Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Discover how to practically and digitally improve your organization’s compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices.
GMP guidelines were established in response to incidents where products were contaminated, adulterated, or improperly manufactured, leading to serious harm. These regulations set forth minimum standards that manufacturers must adhere to, ensuring that their products maintain consistent high quality from one batch to the next and are safe for their intended use.
GMP stands for Good Manufacturing Practices.
As outlined in the GMP for the 21st Century for Food Processing study:
“As the minimum sanitary and processing requirements for producing safe and wholesome food, Good Manufacturing Practices are an important part of regulatory control over the safety of the nation's food supply. GMPs also serve as one basis for FDA inspections.”
According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), both U.S.-based and international food facilities are typically mandated to register under Section 415 of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act).
This means they must adhere to the risk-based preventive controls outlined in Part 117 unless the facilities are subject to specific exemptions.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) ensure products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards across industries including food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics.
GMP compliance involves adhering to risk-based preventive controls as mandated by regulations like the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act).
The core components of GMP, known as the 5 Ps (People, Products, Processes, Procedures, and Premises), highlight the critical areas of focus for maintaining quality in manufacturing.
Documenting every step of the manufacturing process is essential for transparency and consistency, helping to trace and address discrepancies in production.
GMP requires regular internal audits and continuous monitoring to ensure ongoing compliance and identify areas for improvement in manufacturing facilities.
Training across all levels of a company is crucial for maintaining GMP standards, focusing on critical aspects like sanitation, record-keeping, and error minimization.
The 10 principles of GMP cover everything from creating and enforcing SOPs to designing systems and maintaining clean and efficient facilities and equipment.
Validation of processes and equipment is required to confirm that they consistently produce expected results, ensuring the integrity and safety of products.
GMP regulations are enforced by national authorities such as the FDA in the U.S., and involve detailed requirements for quality management systems and operational controls.
FoodDocs can greatly enhance a company's ability to achieve and maintain GMP compliance through streamlined documentation and real-time monitoring.
WHAT WE'LL COVER:
The main components of Good Manufacturing Practices, also known as the 5 Ps of GMP, are People, Products, Processes, Procedures, and Premises.

In manufacturing settings, all personnel must be thoroughly trained and understand their specific roles. Regular performance evaluations help ensure that everyone is competent and adheres to GMP standards.
What this looks like in the workplace: An employee working in a dairy facility should be trained in pasteurization processes and also in hygiene practices to prevent cross-contamination.
Documenting every step of the manufacturing process is a cornerstone of GMP. This ensures that procedures are transparent and adhered to consistently. If discrepancies arise, they must be meticulously analyzed and documented.
What this looks like in the workplace: A chocolate manufacturer must specify the quality of cocoa beans and dairy products used, and ensure each batch meets these specifications before processing. This meticulous detailing helps in standardizing flavors, textures, and safety of the final products.
This refers to both the raw materials used and the finished goods produced. Clear specifications must be established for all materials and products at every stage of production. For example, in food manufacturing, standards for ingredient quality and finished product testing must be explicitly defined to ensure safety and consistency.
What this looks like in the workplace: A bakery might regularly review and improve its baking times and temperatures to ensure product consistency while reducing energy consumption.
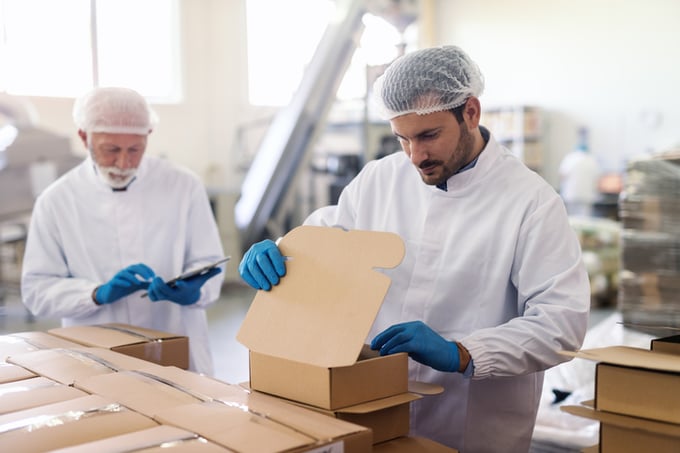

