FOOD SAFETY TERMS
Acidity is the level of acid in food. An acidic food has a pH below 7.0. Foodborne microorganisms typically do not grow in highly acidic food.
Acaricides are pesticides used on livestock in order to kill off parasites such as ticks and mites.
Air curtains is a fan-powered device that creates an invisible air barrier over the doorway to efficiently separate two different environments.
Allergen is any normally harmless substance inside the food that causes an allergic reaction for people. In different countries, there are different allergens defined—for example, 14 in the UK, 8 in the US. More than 2 million people in the UK experience food allergies each year, and the number is rising every year.
Allergy notice poster is an informative poster for your kitchen team to display. Your kitchen team will see at a glance all major allergens and the risks these allergens involve.
Approved suppliers are suppliers that have been inspected and meet applicable local, state, and federal laws.
Backflow is a change of pressure in a water pipe that forces water to flow opposite to its intended direction, allowing contaminants to enter the unprotected system.
Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms like Salmonella, Campylobacter, and Escherichia coli. Those are among the most common foodborne pathogens that affect millions of people by causing most of the foodborne illnesses in the world.
Bacterial growth is an increase in the number of bacteria in a population.
Best before date (BBE) is about food quality, not about safety. The food will be safe to eat after the BBE date but may not be at its best. Its flavor and texture might not be as good as they are supposed to be.
Biological contaminants are the presence of microorganisms, such as viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi, that can contaminate the food.
Biological hazards are microorganisms such as bacteria, molds, and viruses. Pathogenic microorganisms can cause a threat to human health because they cause most foodborne illnesses.
Biological toxins are harmful substances (poisons) that are produced by pathogens, plants, or animals.
Calibration is the process of checking a measuring instrument to see if it is accurate. In the food industry, the most common devices that need to be calibrated are thermometers and scales.
Carriers are people who carry pathogens and infect others, but display no symptoms.
Celiac is a reaction to a protein fraction called gluten. It’s found in wheat and wheat-related cereals such as rye, oats, and barley. As gluten is widely used in processed food, allergic people are in trouble trying to avoid it.
Chemical cleaning is a method to clean surfaces, equipment, pipelines, vessels, kettles, and heat exchangers to reduce the number of microorganisms.
Chemical contaminants are chemical substances, such as cleaners, sanitizers, or polishers, that leak from cookware and equipment, which have contaminated food.
Chemical hazards are chemical substances that can contaminate food. For example cleaners, sanitizers, or polishers, that leach from cookware and equipment.
Clean means free of visible dirt. It refers only to the appearance of a surface, not to bacteria that still can contaminate food.
Cleaners are chemicals that remove food, dirt, rust stains, minerals, or other deposits from surfaces.
Cleaning is the process of removing food and other types of dirt from a surface. It refers only to the appearance of a surface, not to bacteria that still can contaminate food. Don’t confuse cleaning, sanitation, and disinfection.
Cleaning Agents are substances used to remove dirt, and are usually in the form of a spray, liquid, or powder.
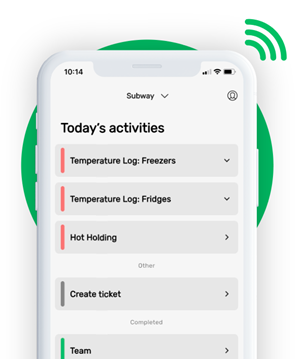
Cleaning checklist is an important part of your HACCP plan. It is a list of all the surfaces and activities that need to be cleaned and is divided by the frequency. The cleaning checklist helps you and your team to stay organized on your cleaning tasks.
Cleaning schedule occurs when bacteria spread between food, equipment, and work areas. For example, bacteria can spread from raw ingredients to the finished product when equipment and utensils are not segregated appropriately. Preventing cross-contamination is a key factor in preventing foodborne illness.
Common food also known as traditional food, is a food that has been passed on and consumed through many generations.
Concentration is the amount of sanitizer in relation to water measured in parts per million (ppm). The concentration of sanitizer affects the effectiveness of the sanitizer solution.
Consumer advisory is a written statement for your customers about the food safety-related risks when eating raw or undercooked food. The customer advisory statement protects customers who are especially vulnerable to foodborne diseases, for example, the elderly, pregnant women, toddlers, and people with compromised immune systems.
