FOOD SAFETY PLAN TEMPLATE | FREE DOWNLOAD

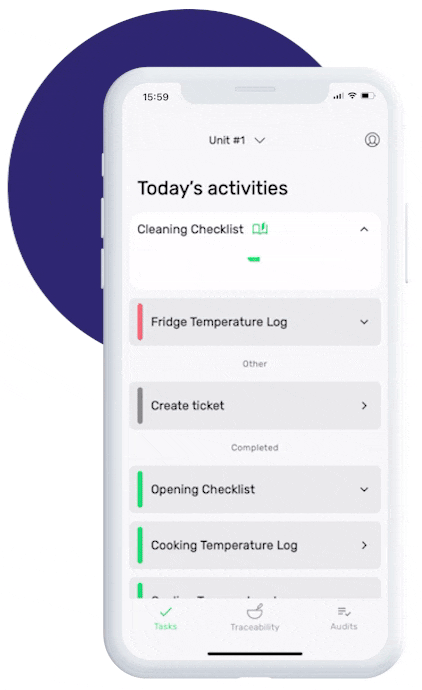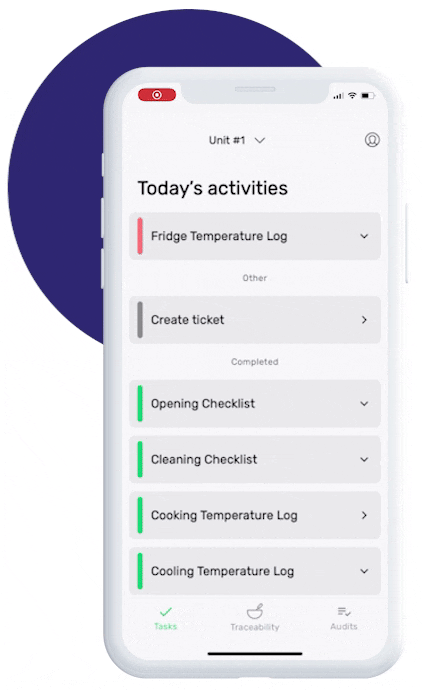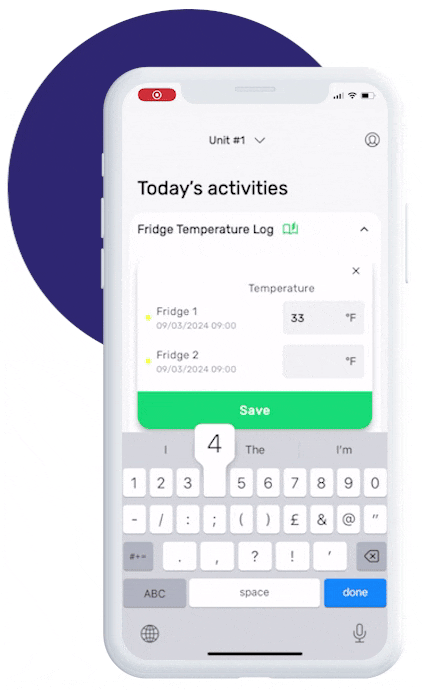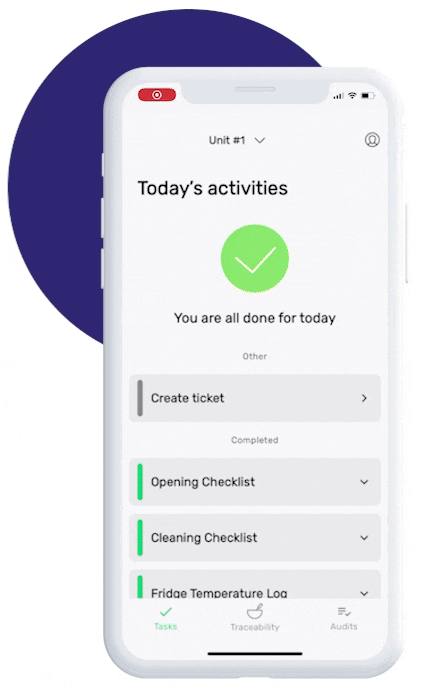
This is how our Digital Food Safety platform saves 20% of your time on daily tasks:
- Get upcoming task notifications
- Add data into the app
- Check the status of tasks in real-time

When food safety was still handled on paper, I typically spent a couple of hours per day getting the papers and going around checking or completing tasks… Now I can sit down and it's just all there in one place. It takes me 5-10 minutes.
