardless of their size or product. Its primary goal is to provide "a layer of reassurance within the global food supply chain, helping products cross borders and bringing people food that they can trust."
According to the ISO 22000 documentation, a successful FSMS is build upon these four key principles:
Interactive communication: Trust is central to an effective FSMS, from the suppliers of food all the way to the consumers of food. Involving relevant stakeholders in the creation of your FSMS early on will help to prevent negative food incidents while ensuring compliance with food laws.
System management: Maintaining control of food safety becomes a lot easier when a food safety team leader builds an FSMS that prioritizes, customer focus, leadership, employee understanding and engagement, food safety protocols, continuous improvement, evidence-based decision making, and relationship management.
Prerequisite programmes: PRPs such as Good Manufacturing Practices and Good Agricultural Practices are another integral piece of any sound FSMS because they help establish operations that reduce potential food safety hazards.
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point principles: They help Quality and Food Protection Managers identify and control food safety hazards. The seven principles of HACCP should be familiar to anyone who's had involvement in food safety and include: conducting a hazard analysis, determining critical control points, establishing critical limits, establishing monitoring procedures, establishing corrective actions, implementing proper verification procedures, and setting up record-keeping and documentation procedures.
Food business teams are responsible for implementing a food safety and quality management system in the facility themselves. As such, the implementation process is a collaborative effort among the management, food safety team, and external auditors.
Let's discuss the responsibility of each member of the FSMS implementation team:
Food safety is a shared responsibility among all members of a food business. While each participant has their own responsibilities, collaboration and communication between them are key to ensuring successful implementation.
Every reliable Food Safety Management System revolves around monitoring whether preventive and control measures can address hazards or not. Monitoring procedures are used to assess whether hazards are controlled or not. The results are also used to decide if the product is ready to be released into the market.
It is critical for the logs to have important information regarding the product, such as the time of monitoring, the result of observation, the person in charge, and a section for remarks.
Despite being very tedious to make, monitoring is a must to address any concern about food safety. At FoodDocs, we understand how difficult it may be to build monitoring logs that are readily customizable to accommodate any changes or improvements. As such, we offer free tools that will help food businesses with monitoring tasks and more:
Use any free helpful tools mentioned above to build and customize any needed food safety logs. Download food safety documents for free anytime! In addition, use other free tools, such as our food safety quiz, to train food business operators on regulatory compliance topics or refresh their food safety knowledge.
The best food safety management system is one that comprehensively covers all areas of a food business and ensures that there are corrective measures in case of non-compliance.
Different restaurants and food businesses have different requirements for their food safety solutions. However, these businesses all share a common goal - food safety in the most efficient way.
Here are some core steps in choosing the best-fit food safety system for the business:
Establish a hazard preventive and control system: Once a proper working environment and conditions for food preparations are established, a hazard prevention and control plan can be operated. Most food safety regulations tailor the required structure of a preventive plan to the HACCP system.
Below are some of the critical areas of a HACCP plan:
Nowadays, there are several ways to streamline the entire selection process. The best example is FoodDocs' intuitive Food Safety Management System Software.
Powered by AI and a machine learning program, our software can be implemented within just 15 minutes. Food safety experts have developed this system to make compliance more efficient.

8 Steps for a good food safety management system strategy
Through the extensive effort of food safety organizations and government agencies, suitable food safety management systems have been established and are made available for all businesses.
The established structures of different FSMS vary in complexity and scope of management.
Some systems are less stringent than others and focus on the food safety basics, whereas some require detailed documentation and higher food safety ratings and food standards.
To illustrate the differences between quality management systems, for example, one research paper published in Economics of Agriculture breaks them down similar to this:
| Quality Assurance System | Attribute managed | Implementation | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| ISO 22000 | Food safety | Mandatory minimum for all suppliers | Good foundation for food safety management Based on HACCP |
Difficult to implement Comprehension of the system Experience to implement |
| GAP |
Environment |
Mandatory minimum for all suppliers | Objectivity (3rd party audits) Reduces monitoring and auditing costs. Specifies production practices |
Not flexible High investment and running costs |
| BRCGS | Food safety Value |
Mandatory minimum for all suppliers | Reduces auditing costs Objectivity (3rd party audits) Includes food safety component (based on HACCP) |
Not as flexible as form-specific quality assurance system |
As you can see, each food safety and quality management system emphasizes different attributes (e.g., quality, environment, food safety) and has its own advantages (e.g., based on HACCP, reduces monitoring and auditing costs) and disadvantages (e.g., lacks flexibility, difficult to implement).