Control of food safety - Food safety is always controlled by a national food control system. The system ensures that food is always safe to eat and a wholesome fit for human consumption. Food safety control helps to ensure safety and quality according to the requirements.
Contamination refers to food that has been corrupted with another substance – either physical, biological, or chemical.
Control of hazards is one of the most important things in food safety. Following all the basic hygiene rules and monitoring processes is crucial when preventing foodborne illnesses.
Cooking temperature chart helps your team to remember all necessary temperatures when cooking. A core temperature inside the food is crucially important to prevent foodborne illnesses and to protect your company.
Corrective action is realizing and defining a problem, containing the problem, determining its cause, and taking appropriate action to prevent it from happening again.
Critical limit is a maximum and/or minimum value to which a biological, chemical or physical parameter must be controlled at a CCP to prevent, eliminate, or reduce to an acceptable level the occurrence of a food safety hazard.
Critical Control points (CCPs) are steps in your food business process where you need to prevent or reduce food safety hazards to an acceptable level. Critical control points exist at every stage of the process, starting from ordering ingredients, ending up with serving the products.
Cross-contact is the transfer of an allergen from a food containing an allergen to a food that does not contain the allergen.
Cross-contamination is the process by which bacteria or other microorganisms are unintentionally transferred from one substance or object to another, with harmful effects.
Danger zone is the range of temperature between 40 °F and 140 °F. This is the range where bacteria grow most rapidly, doubling in number in as little as 20 minutes.
Date marking is a process assuring the food is discarded before bacteria can cause foodborne illness. Date marking is required for ready-to-eat food.
Decision tree is a part of your HACCP plan, a sequence of questions that help to determine whether a particular production process step is a Critical Control Points (CCP) or not. It helps to prevent or eliminate a food safety hazard or reduce it to an acceptable level.
Degreaser is a cleaner designed to remove grease, oils, cutting fluids, and corrosion inhibitors.
Delivery control means monitoring your incoming goods to prevent food safety hazards. The monitor should always include the temperature, labeling, packaging, product characteristics, and condition of the delivery vehicle. Always record your monitoring.
Detergent is a chemical substance, usually in the form of a powder or liquid, used for cleaning kitchen equipment.
Expiry date is the date that the manufacturing company lists on the labeling. Expiry date determines how long a food product will ‘stay good’ for as long as it remains unopened. Don’t confuse it with shelf-life.
E-learning is an online training course that delivers all essential information on food safety, hygiene, and HACCP. Very common in innovative countries, like the US.
First-in, first-out (FIFO) is a method of stock rotation in which products must be shelved based on their use-by or expiration dates, so the oldest products are used first.
Flow chart, also called a HACCP flow diagram, is a pictorial representation of all your production processes. It represents all the steps your raw materials go through before becoming a finished product in your menu.
Food additives are substances added to food to lengthen its shelf life, preserve flavor, or enhance taste, appearance, or other sensory qualities. They are also used to alter food so it does not need time and temperature control. Some are used to enhance flavor.
Food allergen poster helps your team to easily remember all significant allergens that cause 90% of all food allergies. It’s important to display food allergen posters in your workplace - so your kitchen team will see at a glance all major allergens and the risks these allergens involve.
Food allergy the body’s negative reaction to a particular food allergen.
Food and drug administration FDA or sometimes USFDA is a federal agency that is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the supervision of food safety.
Food codes are state-level food safety regulations that are written and adopted to develop or update their own food safety rules.
Food contact surface is any surface that directly touches food, such as a cutting board, knives, forks, or any other dishes.
Food fraud is when a food manufacturer intentionally deceives its customers about the quality or the contents of the food. It can be altering, misrepresenting, mislabeling, substituting, or tampering. Food fraud is usually motivated by profit.
Foodborne illness, also known as food poisoning, is any illness resulting from consuming food contaminated with bacteria, viruses, parasites, or chemical substances. Shortly, a foodborne illness is a disease that is transmitted to people by food.
Food safety management system (FSMS) is a helpful tool to ensure that safe food practices are followed within your business. Usually, the software is designed to prevent foodborne illness by actively controlling risks and hazards.
