HACCP AUDIT CHECKLIST | FREE TOOL



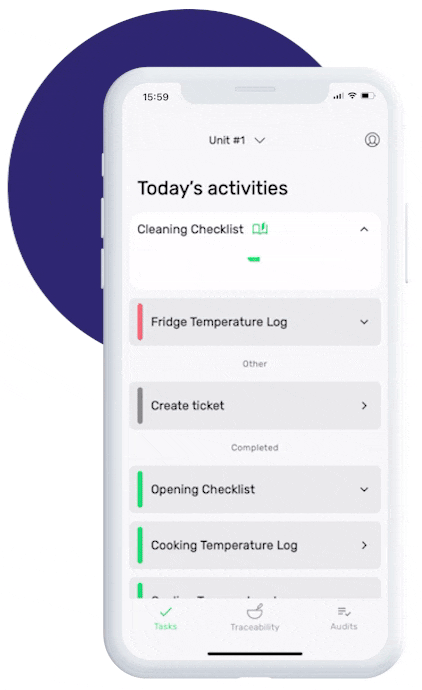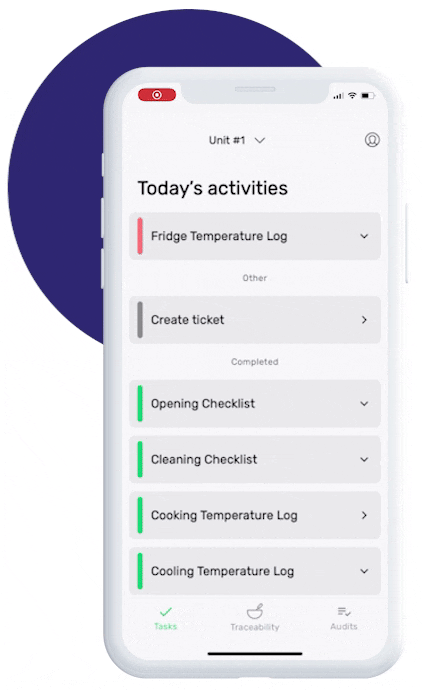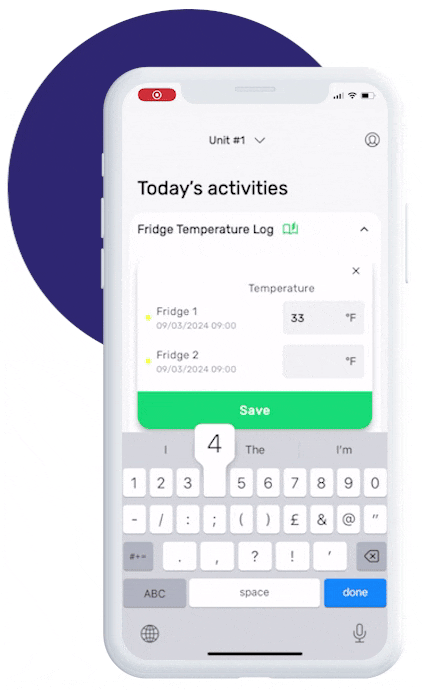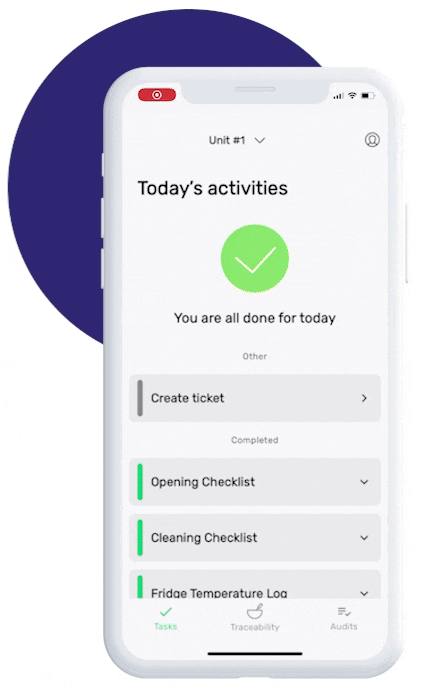
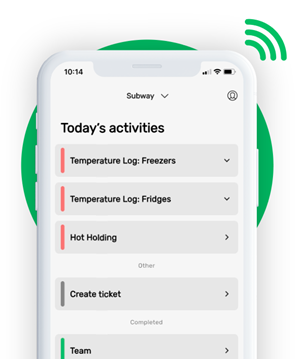
This is how our Digital Food Safety platform saves 20% of your time on daily tasks:
- Get upcoming task notifications
- Add data into the app
- Check the status of tasks in real-time

When food safety was still handled on paper, I typically spent a couple of hours per day getting the papers and going around checking or completing tasks… Now I can sit down and it's just all there in one place. It takes me 5-10 minutes.