Below are some of the most notable food safety systems in the industry:
Prerequisite programs are composed of a wide range of different plans that aim to establish safe and sanitized conditions for food businesses. These programs include basic food handling practices, such as basic food hygiene and minimum food operations.
Although voluntary and does not require stringent monitoring, prerequisite programs are essential for food businesses. Operations included in these programs are very simple and must be observed daily.
Some of the most common prerequisite programs include:
The Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point system or HACCP is a systematic food management system that aims to analyze hazards and establish control measures to minimize them to acceptable levels. The HACCP program is the most widely known food safety plan worldwide.
It is a standard for higher food safety systems as it includes all essential tasks to control hazards and keep customers safe from potential food risks. Establishing a HACCP plan in a food business depends on the requirement of the concerned government agency regarding the nature of the business.
Build your own HACCP plan in just 1 hour using FoodDocs' built-in digital HACCP plan template builder. Get a complete HACCP plan based on your unique operations and customize it further to fit your routines.

Under the U.S. Food Safety Modernization Act of 2011 (FSMA), food production facilities in the U.S. food industry were mandated to establish a risk-based preventive control program in place of a HACCP plan. This food safety program is called the Hazard Analysis and Risk-based Preventive Controls System or HARPC.
The HARPC system is a proactive approach to food safety. It aims to address food safety hazards before they even occur. The scope of the HARPC system is broader than other food safety management systems and uses risk-based data to establish preventive controls.
The International Organization for Standardization, also known as ISO, is a non-governmental organization that establishes food quality and safety standards and management systems for the food industry. This organization has established several different requirements and standards for complete food safety management systems.
One of the most notable requirements published by the organization is ISO 22000. This international standard lays out the most critical food safety standards a food business must have. It incorporates elements of the HACCP system and other versions of ISO standards, such as ISO 9001.
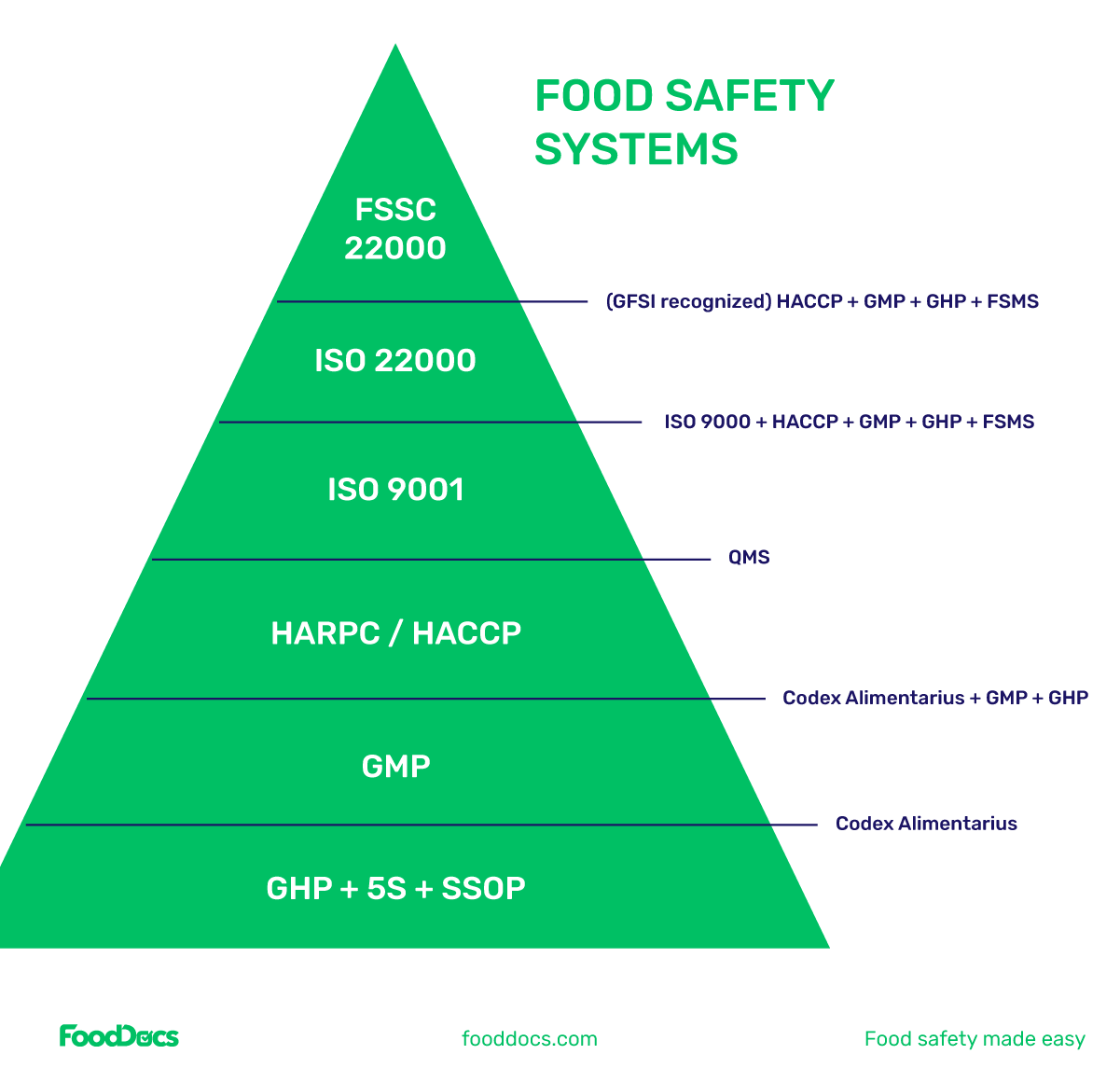
![]()
Food Safety System examples
Some things can go wrong when choosing a solution like restaurant food safety software in a hurry. It is important to note that the systems may be tailored for specific sectors, like retail or large-scale food manufacturers. Food safety is a highly specialized and multi-faceted field.
Here are our 4 tips to consider when choosing the food safety software that bests suits a food business:

4 Tips for choosing the right food safety software
Checklists and types of audit software designed for a very wide audience are often not comprehensive enough for food businesses.
Ensuring food safety is usually a very long and complex process and requires software built by industry experts and adapted specifically to food businesses.