Food poisoning also known as a foodborne illness, is the result of eating contaminated, spoiled, or toxic food.
Food recall is when a food producer removes the product voluntarily off the market to protect the customers from harmful products. Food products are recalled because there is reason to believe the products may be mislabelled, contaminated, faulted, or misbranded.
Food safety standards are applied in every region to lower the incidence of foodborne illnesses. Food safety standards apply to food businesses to produce food that is safe to eat.
Food sanitation is the practice of following certain cleaning and disinfection rules and procedures. Sanitation is for preventing food contamination and keeping food safe to eat.
Food supply is a stock of food that is available for use.
FSMS is an abbreviation from the Food Safety Management System. A helpful tool to ensure that safe food practices are followed within your business. Usually, the software is designed to prevent foodborne illness by actively controlling risks and hazards.
Food traceability helps to track all your ingredients and food items throughout your production supply chain and gives you the tool to perform food recalls. It enables you to track the movement of food items, forward and backward, referred to as “one-up, one-back” record-keeping.
FSMA also known as Food Safety Modernization Act, ensures that the whole US food supply is safe for people. Focuses on protecting public health by preventing foodborne illnesses and strengthening the food safety system.
Fungi yeasts and molds that cause serious spoilage of stored food leading to enormous economic losses.
Good manufacturing practice (GMP) is a quality system to ensure food safety among food businesses in the United Kingdom, United States, Canada, Europe, and other countries. The aim of GMP is to ensure that products are safely produced and controlled according to local quality standards.
HACCP assessment risk matrix is a helpful tool (table) that helps you to determine the type of hazard according to the level of likelihood and severity from low to high.
HACCP definition is a short form of Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points. It’s an internationally recognized method of identifying and managing food safety-related risks. Controlled by the local governmental authorities.
HACCP plan is a comprehensive document that is a part of an internationally recognized system - Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points. It describes all the food-related activities, processes, and associated hazards your food business may have and tells you how to deal with them. The HACCP plan is proof that your business complies with the law.
HACCP training is a crucial part of your HACCP plan. It’s a way to make sure that all of your team members are well trained in food safety practices and understand how to carry out food safety tasks.
Hair restraints are usually hats, hair covering and nets, beard restraints, and clothing that covers body hair, used to keep a food handler’s hair away from food and to keep the individual from touching it.
Hand antiseptic is a liquid or gel used to remove common pathogens or microorganisms on the skin’s surface.
Handwashing station is a sink that is meant only for handwashing. Handwashing stations must be conveniently located in restrooms, food-preparation areas, service areas, and dishwashing areas.
Hazard analysis is the process in your food safety management system of deciding what might be a hazard, and what should be done if someone or something is exposed to this hazard.
Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) is an internationally recognized method of identifying and managing food safety-related risks.
Health inspector is a governmental staff member who conducts food service inspections among food handling companies and helps to ensure food safety.
Heat sanitizing is a cleaning method for reducing the number of microorganisms on a clean surface to sanitize equipment or tableware.
Hepatitis A is an inflammation of the liver. The disease is transmitted to food by poor personal hygiene or contact with contaminated water.
High-risk customers are customer groups who are the most vulnerable to foodborne illness because of their weaker immune systems. High-risk customer groups are children under five years old, sick people, pregnant women, unborn children, and the elderly.
Histamine is a biological toxin associated with temperature-abused scombroid fish, which causes many of the symptoms of allergies, such as a runny nose or sneezing.
Hot-holding equipment is equipment that is designed to hold food at an internal temperature of 135 ̊F (57 ̊C) or higher, such as dishes, steam tables, and heated cabinets.
Ice paddle is a paddle filled with ice to cool hot food quickly.
Ice-water bath is a method to cool the food down quickly. Combining these methods, ice bathing while stirring food with an ice wand provides very effective cooling for soups, sauces, and beans.
Immune system is a body’s defense system against any kind of illness. People with weaker immune systems are high-risk customers to foodborne illnesses.
Incidence is the number of new outbreak cases of foodborne illness. The number is usually given in population during a specified time period.
Infestation generally refers to the presence of pests (rats, insects, etc.).