The condition and cleanliness of manufacturing equipment and facilities are fundamental. Continuous checks and validations ensure that all equipment operates efficiently and safely.
What this looks like in the workplace: A practical example is the routine sterilization of machinery and work surfaces in a food processing plant to meet health and safety standards.
GMP emphasizes the continuous improvement of manufacturing processes. Each process must be clearly defined, routinely evaluated, and enhanced as needed. Regular self-audits help identify areas for improvement, ensuring ongoing compliance with industry standards.
What this looks like in the workplace: A practical example is a meat processing plant that conducts daily sterilization of its processing equipment and periodic deep cleaning of its entire facility to comply with food safety standards.
to get and stay compliant
You can also argue there’s an unwritten sixth P: profit. If a food manufacturer has their first 5 Ps in a row and is executing them daily, there’s a good chance that their business’s food safety reputation and quality standards will — sooner or later — lead to more profitability.
The 10 principles of GMP are:

Establish and meticulously maintain detailed SOPs that outline all critical processes. This ensures consistency in operations and quality control, providing a reference point for both training and evaluation.
Adherence to these SOPs is non-negotiable. Regular and rigorous application of these procedures ensures consistent output and operational efficiency.
Accurate and comprehensive documentation is fundamental in GMP to trace every aspect of the manufacturing process. This allows for clear accountability and the ability to review operations and trace problems when they arise.
Validation ensures that equipment and processes produce results that meet predetermined specifications. This step is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the manufacturing process and ensuring product quality and safety.
All facilities, resources, and operational blueprints should be designed to maximize quality production. This integration ensures seamless operations and reduces the potential for errors or contamination.
Regular equipment and facilities maintenance ensures that every production batch is made under optimal conditions, safeguarding product integrity and worker safety.
Ensuring that all employees are trained and competent in their roles is essential. Regular training and assessments help maintain high standards and adapt to new regulations or technologies.
Personal and environmental cleanliness prevents product contamination. Strict hygiene protocols are critical in environments sensitive to microbial and particulate contamination.
Continuous environmental monitoring must be employed to detect conditions conducive to contamination in production areas. This involves regular checks and balances to ensure that the environment remains within set specifications for cleanliness and safety.
Regular audits verify compliance with all prescribed regulations and internal guidelines. A GMP audit checklist like this one is crucial for continual improvement and maintaining regulatory compliance.


Thank you for downloading free template!
Want to get a customizable HACCP template?
Or set up your food safety system in 15 minutes?
GMP regulations vary from country to country, but a facility’s national government will mandate regulations to help regulate products’ production, verification, and validation.
In the United States, for example, the FDA mandates the regulations for Good Manufacturing Practices. In Canada, Health Canada is responsible for administering and enforcing GMP regulations. In Europe, the European Medicines Agency is in charge of implementing strict GMP guidelines.
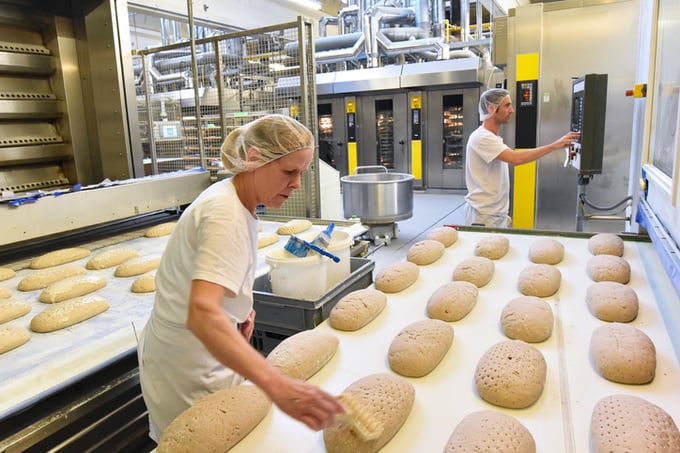

