Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Food safety is the responsibility of all parties involved in the food production process.
Every food business protects two main things to stay thriving - food safety and quality. Food safety is an integral part of continuous growth for any food business. Given this fact, food safety is not an easy task to maintain, and it requires attention to detail. Food safety is a continuous aspect of the food industry that must be consistently observed at every point of the operation.
Every year, at least $110 billion in productivity and medical expenses is lost due to unsafe food handling, just from low- to middle-income countries. Failure to comply with food business regulations causes negative effects on communities. It can lead to a loss of productivity and income and affect the consumer's way of living.
Food safety is a part of every food business owner's responsibility to comply with food safety regulations and adapt to the continuous evolution of food safety. To fulfill this, food processors must be well acquainted with the most essential safety basics for food businesses and use a comprehensive food safety management system.
This article contains the most important practices for food safety for any food business.
Here is a quick rundown of what we will be tackling in this article:
WHAT WE'LL COVER:
FOOD SAFETY RULES
FOOD SAFETY TIPS


Smart food safety tools to improve your food safety for free

Free logs and checklists for a quick download

Food safety posters for a quick download
Food safety quiz to test your employees' knowledge
Food safety terms to boost your knowledge
Food safety practices must be applied at all points of food processing. Food handlers must maintain compliance with food safety basics from raw material purchasing and receiving to the distribution of food products to customers. These practices reduce the chances of contaminating products with foodborne pathogens and other food hazards that may cause any food illness and related concerns about food safety.
Food handling practices range from simple operations, such as neatly tucking your hair with a hairnet, to more complex operations, such as adequate temperature and cooking time monitoring. The most essential food safety basics can be summarized with the 4 C's of food safety. These four operations include:
The four mentioned food safety basics cover the most critical areas of a food business where food safety risks are concentrated. These operations allow food handlers to control the likelihood of causing foodborne diseases and produce safe food. Other important food safety operations stem from these four main tasks.
A part of food safety is conducting basic food safety training for employees. This program will help educate food business operators and handlers on performing tasks with high food hygiene standards to keep food safe. Food safety training, including online training courses, is a legal requirement for most certification programs.
Being considered essential, the 4 C's of food safety must consistently be observed to ensure that any potential foodborne risk is controlled and for continuous improvement. This task can be achieved by establishing a food safety management system. Traditionally, the system was done with pen and paper, but it was very prone to food safety risks and errors. As such, digital solutions have become more popular among food handlers.
At FoodDocs, we offer a smart restaurant food safety management software that will remind and guide any food business operator on when and how to perform a food safety task. Our software was built to make food safety compliance easier and more accessible to all food businesses. You can easily maintain compliance with an efficient FSMS composed of digital monitoring logs.

Food safety content often uses the terms rules, procedures, guidelines, and compliance interchangeably, but they describe different aspects of food safety management.
Understanding the difference between these terms helps food businesses apply food safety controls correctly and avoid misunderstandings during inspections or audits.
Every year, food safety issues affect the health and economic sector of countries all over the world.
Here are some key facts showing the importance of food safety all over the world:
In food safety, there is a lot we can do with some basic knowledge. For example, did you know that diarrheal foodborne diseases can be prevented by up to 50% by simple and correct handwashing? In addition, the most significant pathogens can be significantly reduced by cooking foods to the recommended internal temperature. These operations may be very simple and common but are most effective in controlling food safety concerns.
In the everyday cooking process, food handlers are expected to understand the safest conditions for customers. Remember that consuming undercooked meat can cause foodborne diseases. Some consumers are more vulnerable to infectious diseases and sensitive to some artificial chemical substance and are more prone to danger. This group includes pregnant women, the elderly, children below 5 years old, and individuals with very weak immune systems.
As a food handler, we would like you to also remember the following important facts:
Poor food hygiene & safety are the leading causes of foodborne illnesses around the world. Learn more about food safety from our articles published in Food Safety Academy.
We have mentioned the most essential food safety basics that are used as the basis for other food safety tasks. In this section, we dive deeper into how these basic rules of food safety and tasks help businesses maintain a safe and clean working environment.
Food contamination can come from all stages of production. Food handlers, utensils used to prepare food, and even the food itself can carry contaminants that may get transferred to the other raw materials.
Below, we 5 kitchen safety rules and simple steps for maintaining control of food safety in the food business, including:
 5 food safety rules to follow for maintaining control of food safety in the food business
5 food safety rules to follow for maintaining control of food safety in the food business
Maintaining cleanliness covers a broad range of areas regarding food safety in the entire food chain. Cleanliness includes personal hygiene, surfaces that come in contact with food, and the preparation of foods. Pathogenic microorganisms can be easily spread through cross-contamination. This event is a leading cause of foodborne illness outbreaks and food crises. Maintaining cleanliness is the most effective way to reduce it.
Practicing cleaning is applied in areas such as the following:
Food handlers
Food hygiene rules include how food business operators present themselves during preparation and maintain personal cleanliness. This area refers to the food worker's proper attire, nail length, and handwashing frequency.
The most effective way to stop cross-contamination of food is frequent and proper handwashing. When performed correctly, this task can significantly reduce the food safety risk of spreading foodborne and commensal pathogens or those that naturally live on human organs.