Insecticides chemical substances used to kill insects, as well as preventing them from spreading.
Inspection focuses on ensuring food safety compliance of food businesses with regulatory requirements.
Jaundice is a medical condition with yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes. Could be caused by hepatitis A.
Journal of food safety is a scientific journal, issued on a quarterly basis, covering research on food safety.
Kitchenware are all devices, cookware, and appliances used in kitchens for cooking.
Labeling is a process to add product information on the packages. Labeling includes identity and contents, how to handle, prepare and consume the product safely. It’s the most effective tool to protect the consumers’ health regarding food safety and nutrition.
Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) are sheets supplied by the chemical supplier that include the names of the supplies, potential physical and health hazards, and information about using and handling them safely. An important part of your HACCP plan.
Microorganisms are small, living organisms that can be seen only through a microscope. Microorganisms include bacteria, protozoa, algae, and fungi.
Minimum internal temperature is a required minimum temperature the food must reach to eliminate harmful microorganisms. The temperature is specific to a food that is being cooked.
Modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) is a packaging method involving changing the gaseous atmosphere surrounding a food product inside a package. It prolongs the shelf life compared to other conventional storage methods.
Mold or mould is a type of fungus that breaks down the food and starts to rot.
Monitoring is a periodic check to ensure that food safety hazards are under control. Monitoring is one of the most effective tools to help to ensure food safety because it requires handling food in specific ways.
Monitoring sheet is a sheet or a form that the kitchen team uses to register food safety monitoring. It can be both on paper or in digital form. A digital monitoring sheet helps your team keep in mind all daily monitoring with the help of notifications.
Natasha’s law requires all food businesses in England, Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland to use labeling, including a full list of ingredients on all pre-packaged food. It starts to apply on 1st October 2021.
Nutritional value also called nutritive value. It’s an important part of food quality to measure the detailed consistency of the food concerning the nutrient requirements of their consumer. Nutritional value covers carbohydrates, fat, protein, minerals, and vitamins, etc.
OPRP is an abbreviation from the Operational Prerequisite Program. Control measures put in place to prevent or reduce a significant food safety hazard to an acceptable level. Action criterion and measurement, or examination enable effective control of the process or product. For example - metal detection, video surveillance, sensors, etc .
Outbreak is an incident when two or more people experience the same illness after eating the same food or drink.
Parasites are microorganisms that can cause foodborne and waterborne illnesses. Parasites are usually associated with raw or undercooked meat and fish, including pork and others.
Pathogens is an incident when two or more people experience the same illness after eating the same food or drink.
Personal hygiene are daily habits to prevent foodborne illness. Personal hygiene includes keeping the hands, hair, and body clean and wearing clean and appropriate uniforms.
Pest control checklist is a part of your HACCP plan documentation. This document assists you when completing a periodic pest control inspection and helps to determine whether these areas need treatment or not.
Pest control operator is the licensed service provider who uses safe and current methods to prevent and control pests in the food entity.
Pesticide are the chemicals that are used to control pests, including insects.
Pest management plan is a mandatory document in your HACCP plan. The document provides a quick overview of pest management - the likelihood of occurrence, preventive and corrective actions, control density, and responsible people.
PH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of the food. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14.0, where between 7.1 and 14 is alkaline, and between 0.0 and 6.9 is acidic. A pH of 7.0 is neutral. Foodborne microorganisms grow well in a neutral to slightly acidic pH (7.5 to 4.6) environment.
Physical hazards foreign objects that can accidentally get into food and contaminate it. Some examples are hair, dirt, metal staples, broken glass, and bones in fillets.
Prerequisite Program (PRP) are the basic conditions and activities necessary to maintain a hygienic environment throughout the production, handling, and supplying of products and safe foods for human consumption. Examples: maintenance of rooms and equipment, pest control, cleaning, and disinfection, etc
Quality Assurance (QA) is a set of activities ensuring the quality standards and specifications in food safety. For example monitorings, checklists, standards, documentation and audits.
Ready-to-eat food is food that will not be cooked or reheated before serving. Ready-to-eat food includes washed fruit and vegetables, both whole and cut, deli meats, and bakery items. Sugars, spices, seasonings, and correctly cooked food items are also considered ready-to-eat.