Consider how well the food safety software integrates with existing systems and technologies. Determine if it can seamlessly connect with inventory management systems, point-of-sale systems, or other relevant platforms. Integration capabilities can streamline data sharing, reduce duplication of efforts, and enhance overall efficiency.
In most cases, the food safety software either takes care of traceability or monitoring, but not both. A traceability system promotes accountability and helps keep track of product movement along the food supply chain. Choose software that covers both for more efficient handling of information.
Switching from a paper-based system to a digital platform can be a difficult task for some employees. As such, choose a platform that features an intuitive and user-friendly interface. It should be easy for staff to navigate and use effectively.
Here is a quick comparison of digital platforms available today:
| Food safety management system | FoodDocs | Competitors | Digital checklist apps | Paper-based FSMS |
| Best suited to multiple locations | Best |
|||
| Best suited to small-medium scale producers | ||||
| Full customizability | ||||
| AI-powered HACCP system builder | ||||
| Free trial | ||||
| Food traceability and recall capabilities |
We've created in-depth comparisons with other food safety management software solutions, including
Establishing a strong food safety management system takes time. All steps and components we mentioned must be considered and assembled into a cohesive system.
Every monitoring process will require much attention and customization, and the improvements will keep coming with time.
To help solve this problem, use a smart, digital solution to produce a food safety and quality management system in just minutes.
Using our digital Food Safety System Software, you will gain access to the following benefits:
One of the essential features of our software is a smart notification system that will help remind employees of tasks that need to be done.
The system will send intuitive alerts through our Food Safety App, reminding employees of a particular food safety task. With this feature, you can ensure that all controls in the food safety system will be followed efficiently.
The notification system can also help remind managers whenever certifications or training programs require renewal based on their effectivity dates.
Task notifications from FoodDocs software
Obtain a digital FSMS powered by AI and a machine-learning program, which generates monitoring logs automatically. All logs and checklists have step-by-step instructions to help the team perform tasks correctly and ensure compliance.
Use the instructions to train new employees or remind the team to monitor every control procedure.
By providing the team with accurate instructions, you can ensure consistent compliance with food safety regulations.
Monitoring log with detailed instructions from FoodDocs software
To accommodate the unique operations of every food business, our smart FSMS features customizable selections. Tailor the generated monitoring logs and checks to fit operations. Set any preferred standards and parameters to control. You can even build new detailed forms from scratch.
Add the option to upload your own educative instructions as photos or videos for a better understanding of the tasks. Make every control measure the best fit for operations with our customizable features.