Surfaces, equipment, and utensils
Food equipment, utensils, and surfaces must be cleaned and sanitized to ensure that no food particles that may attract bacteria are stuck in any corner. To become effective, cleaning and sanitation must be done frequently and correctly.
Cleaning these surfaces must be done before and after preparing food, whereas sanitation is mandatory when food operations are running continuously for four hours.
Food
Cleaning hard vegetables such as potatoes may be done using soft water and a clean produce brush. It is important to remember that some foods, such as raw meat from an animal, are not recommended to be washed prior to use. Water droplets during rinsing may potentially carry foodborne pathogens and stick to preparation tables and other contact surfaces.
Food premises
A regular schedule for cleaning and sanitizing storage and food preparation areas must be followed. This schedule must identify which areas require everyday, weekly, or monthly cleaning to optimize the efforts of food handlers. For example, light fixtures and windows do not require everyday cleaning when compared to floors.
Additionally, cleaning food service premises involves having a proper waste management plan that lays out how and when to dispose of food waste.
Cooking is a critical process for food protection. The adequate application period of elevated temperatures during cooking inactivates foodborne pathogens to acceptable levels. While contaminants in food, especially raw materials, are sometimes unavoidable, cooking serves as the last critical step to make foods safe for consumption.
The process of cooking is significantly affected by major factors such as the recommended internal temperature, time of cooking, the food being cooked, and the method of cooking used. Different types of food will require different target internal temperatures.
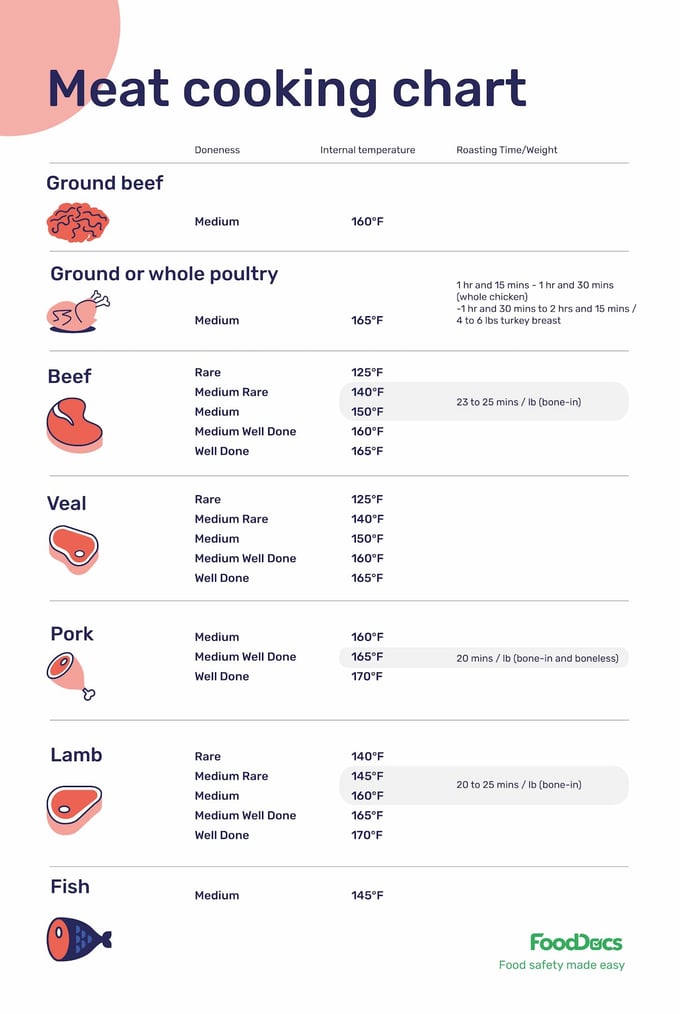 FoodDocs Meat Cooking Chart
FoodDocs Meat Cooking Chart
Some foods, such as any whole cuts of pork and beef, require a minimum internal temperature of 63°C (145°F) with a rest time of three minutes before carving to make the cooked meat safe for consumption. On the other hand, other food ingredients, such as poultry and raw ground meat, require a higher cooking temperature of 74°C (165°F) to become safe for consumption.
In the case of some types of food, such as steak cuts, restaurants tend to offer undercooked meat for the sake of quality. This is evident when it comes to beef, veal, and lamb steaks. These raw meats can be offered cooked medium doneness, which presents a slightly pink center and a well-seared exterior. In this case, food businesses must be responsible enough to inform customers of the potential health risks of consuming undercooked meat with a consumer adivsory.
Using a properly calibrated food thermometer is the key to ensuring that your foods are always cooked thoroughly. This kitchen appliance will accurately measure the core temperature of foods and will tell you if it has been cooked to the correct internal temperature.
When cooking foods, the final internal temperature of the product must always be recorded as proof of food safety compliance. The cook or sous chef in charge must record the accurate temperature reading and report if the temperature has not yet been reached. Use a detailed cooking temperature chart for food handlers.
Similar to cooking, the storage of foods is highly affected by temperature. Biological hazards, such as harmful bacteria, molds, and viruses, are all affected by food storage temperatures. These pathogens optimally double in size within two hours of storage at the temperature danger zone.
As such, cooked foods are recommended to be stored either in cold temperature or elevated temperature storage to prevent the unwanted growth of microorganisms. As a general rule, food handlers should keep cold foods cold and hot foods hot.