Regulations are rules or directives that are made and maintained by an authority. Food safety regulations describe food handling, preparation, and storage in ways that prevent foodborne illness.
Record sheet also called a monitoring sheet. It’s a form to register and keep track of your food safety monitoring. The most useful is the digital monitoring sheet because it helps your team keep in mind all daily monitoring with the help of notifications.
Risk assessment is needed to define all food safety hazards, preventive measures, control measures, and record-keeping to ensure the safety of the final food product. HACCP plan is a risk assessment approach.
Risk matrix is a helpful tool (table) that helps you to determine the type of hazard according to the level of likelihood and severity from low to high.
Safe food is a food free from contamination, involving all production processes, like growing, preparing, processing, storing, selling, or serving food.
Sanitizer is a chemical that is used for sanitizing. Three primary chemical compounds are used as sanitizers in the foodservice industry: chlorine-based cleaners, quaternary ammonium, and iodine sanitizers.
Sanitizer is a chemical that is used for sanitizing. Three primary chemical compounds are used as sanitizers in the foodservice industry: chlorine-based cleaners, quaternary ammonium, and iodine sanitizers.
Sanitizing follows cleaning and helps to reduce the number of harmful microorganisms like pathogens and germs. It’s important to understand that cleaning, disinfecting, and sanitizing are not the same.
Shelf-life is the time period when food remains effective, useful, or suitable for consumption.
Single-use gloves are gloves designed for one-time use. Single-use gloves have become a symbol of food safety, but they can inspire a false sense of security when food handlers don’t follow basic hygiene rules.
Step is a point, process, procedure, or stage in the food chain to produce a product from the beginning to final consumption.
Sous-vide means “under vacuum” in French. Sous vide cooking is the process of sealing food in an airtight container, and afterwards cooking that food in temperature-controlled water.
Spores are bacteria or fungi in a dormant state, where they are generally not actively metabolizing. This might occur when food is not held at the correct temperature, or cooled or reheated correctly.
Temperature is a critical measurement for ensuring food safety and quality. It is measured in Fahrenheit or Celsius.
Temperature log sheet is the most widespread food safety checklist in the HACCP plan. It helps to ensure the cold chain, in other words, that all food is stored at the right temperature. Temperature log sheets can be applied to the refrigerator, freezer, pantry, and transportation vehicle.
Thermistors are also called temperature sensors. Help to check the temperature automatically, with the help of sensors or metal probes.
Thermocouples are devices that check the food temperature through a sensor on the tip of a metal probe.
Time-temperature indicators (TTIs) are devices used for recording temperature and indicating the remaining shelf-life of the food products throughout their storage, distribution, and consumption.
Toxins are poisons produced by microorganisms inside the food. Toxins can cause foodborne illnesses.
Traceability is the capability of a food business to track the movement of food materials in the supply chain until it becomes a finished product.
Undercooked meat is one of the most common food safety risks. Undercooked food carries an increased risk of foodborne illnesses, and the customers need to be informed by using written consumer advisory.
Under modification is when production process is being modified or improved. For example, instead of manual temperature checks, sensors are installed, or a new device is installed in the production line to improve cross-contamination hazards, etc.
Utensils are kitchen implements such as pots, pans, or food containers used in the preparation, storage, transportation, or serving of food.
UV light (Ultraviolet light) is used in food industry applications to kill pathogens. UV light is completely safe, and effectively eliminates viruses like E. Coli and Salmonella.
Vacuum-packed food is a packing method that removes the air from the package so the contents can be stored longer.
Validation is defined as that part of verification, focused on evaluating technical information to determine whether the HACCP plan is operating effectively enough.
Verification is the number of methods, procedures, or tests to determine compliance with the HACCP plan. Verification will ensure that the HACCP plan is operating according to the plan and food safety is ensured.
Viruses spread through the consumption of food and beverages. They are typically highly resistant to environmental factors which makes them highly persistent.
Waste management plan is a mandatory document in your HACCP plan. It covers everything related to waste management and how food safety is ensured. The document includes the list of waste, preventive and corrective activities to ensure food safety, the frequency of disposal, and responsible people.