Ruth B.
Store Manager
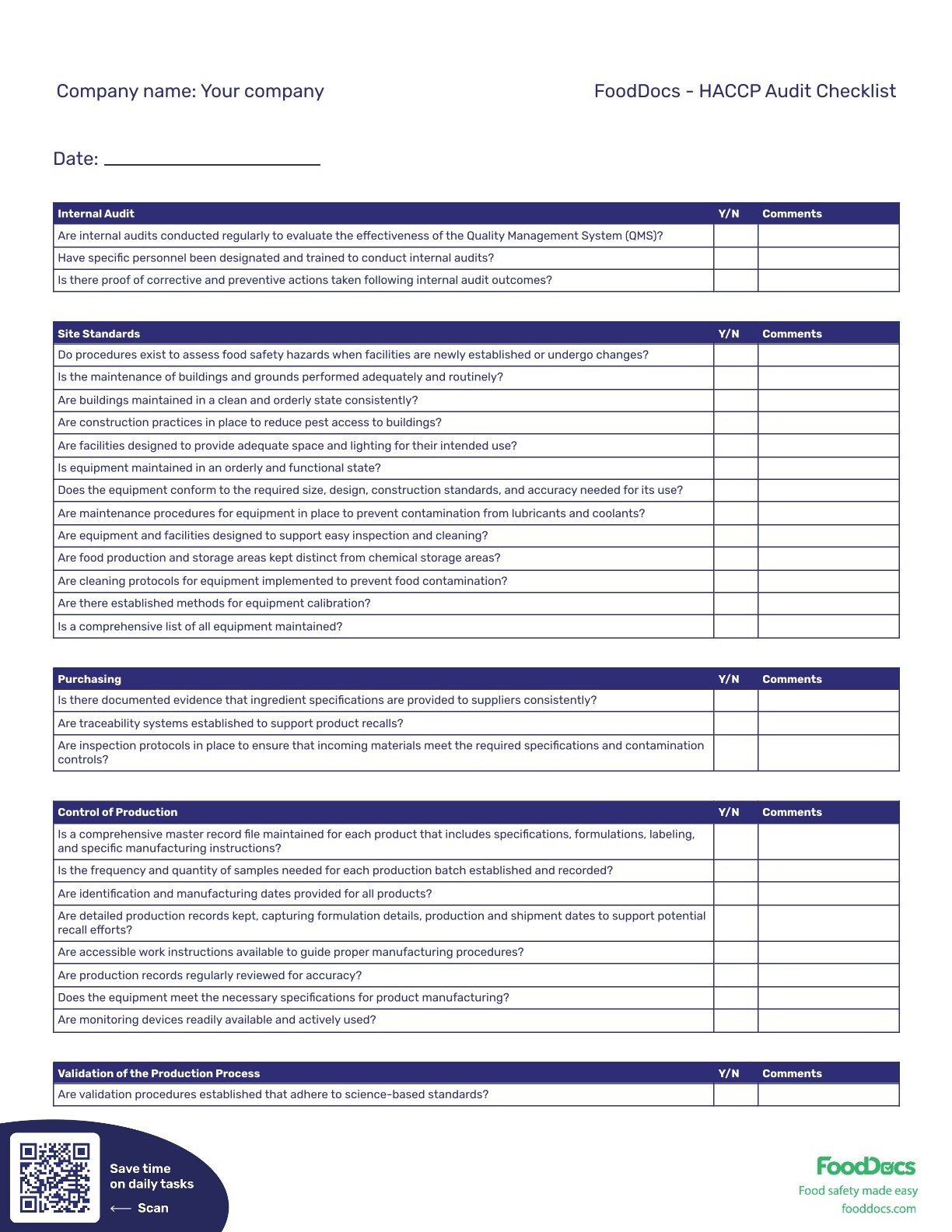
| Company name: Your company | _ |
| Internal Audit | Y/N | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Are internal audits conducted regularly to evaluate the effectiveness of the Quality Management System (QMS)? | ||
| Have specific personnel been designated and trained to conduct internal audits? | ||
| Is there proof of corrective and preventive actions taken following internal audit outcomes? |
| Site Standards | Y/N | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Do procedures exist to assess food safety hazards when facilities are newly established or undergo changes? | ||
| Is the maintenance of buildings and grounds performed adequately and routinely? | ||
| Are buildings maintained in a clean and orderly state consistently? | ||
| Are construction practices in place to reduce pest access to buildings? | ||
| Are facilities designed to provide adequate space and lighting for their intended use? | ||
| Is equipment maintained in an orderly and functional state? | ||
| Does the equipment conform to the required size, design, construction standards, and accuracy needed for its use? | ||
| Are maintenance procedures for equipment in place to prevent contamination from lubricants and coolants? | ||
| Are equipment and facilities designed to support easy inspection and cleaning? | ||
| Are food production and storage areas kept distinct from chemical storage areas? | ||
| Are cleaning protocols for equipment implemented to prevent food contamination? | ||
| Are there established methods for equipment calibration? | ||
| Is a comprehensive list of all equipment maintained? |
| Purchasing | Y/N | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Is there documented evidence that ingredient specifications are provided to suppliers consistently? | ||
| Are traceability systems established to support product recalls? | ||
| Are inspection protocols in place to ensure that incoming materials meet the required specifications and contamination controls? |
| Control of Production | Y/N | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Is a comprehensive master record file maintained for each product that includes specifications, formulations, labeling, and specific manufacturing instructions? | ||
| Is the frequency and quantity of samples needed for each production batch established and recorded? | ||
| Are identification and manufacturing dates provided for all products? | ||
| Are detailed production records kept, capturing formulation details, production and shipment dates to support potential recall efforts? | ||
| Are accessible work instructions available to guide proper manufacturing procedures? | ||
| Are production records regularly reviewed for accuracy? | ||
| Does the equipment meet the necessary specifications for product manufacturing? | ||
| Are monitoring devices readily available and actively used? |
| Validation of the Production Process | Y/N | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Are validation procedures established that adhere to science-based standards? |
| Identification and Traceability | Y/N | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Is the finished product adequately packaged and labeled with essential details like product name, description, net weight, lot number, shelf life, and compliance with labeling regulations? | ||
| Are traceability procedures thoroughly documented? | ||
| Are retained samples marked for traceability purposes? |
| Control of Monitoring and Measuring Devices | Y/N | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Are monitoring and measuring devices involved in production adequately maintained, calibrated, and their usage documented? | ||
| Is the calibration of these devices regularly verified against established standards? |
| Monitoring and Measurement of Processes | Y/N | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Are monitoring protocols in place to assess the adequacy of manufacturing processes? | ||
| Are routine monitoring activities scheduled? |
| Monitoring and Measurement of the Product | Y/N | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Are there protocols ensuring that the product meets specified requirements? |