GMP requirements are areas of focus that enable food manufacturers to produce products with high degrees of quality and safety, from record-keeping and process controls to sanitation and recall plans. Below we cover eight key GMP requirements:
The foundation of GMP is the requirement for a robust Quality Management System (QMS). This system ensures that each aspect of the manufacturing process is controlled and consistent, aiming to minimize or eliminate instances of contamination, mix-ups, and errors. This means having clearly defined and well-controlled processes, verified by independent quality testing, and staff adherence to quality standards throughout production.
Accurate documentation and record-keeping are mandatory to achieve traceability and accountability in manufacturing processes. This includes the creation and maintenance of batch records, equipment logs, and training records, which help in tracking the history of a product batch and investigating any issues that arise.
Personnel working in manufacturing facilities must have the appropriate qualifications, training, and cleanliness to prevent product contamination. GMP requires that all personnel understand their roles and responsibilities, and that they are trained to maintain high levels of hygiene, including the use of proper attire and grooming standards.
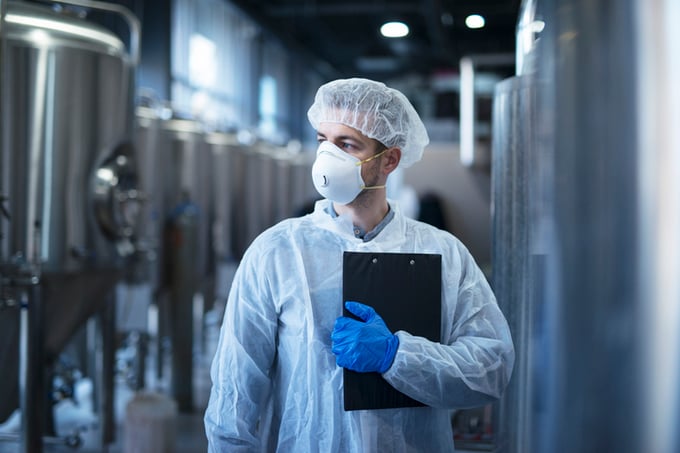