Ruth B.
Store Manager
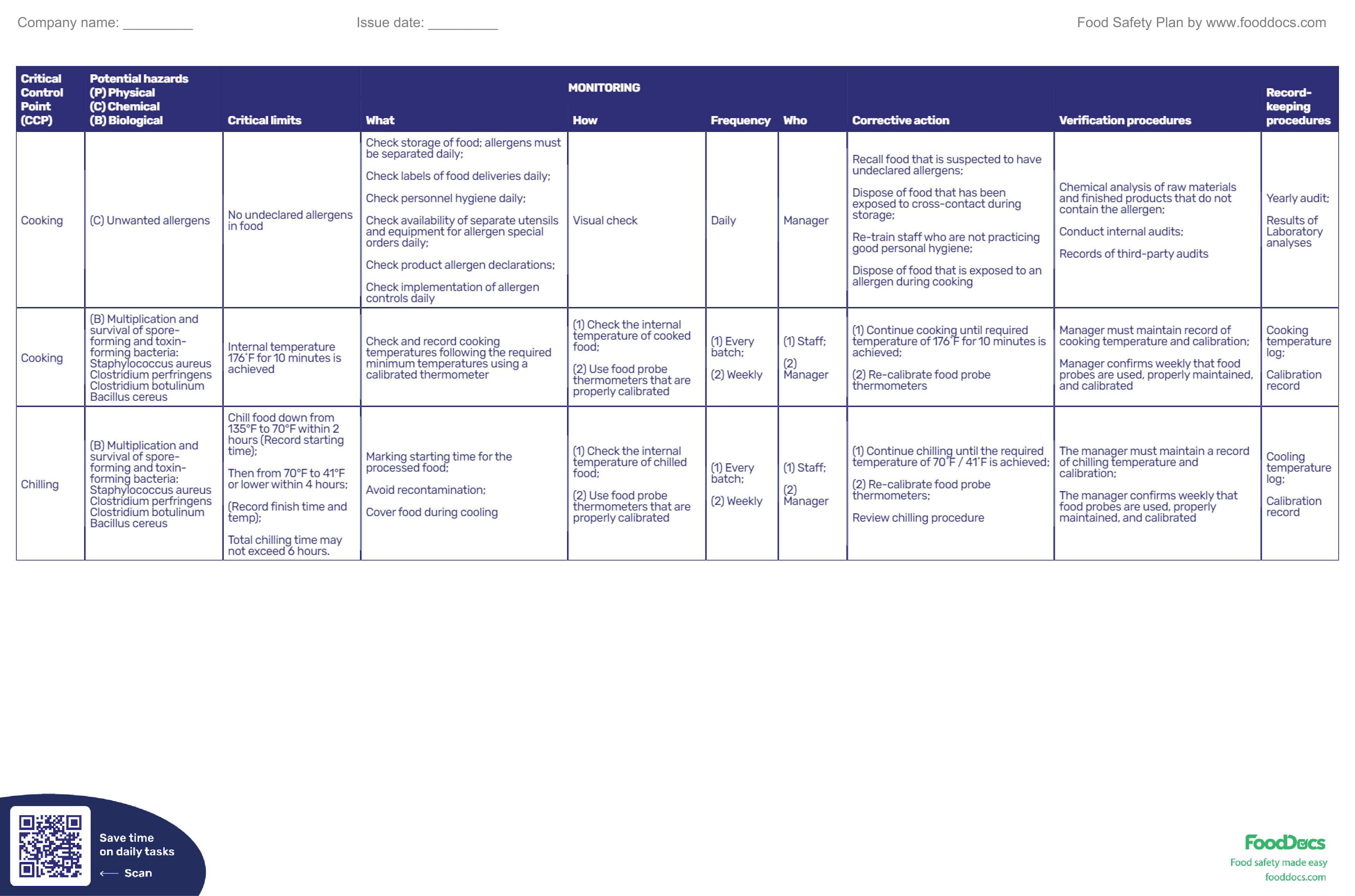
| Critical Control Point (CCP) | Potential hazards (P) Physical (C) Chemical (B) Biological |
Critical limits | MONITORING | Corrective action | Verification procedures | Record-keeping procedures | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| What | How | Frequency | Who | |||||||
| Cooking | (C) Unwanted allergens | No undeclared allergens in food | Check storage of food; allergens must be separated daily; Check labels of food deliveries daily; Check personnel hygiene daily; Check availability of separate utensils and equipment for allergen special orders daily; Check product allergen declarations; Check implementation of allergen controls daily |
Visual check | Daily | Manager | Recall food that is suspected to have undeclared allergens; Dispose of food that has been exposed to cross-contact during storage; Re-train staff who are not practicing good personal hygiene; Dispose of food that is exposed to an allergen during cooking |
Chemical analysis of raw materials and finished products that do not contain the allergen; Conduct internal audits; Records of third-party audits |
Yearly audit; Results of Laboratory analyses |
|
| Cooking | (B) Multiplication and survival of spore-forming and toxin-forming bacteria: Staphylococcus aureus Clostridium perfringens Clostridium botulinum Bacillus cereus | Internal temperature 176˚F for 10 minutes is achieved | Check and record cooking temperatures following the required minimum temperatures using a calibrated thermometer | (1) Check the internal temperature of cooked food; (2) Use food probe thermometers that are properly calibrated |
(1) Every batch; (2) Weekly |
(1) Staff; (2) Manager |
(1) Continue cooking until required temperature of 176˚F for 10 minutes is achieved; (2) Re-calibrate food probe thermometers |
Manager must maintain record of cooking temperature and calibration; Manager confirms weekly that food probes are used, properly maintained, and calibrated |
Cooking temperature log; Calibration record |
|
| Chilling | (B) Multiplication and survival of spore-forming and toxin-forming bacteria: Staphylococcus aureus Clostridium perfringens Clostridium botulinum Bacillus cereus | Chill food down from 135°F to 70°F within 2 hours (Record starting time); Then from 70°F to 41°F or lower within 4 hours; (Record finish time and temp); Total chilling time may not exceed 6 hours. |
Marking starting time for the processed food; Avoid recontamination; Cover food during cooling |
(1) Check the internal temperature of chilled food; (2) Use food probe thermometers that are properly calibrated |
(1) Every batch; (2) Weekly |
(1) Staff; (2) Manager |
(1) Continue chilling until the required temperature of 70˚F / 41˚F is achieved; (2) Re-calibrate food probe thermometers; Review chilling procedure |