Water activity is a measure of the amount of available water in the food. The water activity is a value between 0 and 1, where 0 means there is absolutely no available water, and 1 means all water in the product is available (pure water). Most foods are within a range of 0.2 and 0.99.
Yeast is single-celled fungi that causes food spoilage.
Food safety glossary - daily helping tool
This food safety glossary will help food business operators to navigate inside the complex world of food safety. It includes all terms associated with foodborne illness, food safety hazards, managing HACCP, and food safety along with food chain. As food safety is part of public health for food service industries, it's heavily regulated by rules and laws and inspected by the Food and Drug Administration.
All of these requirements, rules, laws and technical food safety regulations mean that you have to learn loads of specific terms that might be unclear at first sight. Because of the wide field of food safety, there can be words and terms that are new to you every day. Not all food processors are experts with the food industry terminologies. No one expects you to be! That's why we at FoodDocs made this food safety glossary to help you along your food safety journey.
We understand how crucially important it is to understand most HACCP terms to provide safe food and to prevent food poisoning. We also consider acquainting your whole team with food safety terms as part of basic food safety training. Feel free to use this glossary in your everyday business to provide safe food and when communicating with any food safety and inspection service.
How do food safety terms work?
Food safety vocabulary works according to the alphabet. You can find your needed food safety terms by the first letter of the word. Just click on the first letter of the word you are looking for to see a list of food safety terms starting with this letter. The links help you to understand the next topics.
For example, when clicking on the letter "F", you'll find all the most popular terms starting with this letter -
- Food contamination
- Foodborne illness
- Food and drug administration
- Food poisoning
- Food fraud
- Food recall
- Food safety standards, and much more.
Clicking on the letter "C", you'll find food safety terms like
- Common food
- Cross-contamination
- Control of food safety
- Correct procedures
- Control of hazards, and others.
Some of the food safety terms are underlined such as foodborne illness. This line means you can click on that word and you'll find much more information about the topic. The browser will redirect you to a more detailed explanation of the word and may even have an example of how it is used and other related information.
Related information to your chosen words such as for foodborne illness can be,
- how to prevent food-borne illness
- what are disease-causing microorganisms and types of illness
- natural toxins
- poisonous substances
- biological contamination
- harmful substance
- microbial contamination
- biological hazards
- why is measuring internal temperature so important among monitoring procedures?
How can the food safety glossary help me?
Food safety terms glossary makes your life much easier. It means whenever you hear unfamiliar food safety terms in a phrase, you can come and check the meaning of the terms from our glossary. It's always better to check instead of keeping yourself in the darkness. Understanding and following food safety plans and food safety standards across the whole food supply chain are crucially important to provide safe food for all consumers and prevent adverse health hazards.
If the food establishment owner, food processors, or anyone on the team doesn't understand important phrases like hazard analysis, major food allergen, and hazardous foods, it becomes a great risk to food safety. When dealing with food contact surfaces, handling raw foods such as raw meat, and preventing cross - contamination through contact with food, knowing the technical terms can save your business.
It can be a bit hard for food business operators to not understand the basic rules and terminologies of personal hygiene to control the presence of physical contaminants and prevent food contamination or don't know any major food allergen. This lack of knowledge can lead to losses for food processors through a breach of federal regulations. Understanding your food safety plan together with providing basic food safety training to introduce all named food safety terms are some of the most important parts of improving the food supply chain.
How can a digital HACCP builder help me with unclear food safety terms?
Our HACCP builder at FoodDocs is a digital program that helps to create your HACCP food safety plan in 1 hour and also enables you to store it digitally. One of the most important benefits of a digital HACCP plan is that it's easily customizable at any time.
When your HACCP plan includes complex food safety terms, you can always add additional explanations to your food safety plan for more context. This makes your plan easily readable and understandable for the whole HACCP team. Don't let vague and hard-to-understand words get in the way of making a comprehensive HACCP food safety plan. Through the help of this glossary, you can now explain "harmful substance" by adding "dangerous to human health" as a supporting line. Replace technical terms such as "perishable food" with "short-lived food" to make your documents reader-friendly.
Feel free to sign up to FoodDocs and try it free for 14 days.