Foods that are meant to be served hot, such as in retail food establishments or catering services, must be contained in specialized equipment that can maintain elevated temperatures. During hot holding, certain food hygiene legislations must be followed, such as not mixing in an old batch of food with the new one or constantly stirring displayed food for catering purposes.
 Hot holding temperature chart from FoodDocs
Hot holding temperature chart from FoodDocs
Alternatively, some foods are better stored in low-temperature conditions. Cold holding may refer to refrigeration or freezing foods. This storage type stops the growth of pathogens until the food item is taken out of the storage conditions and cooked. Proper temperature control must be maintained for both operations, as fluctuations in temperature may give pathogens the opportunity to grow and spoil foods.
Avoiding cross-contamination is a critical task for any food business. The unintentional transfer of pathogens and other biological contaminants from one place to another is one of the most common causes of a widespread foodborne illness outbreak. Cross-contamination can happen as a result of a lack of proper hygiene, inadequate cleaning of the kitchen, and a lack of food organization.
An example of cross-contamination is when food handlers stuff all food ingredients in the refrigerator without proper arrangement and containment of food. When foods such as raw meat products and fresh vegetables are placed beside cooked or ready-to-eat foods, including shredded cheeses, deli meats, and fresh fruits that will not be cooked, pathogens from the raw meat may transfer to the cheese. As the latter type of food will no longer undergo processing, customers will consume these foods right away and will be affected by the contamination.
Another scenario where cross-contamination can occur is when food handlers are preparing the food. When preparing fresh produce, such as slicing raw vegetables, you need to clean the chopping board or use a different one prior to switching to a different food ingredient. Additionally, food handlers are required to wash their hands during the switch. When improperly done, the potentially present pathogens from one raw ingredient may cross-contaminate the next.
Follow these tips to avoid cross-contamination in the kitchen:
As mentioned, food is one of the common sources of pathogenic microorganisms that cause foodborne infections. A good way to control the potentially present pathogens from food is to only accept good quality raw materials.
When receiving materials from the supplier, it is the responsibility of a food handler in charge of food safety to inspect if the food supply is of good quality. When raw ingredients are processed and delivered with the same food safety standards that you employ in your food business, it will take less effort from your side to clean and ensure a low harmful bacterial load on foods.
In addition to the food product quality, the condition of delivery must also be considered. Highly perishable foods must be delivered in refrigerated conditions. When the required temperature is not met, the food materials are more likely to spoil faster than expected. Food handlers must be oriented when to refuse a shipment to protect the health of consumers.
Learn more about food safety guidelines.

There are many sources of food safety hazards in the food business. All corners of a kitchen and service area may bring food safety hazards. Despite this fact, pinning down the most common sources and errors with the most useful practices may significantly reduce the likelihood of causing foodborne illnesses.
Some food safety practices are essential for particular types of businesses, whereas others are needed by all types in general. Below are some food safety practices that food businesses can significantly benefit from.
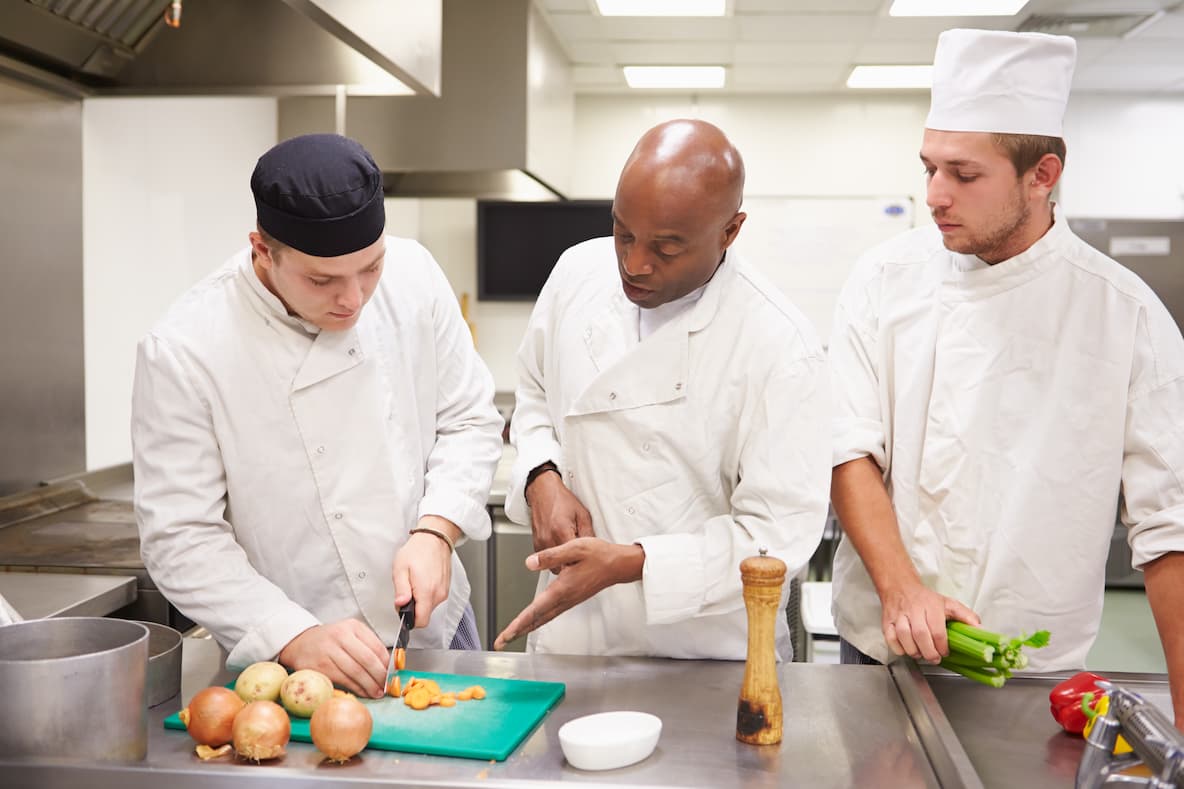

The monitoring logs produced in an FSMS will serve as proof that your business is complying with food safety standardsand current regulations. This plan will cover pathogen detection up to controlling them to safe levels.