The manager must maintain a record of chilling temperature and calibration; The manager confirms weekly that food probes are used, properly maintained, and calibrated |
Cooling temperature log; Calibration record |
|
| Critical Control Point (CCP) | Cooking | |
|
Potential hazards: (P) Physical; (C) Chemical; (B) Biological |
(C) Unwanted allergens | |
| Critical limits | No undeclared allergens in food | |
| MONITORING: What | Check storage of food; allergens must be separated daily; Check labels of food deliveries daily; Check personnel hygiene daily; Check availability of separate utensils and equipment for allergen special orders daily; Check product allergen declarations; Check implementation of allergen controls daily |
|
| MONITORING: How | Visual check | |
| MONITORING: Frequency | Daily | |
| MONITORING: Who | Manager | |
| Corrective action | Recall food that is suspected to have undeclared allergens; Dispose of food that has been exposed to cross-contact during storage; Re-train staff who are not practicing good personal hygiene; Dispose of food that is exposed to an allergen during cooking |
|
| Verification procedures | Chemical analysis of raw materials and finished products that do not contain the allergen; Conduct internal audits; Records of third-party audits |
|
| Record-keeping procedures | Yearly audit; Results of Laboratory analyses |
|
| Critical Control Point (CCP) | Cooking | |
| Potential hazards: (P) Physical; (C) Chemical; (B) Biological |
(B) Multiplication and survival of spore-forming and toxin-forming bacteria: Staphylococcus aureus Clostridium perfringens Clostridium botulinum Bacillus cereus | |
| Critical limits | Internal temperature 176˚F for 10 minutes is achieved | |
| MONITORING: What | Check and record cooking temperatures following the required minimum temperatures using a calibrated thermometer | |
| MONITORING: How | (1) Check the internal temperature of cooked food; (2) Use food probe thermometers that are properly calibrated |
|
| MONITORING: Frequency | (1) Every batch; (2) Weekly |
|
| MONITORING: Who | (1) Staff; (2) Manager |
|
| Corrective action | (1) Continue cooking until required temperature of 176˚F for 10 minutes is achieved; (2) Re-calibrate food probe thermometers |
|
| Verification procedures | Manager must maintain record of cooking temperature and calibration; Manager confirms weekly that food probes are used, properly maintained, and calibrated |
|
| Record-keeping procedures | Cooking temperature log; Calibration record |
Maintaining food safety is a multi-layered task, requiring meticulous documentation and adherence to procedures across all aspects of food production and service. At the heart of this process is a Food Safety Plan, a fundamental requirement for any food business.