| Storage of Product | Y/N | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Are products appropriately identified, stored, handled, and controlled to preserve their identity and integrity? |
| Customer Satisfaction | Y/N | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Are there protocols for logging and assessing customer feedback? |
| Management Commitment | Y/N | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Does senior management actively define and communicate responsibilities within the organization? |
| Control of Non-Conforming Product | Y/N | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Are there clear procedures for managing non-conforming products? | ||
| Is non-conforming product distinctly identified and stored separately? | ||
| Is documentation maintained that outlines the handling of non-conforming products, including potential rework and verification? | ||
| Are there procedures for notifying customers and recalling products if non-conformities are discovered post-delivery? | ||
| Are processes in place to manage returned goods effectively? | ||
| Are comprehensive procedures established to review, address, and prevent recurrences of non-conformities? |
| Internal Communication | Y/N | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Is there a robust communication channel between senior management and staff? |
| Training | Y/N | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Are there records that show personnel have been trained and are competent? | ||
| Are job descriptions that detail the required responsibilities and skills for each role readily available? | ||
| Is personnel training in personal hygiene sufficiently rigorous to prevent contamination? | ||
| Is a training framework established? | ||
| Are refresher training protocols in place? | ||
| Are training records for personnel who manage Critical Control Points (CCPs) maintained and accessible? |
| Management Review | Y/N | Comments |
|---|---|---|
|
Management review covers:
|
| HACCP Team and Training | Y/N | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Are HACCP team members listed with relevant training and job experiences that qualify them to apply HACCP principles? | ||
| Has the person responsible for developing hazard analyses and control measures been trained in HACCP principles? | ||
| Has the HACCP plan developer for a specific site completed training in HACCP principles? | ||
| Has the individual verifying and modifying the HACCP plan been trained in HACCP principles? | ||
| Has the individual conducting the record review been trained in HACCP principles? |
| HACCP Plan Specificity and Evaluation | Y/N | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Is the HACCP plan tailored specifically to the site and location? | ||
| Is the HACCP plan designed to address the specific ingredients, food, or processes it covers? | ||
| For grouped ingredients or processes in a single plan, is there documented evidence that they share common hazards? | ||
| Does the hazard analysis identify and evaluate all relevant hazards for each process step? | ||
| Are control measures for significant hazards clearly identified and documented? | ||
| Are prerequisite programs for significant hazards included and correctly cited in the HACCP plan? | ||
| Was an evaluation of Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) part of the hazard analysis, with necessary modifications made? | ||
| Are critical control points identified for each significant hazard? | ||
| Does the hazard analysis consider both internal and external hazards? | ||
| Does the hazard analysis address potential sources of adulteration, including considerations for all steps from packaging to sanitation? |
| Critical Control Points (CCPs) and Hazard Significance | Y/N | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Have all identified hazards been evaluated for their significance? | ||
| Are CCPs designated for significant hazards within and, if applicable, outside the site? | ||
| Are critical limits set for each CCP? | ||
| Are there established procedures to monitor each CCP, with frequencies that ensure adherence to critical limits? |