Our software's monitoring system can be easily customized and improved to fit audit findings or when changes in food safety legislation are announced.
Save at least 20% of the time dedicated to supervising using our real-time dashboard. Using the instant overview, you can get a clear picture of your entire operations and easily perform evaluations and verifications of your FSMS. Monitor the company's food safety compliance and immediately address any concerns about food safety operations.
This overview shows the status of all your food company branches and gives you the necessary information to make informed decisions.
When you use our digital FSMS, you not only become more efficient, but you also become more sustainable. With our food safety software, you can ditch the pen-and-paper system and use a completely digital food safety system. No more piles of papers for your team while your business is contributing to saving trees.
Using a digital platform can sometimes be overwhelming. That is why at FoodDocs, we made everything easier for managers and employees alike. We've set up our system with multiple guides, and easy-to-understand instructions to help food workers become more adept with the digital FSMS.
Experience the benefits of our digital Food Safety Management System first-hand by using our free 14-day trial.
Our impressive system does not only create a digital FSMS monitoring program for you. We also feature a built-in HACCP plan template builder that can create a complete HACCP plan within 1 hour. Get a comprehensive HACCP plan based on the key principles of the food safety program.
Want to experience the benefits of our software and get compliant now? Use our free 14-day trial and build your Food Safety Management System today.
Do you need more information on the Food Safety Management Systems topic, or do you have any particular questions? Here are a few frequently asked questions to help you.
FSMS stands for Food Safety Management System.
A food safety management system, or FSMS, is a collection of operations for food companies to control potential food hazards and ensure the safety of public health. This program consists of different preventive and control measures with appropriate monitoring procedures as compliance with food safety rules.
FSMS implements processes and controls to identify, assess, and manage food safety hazards and risks throughout the food production and supply chain
The key elements of a food safety management system include hazard analysis, critical control points, monitoring procedures, corrective actions, verification activities, and documentation.
The Food Safety Management System is a comprehensive framework of food safety processes designed to evaluate and control hazards in a food business.
The main importance of a food safety management system is its ability to ensure food safety and protect public health from potential foodborne illnesses with adverse health risks. An FSMS can also help food companies control the quality of their products and boost customer loyalty and customer confidence.
The key elements of a reliable food safety management system include the following:
Some of the most widely known examples of food safety management programs include the following:
HACCP is regarded as one of the most useful and comprehensive food safety management systems.
Yes, ISO 22000 is an FSMS standard. This standard focuses on principles of hazard analysis, communication, and continual improvement to ensure food safety.
The key food safety principles include the following food safety management practices: keep clean, segregate raw materials and cooked foods, store foods in safe temperatures, cook foods thoroughly, and practice personal hygiene.
Food safety management is important to protect consumer health, prevent foodborne illnesses, comply with regulations, maintain reputation, and ensure the quality of food products.
A food safety system aims to ensure the safety and quality of the food served, protect consumer health, and comply with food safety regulations.
Food safety management systems refer to a general framework that aims to control food safety hazards. On the other hand, HACCP is a type of food safety system that covers all essential food safety practices.
A Quality Management System (QMS) in food safety is a structured framework designed to ensure that food products meet established safety and quality standards throughout the entire production process. It encompasses a set of policies, processes, and procedures required for planning and execution in the core business areas of an organization. By implementing a QMS, food businesses can systematically control and improve their processes to consistently deliver safe and high-quality food products to consumers.
The three main quality management systems widely recognized in the food industry are:
A Safety and Quality Management System (SQMS) in the food industry is an integrated approach that combines the principles of both safety and quality management. It ensures that all aspects of food production, from raw material sourcing to final product distribution, adhere to strict safety and quality standards. This system aims to prevent foodborne illnesses, ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, and deliver products that meet customer expectations for quality and safety.
An example of a food safety system is the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) system. HACCP is a preventive approach that identifies, evaluates, and controls food safety hazards at critical points in the production process. By implementing HACCP, food businesses can systematically monitor and manage potential hazards, ensuring that food products are safe for consumption.
The difference between HACCP and a Food Safety Management System (FSMS) lies in their scope and application. HACCP is a systematic approach that identifies and controls hazards at critical points in the food production process. It's a component of a broader FSMS. An FSMS, on the other hand, is a comprehensive framework that integrates various food safety practices, including HACCP, into a unified system. An FSMS encompasses policies, procedures, and processes to manage food safety across the entire supply chain, ensuring ongoing compliance and continuous improvement in food safety standards.
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...