In the food industry, safety must never be compromised. The cost of food issues far outweighs any food safety program expenses in the long run. The saying of most food supply chains, "When in doubt, throw it out," shows how food safety is more important than putting the lives of customers at risk just to optimize materials.
While the traditional pen-and-paper format of FSMS has proven to be effective, the evolution of food safety and technological developments, among other trends in the food industry, demand more innovative solutions. At FoodDocs, we offer a smart digital platform powered by advanced technologies that intuitively ensures that food safety compliance is always present.
Business owners can get a tailor-fit food safety monitoring system in just 15 minutes using our digital Food Safety Management System. Our digital software can automatically generate the most essential food safety documents, such as monitoring logs and checklists, for your team and even provide a smart notification system to ensure that all the best practices for food safety are performed.
Food safety regulations are legally binding requirements that food businesses must follow.
Food safety guidelines, on the other hand, are recommendations or best practices issued by authorities or industry organizations to help businesses meet regulatory expectations.
While guidelines are not always legally enforceable, they are often used by inspectors as a reference for what constitutes good food safety practice. Following recognized guidelines can help food businesses demonstrate due diligence and support compliance.
Food safety is the responsibility of all participating individuals within a food supply chain, even the customers. All handlers working from raw material and agricultural production to food processing and delivery are responsible for food safety.
Food safety agencies, such as the FDA and USDA FSIS in the United States, establish food safety laws and oversee their implementation. Down the line, state and local food safety agencies help with the enforcement of food safety laws.
As food business owners, your responsibility is to train your team of food handlers and ensure that they are applying the proper food practices. In some countries, food processors are required to at least have proof, such as a food handler certification or food handlers card, that they are competent enough to produce safe food. This, is in addition to the EHO Food Hygiene certification, is required in some countries for the processing and distribution of foods.
Food safety compliance means operating in accordance with applicable food safety laws, regulations, and inspection requirements on an ongoing basis.
Compliance is not a one-time activity. It involves:
A food business may have procedures in place but still fall out of compliance if those procedures are not consistently followed or reviewed.
A food safety plan is a systematic program that contains complete hazard or pathogen detection and analysis in a food business and appropriate control methods. The majority of food safety plans aim to address the sources of potential issues to prevent them from even occurring.
A food safety plan is a mandatory requirement for food businesses. It must properly assess all food safety risks and hazards in the operating system and set up controls for a high level of health protection. This includes issues that may be an indirect risk to health.
The most important tool for food safety compliance is a food safety plan. Two of the most widely known food safety plans include the Hazard Analysis Critical Control Plan (HACCP) and the Hazard Analysis and Risk-based Control Plan (HARPC). The former plan is widely adapted all over the world, whereas the latter is a risk-based plan derived from the HACCP plan.
A food safety plan is normally composed of the following parts:
These components strategically assess hazards and layout measures to control them to acceptable levels and make safe food. The monitoring system incorporated in a food safety plan evaluates whether a food business complies with regulations or not.
Tips and free tools to start using today
In addition to the best practices for food safety that we have provided, there are other practical and useful tips for food safety. Some operations may be very obvious, whereas others need a bit of basic food safety training. Regardless of the complexity of a food safety process, employees must familiarize themselves to ensure that they are performing the task correctly.
Below are good examples of top-level food safety that you can adapt to your food business:

Safety tips in the kitchen
The kitchen is the core of a food service establishment. It is where all the food preparation occurs. This fact means that it is also where food contamination is the most likely to happen. As such, food handlers must always be aware of their surroundings and follow food safety protocols.
Here are a few safety tips, particularly for kitchen operations:
Unplanned circumstances such as a power outage are never impossible when it comes to running a food business. Even with a backup generator, your electrical equipment may still run on limited power. In such cases, food handlers in charge of food safety must know which operations to prioritize.
To help you maintain food safety during a power outage, here are a few tips:
Having a checklist for operations before and after the commencement of operations is a good practice to keep all of these in mind. This way, food handlers will not forget which tasks to perform, and they can review the tasks repeatedly. All the mentioned food safety tips can save your food business from a potential outbreak of foodborne illness.
Food safety agencies, such as the Food and Drug Administration, have established sets of federal regulations and food codes to standardize the food industry. These business regulations and national food laws help protect public health by addressing concerns, such as foodborne infections with diarrheal and abdominal pain, using sound approaches.
Matters of food safety issues and common food safety mistakes may result from different sources and have different effects on public health. Depending on the issue, it may also affect your business profitability and consumer confidence. Food safety issues may signal underlying problems in your operations and must be immediately assessed.