This plan outlines a company’s approach to food safety, aiming to protect public health by mitigating potential hazards.
Whether mandated by regulatory bodies or voluntarily implemented, a well-constructed food safety plan significantly reduces the risk of foodborne illness and promotes operational safety.
Despite its importance, creating an effective plan requires several technical steps, often benefitting from the expertise of a food safety software or consultant. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to building a food safety plan, from traditional methods (with and without a template) to more advanced digital solutions.
Key points from this article
- A Food Safety Plan is a detailed document that identifies potential food safety hazards and outlines controls, limits, and corrective actions tailored to a specific business.
- Grounded in the principles of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP), it adopts a broader approach to cover additional safety aspects.
- A food safety plan template is a structured guide designed to help food businesses systematically identify, assess, and manage food safety risks.
- Food safety plans are important because they help reduce risk of foodborne illnesses, maximize resource efficiency, increase employee accountability, and improve customer trust.
- All food-related businesses, from restaurants to manufacturers and distributors, require a food safety plan to comply with industry regulations.
- Using a food safety plan template will help teams remain compliant with regulations, improve overall food safety, increase operational consistency, and create a more accountable company culture.
- Using this food safety template requires you to: identify Critical Control Points, define hazards and critical limits, establish monitoring procedures, set corrective actions, and outline verification and record-keeping methods.
- The FDA requires food businesses to incorporate additional preventive controls and programs, such as supply-chain management, which may not be covered by HACCP.
- In the United States, you should update or re-evaluate your food safety plan every three years or when significant regulatory changes occur. However, other countries advise that companies do this once a year.
- FoodDocs' software allows businesses to create digital food safety plans, easily set up monitoring procedures, and implement an easy-to-use food traceability system.
What is a Food Safety Plan?
A Food Safety Plan is a detailed document that identifies potential food safety hazards and outlines controls, limits, and corrective actions tailored to a specific business.
This plan, designed around the food company’s operations, extends from raw material handling to food distribution, ensuring safe handling practices at every stage. Grounded in the principles of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP), it adopts a broader approach to cover additional safety aspects.
What is a Food Safety Plan template?
A food safety plan template is a structured guide designed to help food businesses systematically identify, assess, and manage food safety risks.
It outlines critical elements, such as Critical Control Points (CCPs), hazard identification, monitoring procedures, corrective actions, and record-keeping, ensuring that teams can manage and document each stage of food production to prevent safety hazards.
This comprehensive template serves as the backbone of a business’s HACCP or FSMA-compliant food safety management system.
Why is a Food Safety Plan Important?
The primary goal of a food safety plan is to safeguard public health, reducing risks of foodborne illness while also enhancing business operations. Key benefits include:
- Risk reduction: Fewer foodborne illness outbreaks and safety issues.
- Resource efficiency: Minimizing food waste through safe practices.
- Employee accountability: Staff training improves adherence to safety standards and audit preparedness.
- Customer trust: Demonstrated commitment to safety can build consumer loyalty.