| Corrective Action Plans and Verification Procedures | Y/N | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Are corrective action plans in place detailing responsibilities and steps to address deviations from critical limits? | ||
| For deviations without existing corrective action plans, are there protocols for product segregation and assessment until compliance is restored? | ||
| Are records available showing that corrective actions have been implemented as planned? | ||
| Are validation and verification procedures documented, including their frequencies? | ||
| Are consumer complaints reviewed for their relevance to the HACCP plan's performance or to identify new hazards? | ||
| Is equipment calibration verified as per the HACCP plan? | ||
| Is end-product testing conducted if specified in the HACCP plan, with verification completed within seven days for critical control points? |
| Recordkeeping and Documentation | Y/N | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Is a comprehensive recordkeeping system in place for monitoring CCPs, including all necessary details like critical limits and corrective actions taken? | ||
| Are all significant hazards documented in the hazard analysis? | ||
| Is the HACCP plan reviewed and updated regularly, ensuring that any new hazards or changes in process are captured? |
| Quality Manual and Document Control | Y/N | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Is there a quality manual that includes all necessary processes and procedures? | ||
| Are document control procedures in place ensuring documents are approved before use, regularly updated, and correctly identified as current versions? | ||
| Are records controlled specifying which are needed and for how long, and are they maintained appropriately for products such as those relating to GMPs, production, and master files? |
To maximize the benefits of our free HACCP audit checklist, it's important to integrate its use into your regular audit preparations and review processes. This checklist serves as a comprehensive guide to ensure that nothing is overlooked during both internal and external audits.
Start by familiarizing yourself with the checklist ahead of time, and then use it as a living document during the audit to record findings and corrective actions.
Regular use of the checklist will help streamline your audit process, ensuring that you consistently meet compliance standards and improve your food safety practices.
For best results, review and update the checklist periodically to align with any updates in HACCP regulations or changes in your operations.
Check out our other free HACCP resources
Easily conduct internal HACCP audits with FoodDocs
Our digital Food Safety Management System allows teams to create, complete, schedule, and manage food safety audits with ease.
Using the FoodDocs' Audits tool promotes accountability among your team and helps ensure that your business's food safety standards are high. Here's how it works:
- Create: Conduct any food safety audit based on HACCP compliance requirements as well as other food industry regulatory standards such as ISO 22000, FSSC, SQF audits, and more.
- Schedule: Perform your audits using any mobile device and remind members about your upcoming audits through notifications.
- Complete: Choose from different scoring formats depending on how food safety audits are done in your location. Users can fill in “yes/no” checklists or scored questionnaires.
- Manage: Review results in one organized cloud storage and manage anything you need any time you need.
Simplify your internal auditing process today and try FoodDocs free for 14 days.
Need a HACCP Plan? Get yours in 1 hour.
Our HACCP plan software creates a HACCP Plan to meet your business's legal requirements 500x faster than average without filling loads of paper.
It automatically generates your Hazard Analysis, Critical Control Points, Flow Chart, Pre-Requisite Programs, and Standard Operating Procedures. Plus, the HACCP plan is fully customizable so you can edit it according to your specific business needs or according to the inspector's feedback.
All you need to do is answer a few questions and watch as our AI compiles your essential HACCP compliance documents.