Some of the most common concerns about food safety reported within the food industry include the following:

These food safety issues can harm public health and significantly affect consumer confidence. In addition, food safety program expenses related to addressing these issues may affect your profits. Understanding these issues may help your team decide the most appropriate course of action. In creating an approach to food safety issues, setting up preventive plans for food protection is more cost-effective and efficient than addressing the problems.
The significance of one food safety practice in saving lives must always be emphasized for food businesses. An approximate 1% decrease in foodborne illness cases in the United States can save about 500,000 Americans from getting sick.
It is part of a food business owner's responsibility to protect public health by complying with federal regulations on food safety.
Test your team's aptitude when it comes to food safety topics using our free food safety quiz.
However, even with the strictest food safety management systems in place, food safety issues may sometimes still occur. When food safety issues arise, customers are given the option to file a complaint to escalate the situation with the proper authority of food safety.
If in case a customer reports experiencing any severe health effects from consuming a product, immediately advise them to seek medical attention first. If possible, advise them to keep a sample of the food item that could have potentially caused the foodborne illness.
As different government agencies handle different types of food products, make sure that you will contact the correct department. In the U.S., you can use the provided health agency hotlines to report food-related problems.
Food business owners facing food safety-related problems can seek the aid of food safety agencies. To help speed up the process, always ask customers the following if possible:
Food businesses are obligated to cooperate with food safety agencies in case an issue is filed by a customer. Your team must be able to present information related to the incident as proof of food safety compliance.

Every year, different food safety issues occur. Food businesses are often faced with these issues as a result of poor food handling practices and non-compliance with food safety regulations.
Some of the most common problems reported to food safety agencies include the following:
These food safety issues can be submitted to the local food safety agencies or taken to the national level. With serious health concerns resulting from consuming food in question from an establishment, immediately seek medical attention and then contact the local health department with food control jurisdiction.
Food safety agencies will help food businesses investigate the cause of the issue and give proper advice on the appropriate course of action for food protection. In case of an outbreak, agencies such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention will take over.
Issues concerning the quality of the market products and customer service are not part of the food safety authority's mandate. Quality concerns may include the flavor of the food, its appearance, and portion size. Customer service issues, such as concerns with the work ethics of a server, must be reported directly to the management of the food business.
Different countries have varying food safety agencies, food laws, regulations, and overall scope. The food standards and regulations established by a food safety authority of a country are significantly influenced by the consumer lifestyle, traditions, economic factors, scientific evidence, and many more.
In some countries, there is only one major federal food safety authority, whereas, in others, there are groups of different agencies. Some agencies may have authority for imports and exports of food as well as facilitating feed regulations and food labelling and other information, whereas other countries may require two or more different departments.
Members of international organizations for food safety often use a common, international food safety standard reference, such as the Codex Alimentarius. Below, we compare some of the most notable differences in food safety systems and regulations of the United States, the United Kingdom, and Canada.
| Food Safety in United States | Food Safety UK | Food Safety in Canada | |
| Federal food safety system | |||
| Federal laws | |||
| Requirement for HACCP |
|
|
|
| Common food allergens |
|
|
|
Complying with the complex food safety regulations may be difficult, especially if you do not have basic knowledge about food safety. At FoodDocs, we aim to make compliance easier and more accessible to all food businesses. Our digital Food Safety Management System can accommodate businesses from around the globe. With the help of artificial intelligence and a machine-learning program, our software can build a comprehensive food safety system for you in just 15 minutes.
Establishing a working food safety management system (FSMS) is the best way to achieve high food safety standards. Programs that are designed to ensure food safety compliance is required for every food business. An FSMS consists of preventive controls and appropriate monitoring logs to ensure that the controls are effective in achieving food safety standards.
Food safety standards and current regulations, such as the FDA Food Code, are established through the efforts of national food control systems, together with the help of state and local food agencies. These food safety standards aim to create a uniform understanding of what is safe for consumers and what might lead to serving unsafe foods.
In some cases, food safety standards are rated with a scale, such as in the UK and its food hygiene rating scheme (FHRS). This food hygiene legislation reflects the level of compliance of a food business and allows customers to understand how seriously you take food safety.
A complete food safety management system can help you remember and perform all food safety operations essential for everyday operations.

Food safety compliance is more than just the protective measure in place. Other food safety principles, such as the expertise of food safety and risk manager in handling employees, must be considered. Food safety compliance involves understanding food safety basics up to the technical aspects of managing your food business.
Below are some of the key elements to achieve food safety compliance and maintain food service operations with high food safety standards:
1. Strong foundation of food safety. The first key may perhaps be the broadest element of food safety. A strong food safety system is built upon a solid foundation of knowledge and operations of food safety. Your team must be properly trained on how to establish prerequisite programs, maintain cleanliness, and follow food safety procedures in addition to the sale of food.
A strong foundation of food safety also includes familiarizing food handlers with the most significant objectives of food law and regulations. Employees who understand the importance of food safety and achieving compliance are more likely to follow the food establishment rules and regulations.
2. Comprehensive risk assessment and hazard control. Once food employees are familiar with the required food safety elements, you must lay out procedures for them to follow. These procedures involve operations that will help control food safety risks and hazards.
The food safety control procedures that you will need to apply must be based on a proper and comprehensive risk assessment of your operations. This means that the procedures for making safe food will be specific to your food business.