Who needs a food safety plan template?
All food-related businesses, from restaurants to manufacturers and distributors, require a food safety plan to comply with industry regulations, protect consumer health, and avoid foodborne illness.
A free, standardized template provides an accessible starting point for businesses of all sizes, ensuring they meet critical food safety standards.
What are the benefits of a food safety plan template?
A food safety plan template offers numerous advantages:
- Compliance with regulations: Provides a clear structure for meeting HACCP, FSMA, or local food safety requirements.
- Improved safety: Identifies and manages hazards proactively to reduce contamination risks.
- Operational consistency: Establishes clear procedures, roles, and responsibilities, ensuring uniform practices.
- Accountability: Documents every stage, from monitoring to corrective actions, for effective audits and transparency.
How to use this food safety plan template for your food business
- Identify CCPs: Map out critical control points in your production process where hazards could arise.
- Define hazards and critical limits: Document potential physical, chemical, or biological hazards, and set acceptable safety thresholds (critical limits).
- Establish monitoring procedures: Specify what to monitor, how and when to monitor, and assign responsible personnel.
- Set corrective actions: Plan corrective actions to take if any critical limits are breached.
- Verification and record-keeping: Outline verification methods and ensure all monitoring is recorded for accountability.
5 Steps to create a Food Safety Plan from scratch
Of course, you can fast-track the process and save time by using the food safety plan template above. But if you prefer creating one from the ground up, keep reading.
Crafting a Food Safety Plan follows risk-based HACCP principles and involves documenting all food-related operations and controls. Key steps include:
1. Assemble a food safety team
Form a team with members from different departments, ideally led by a Preventive Controls Qualified Individual (PCQI). The PCQI, either an internal employee or a certified consultant, oversees the plan’s creation and implementation.
2. Diagram your process flow
Create a block-style flow chart diagram of all operational steps, from ingredient handling to food distribution. This visual aids in identifying hazards throughout the process.
3. Develop the plan
Break down your food safety plan into the following components:
- Hazard analysis: Identify all potential hazards (biological, chemical, physical, and radiological) and assess their likelihood and impact.
- Preventive controls: Implement actions to mitigate identified hazards, including cooking protocols, temperature controls, and cross-contamination prevention.
- Monitoring procedures: Set up a monitoring plan to verify the efficacy of preventive controls, noting who will monitor, how often, and what specific actions will be taken.
- Corrective actions: Develop procedures to address non-compliance or hazard occurrences, ensuring any affected products are assessed and root causes are documented.
- Verification: Regularly verify that monitoring records and actions align with the plan’s safety standards, updating procedures as necessary.
Each step of the food safety plan should be consistently documented and retained for reference, especially during audits.
An optional step is coordinating with your local food authorities. U.S. regulations offer flexibility in food safety plan formatting, so check with local regulatory authorities for specific requirements. In other countries like Canada, Australia, and the UK, food safety plans strictly adhere to HACCP principles.
Food Safety Plan vs HACCP
In the U.S., food safety plans cover a wider scope than HACCP plans, which focus on critical control points for hazards specific to seafood, juice, and USDA-regulated products. The FDA requires food businesses to incorporate additional preventive controls and programs, such as supply-chain management, which may not be covered by HACCP.
When should you update your Food Safety Plan?
You should update or re-evaluate your food safety plan every three years or when significant regulatory changes occur. Continuous updates ensure compliance and improve the plan’s effectiveness. Previous versions should be documented for reference.
However, if you're able to incorporate more frequent evaluations into your food safety standards (e.g., once every year).
Streamline your Food Safety Plan creation with FoodDocs
Developing a food safety plan can be time-intensive, especially for new business owners. FoodDocs offers an all-in-one digital food safety system.

Key features include:
- Customizable hazard analysis and control points
- Comprehensive monitoring and corrective action procedures
- Additional tools like allergen management, pest control, and recall plans
In addition to those Monitoring and Traceability systems, you get an AI-powered food safety plan builder that streamlines plan creation in just one hour.

This helps you get almost instantly ready for regulatory compliance. Plus it's easily and fully customizable. Get started with a 14-day free trial and get your food safety plan today!