Perhaps the most effective food safety step for this element is to establish a Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point, which is a comprehensive hazard control plan for food protection. The HACCP plan contains the most significant steps to prevent hazards from causing food poisoning and infections.
3. Effective organizational management. Once you have a system in place, you will need to manage your team every day. As a food business owner, you are responsible for overseeing all of your operations and effectively influencing your team to achieve food safety compliance.
Managing food safety is a different topic than managing your entire business. Traditionally, food safety requires constant attention and proper delegation of activities. At times, food business owners can assign a co-manager for food safety.
More recent innovations, such as food safety software, can help improve organizational management by giving you access to food preparation and an instant overview of your everyday operations. Such solutions like FoodDocs can help you identify problems and efficiently apply solutions quickly.
4. Food safety culture. This term refers to the collective understanding and values of a food business team regarding food safety. A strong food safety culture shows concern for food safety as a commitment to uphold public health. A significant appreciation of food safety and a significant sense of accountability can help maintain food safety compliance even without constant reminding..
When team members value food safety, they need less supervision to perform tasks and are more likely to be very conscious of how they do things. A team's food safety culture can be improved with strong leadership and an adequate understanding of food safety compliance.
5. Food safety management system. Food safety compliance can be measured and verified through collected data. Verification and analysis of effectiveness are crucial to understanding which areas need more attention and addressing them properly. A comprehensive food safety management collects the necessary data through monitoring logs, checklists, and other documentation.
The ability of an FSMS to capture real-time data is crucial to apply immediate solutions to non-compliances. It also allows complete transparency and safety of the food supply chain and movement of food for better communication with the customers buying safe food.4
Food safety compliance used to be difficult to achieve, especially for food business owners who do not have enough background in food safety. Not to mention, food safety program expenses were significantly high. Despite this, innovations in the world of technology now opened doors to make compliance more accessible and manageable.
Powered by artificial intelligence and a machine-learning program, our digital Food Safety Management System at FoodDocs can help you set up everything you need for compliance management within 15 min. With a few clicks and answers to our questions, our software can build a comprehensive and customizable digital monitoring system specifically based on your food operations!
Food safety compliance is an ever-evolving task for food businesses. Compliance means having to repeatedly shape your food safety system to the requirements and food safety considerations of your food regulatory agency.
In addition to being constantly evolving, these food establishment rules and regulations must be efficiently adapted to your system. Food processors must swiftly learn how to comply with them to maintain control of food safety.
With the traditional pen-and-paper food safety system, quick adaptations, let alone initial establishment, may be quite difficult to perform. With this problem, you may need to ask what is the best tool for food safety.
As the food industry starts to embrace technological advances, the easiest way is to start a food safety journey with a digital platform.
Your best solution to fulfill food safety compliance fastest is to use our digital Food Safety Management System at FoodDocs. With our digital solution, you can get the following benefits:
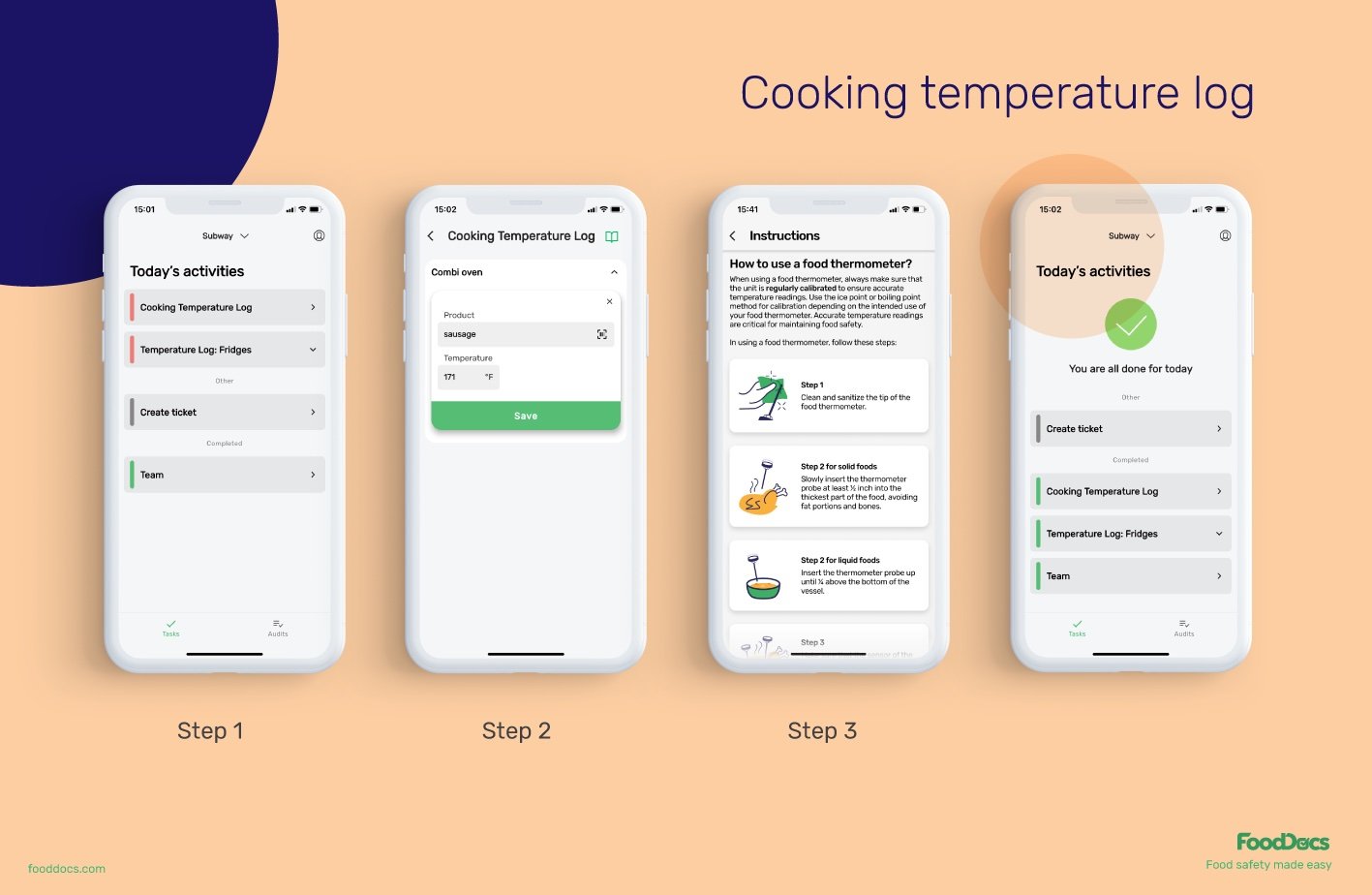 Cooking temperature log in FoodDocs
Cooking temperature log in FoodDocs
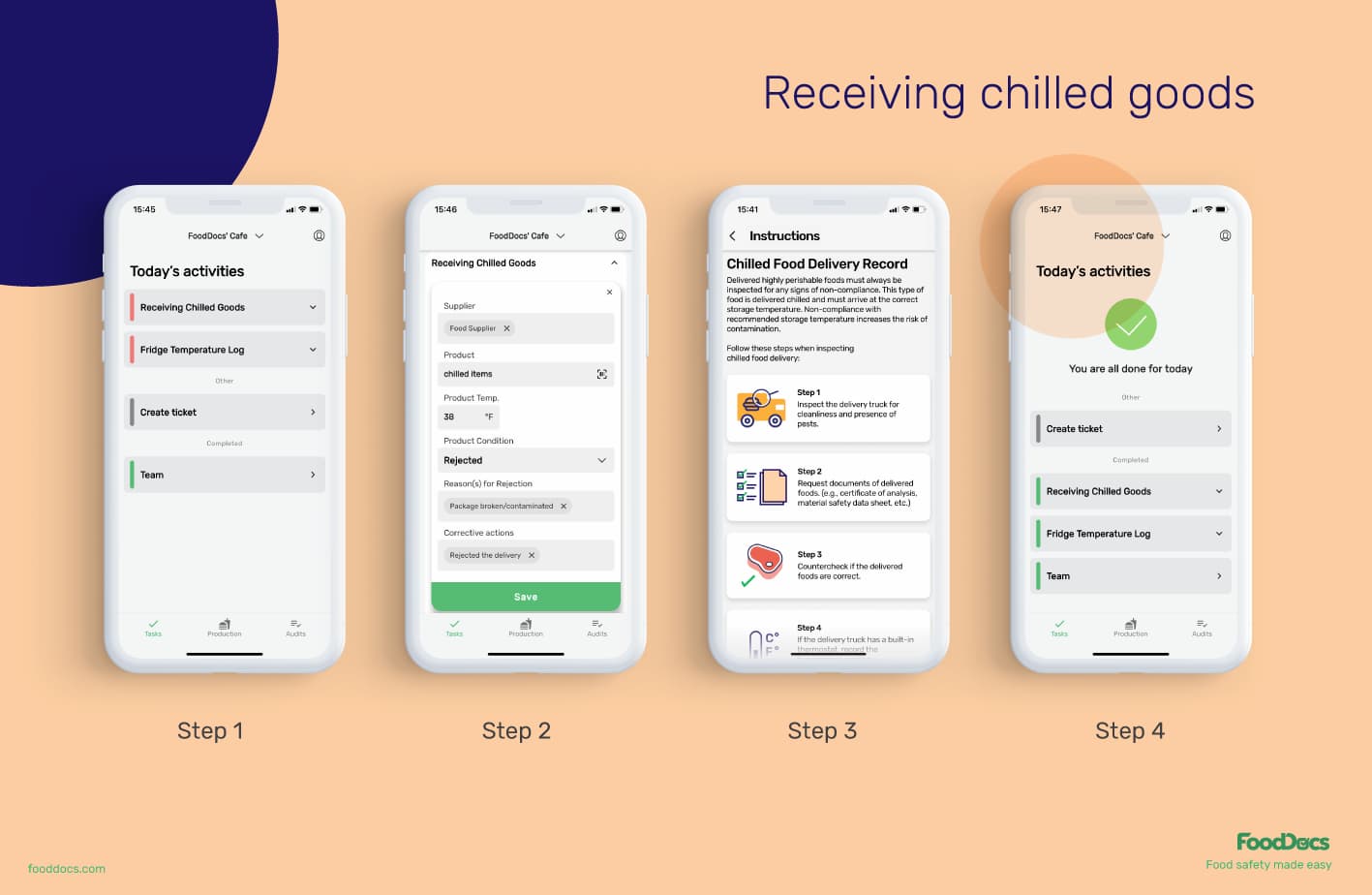 Receiving chilled goods in FoodDocs
Receiving chilled goods in FoodDocs
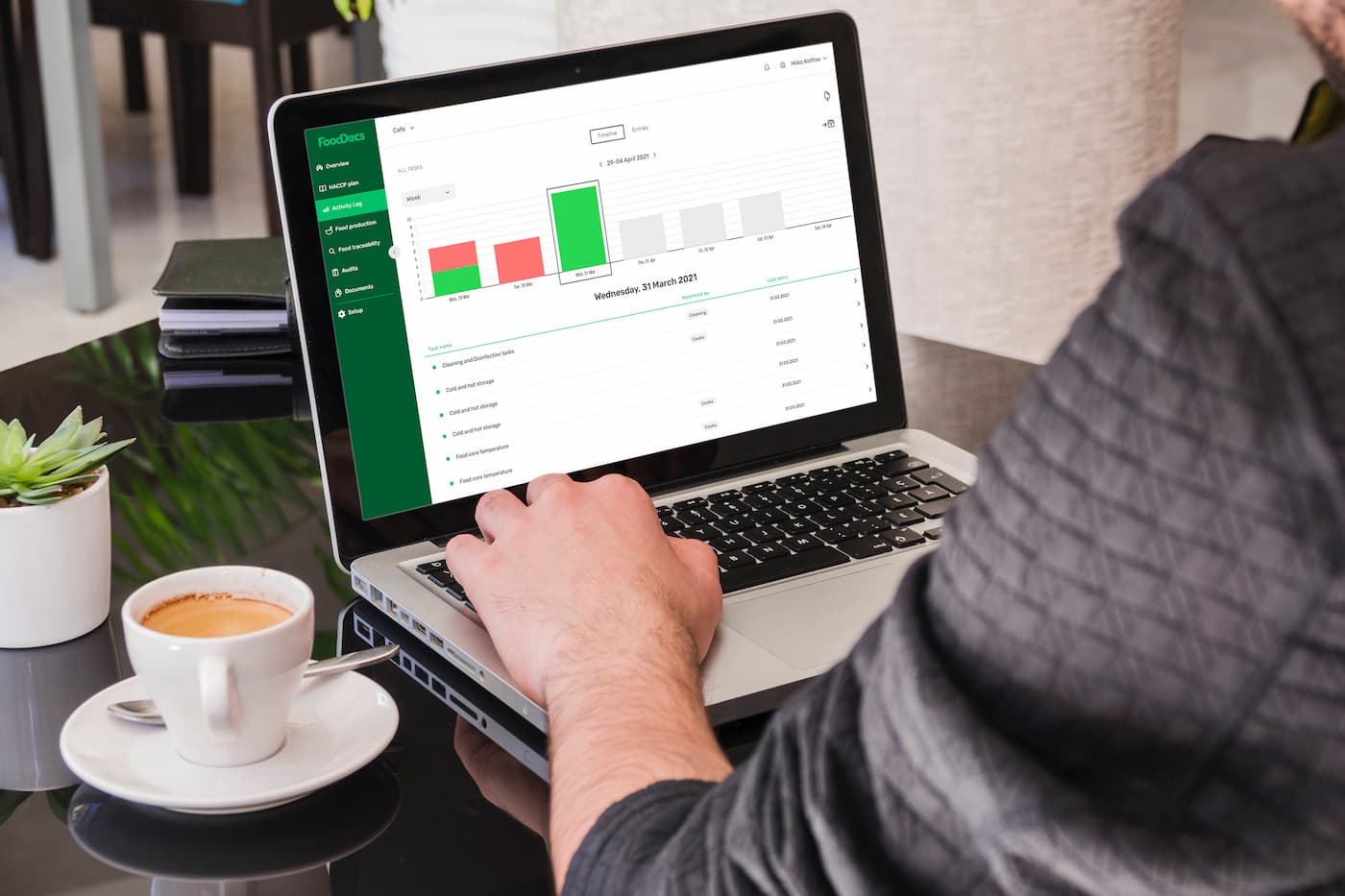 Monitoring checks overview in FoodDocs
Monitoring checks overview in FoodDocs
Our system has features that can help ensure that employees will not forget all food safety tasks and improve the accuracy of recording:
 Food Safety System setup in FoodDocs
Food Safety System setup in FoodDocs
One of the main components of a comprehensive FSMS is to have a health hazard control plan. Luckily at FoodDocs, we also offer a HACCP food safety plan together with our HACCP-based monitoring system. With our built-in HACCP plan template builder, you can build a customizable HACCP plan in just 1 hour. You can become compliant right away and continue food safety compliance with our digital monitoring system.
What do you get when you use our built-in HACCP plan template software? Our system can generate a food safety plan with the most important components:
You can think of FoodDocs as your one-stop shop for getting compliant with the strictest food safety regulations and maintaining compliance throughout your operations. With our digital solutions, you can achieve compliance without extensive knowledge of food safety.
Our software was made by a team of food safety experts who understand the everyday struggles of the food business around the world. The main objective of FoodDocs is to make compliance accessible for everyone, thereby making food safe to eat at all times.
Start your food safety journey by using our free 14-day trial now to get and stay compliant.
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...