Manufacturing facilities must be designed to facilitate proper maintenance, cleaning, and sanitary operations. The layout should prevent cross-contamination between different materials. Equipment must be appropriately designed, sized, placed, and maintained to function according to the process specifications.
Processes and equipment must be validated to demonstrate that they work reliably. This involves qualifying that the machines, systems, and processes do what they are supposed to do based on predetermined specifications. Validation ensures consistent production and product quality.
GMP requires tight control over all aspects of production. This includes clearly defined and controlled formulas, manufacturing processes, and packaging systems. Controls must ensure that all production processes produce a product that meets predetermined quality specifications.
Regular quality control testing is a must under GMP. This involves testing raw materials, in-process materials, and finished products to ensure they meet established standards of quality and safety. There must be a system in place for approving or rejecting all materials, with each batch documented and filed.
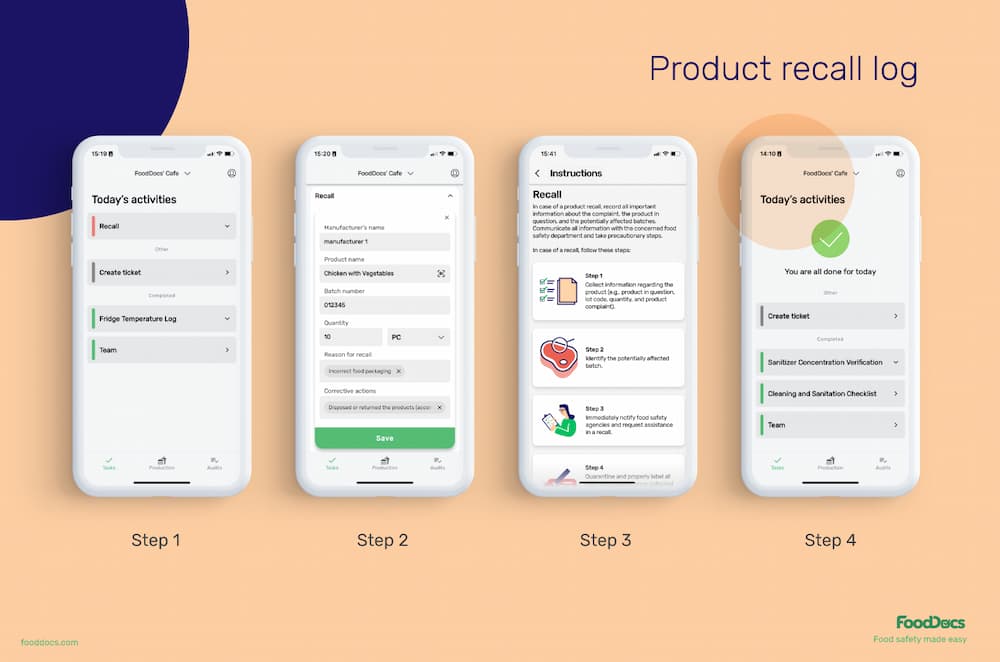
A system must be in place for handling complaints, with procedures for investigation and documentation. Similarly, there should be a system for product recalls to remove potentially harmful or non-compliant products from the market swiftly.
GMP compliance is the process of ensuring that food and pharmaceutical manufacturers produce and control products that meet Good Manufacturing Practices, and minimize risks that they cannot eliminate through testing the final product.
One answer is that GMP compliance is everyone’s responsibility. Both internal and external stakeholders play important roles in the success (or failure) of a food business's GMP compliance journey.
To understand each of their roles, let's look closer at the compliance responsibilities of both internal team members and external auditors.
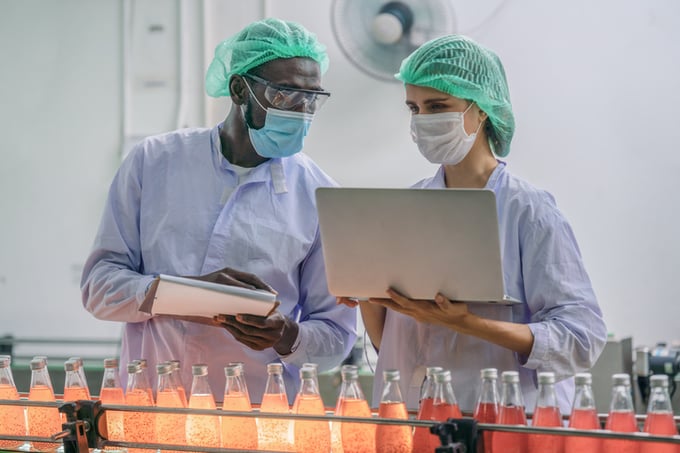

A GMP-compliant facility is one that meets high quality and safety standards as outlined in the Good Manufacturing Practices by the FDA (or another country’s agency) to prevent incidents such as contamination, deviations, ingredient issues, and manufacturing failures.
In cases where GMP compliance is at risk or worse, Francis Goodwin (Director of the Office of Manufacturing Quality of the Office of Compliance at FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research) shared at a PDA/FDA Joint Regulatory Conference in September 2024:
“[The] agency was seeing a lot of sponsors, product owners, whatever you want to call them, and contractors where they hadn’t delineated who was responsible for what or who conducts inspections and neither party was doing something that needed to be done.”
When FDA sees gaps of that sort, Godwin stressed, “We are not yelling at the sponsor, we are not yelling at the manufacturer, we are yelling at both. We have actually had multiple meetings where we call in the sponsor and the contract manufacturer and say, ‘This relationship is toxic. You are not doing this. You need to fix this.’”
You can comply with GMP standards by following six measures, whether you manufacture human food or pharmaceuticals:

Whether it’s GMP or another standard, digitizing your food safety management system will make staying compliant easier, faster, and more accurate.
Judy Sebastian has a dual specialization in food safety management and organizational culture transformation and is the Principal Consultant at Apex Global Consultants, as well as the senior food safety consultant at Apex Food Consultants in Dubai.
She believes you should build the food safety system and then break it.
“When it comes to integrating or implementing new technology, try breaking it before it goes live,” says Judy. “This is the advice I often share with my clients when they’re on the path to digitizing a food safety system. By being aware of the system’s points of vulnerability, it better equips the operational personnel to stay prepared in the event the technology stalls or fails. Just like most things, the digital era of food safety auditing and management will remain a constantly evolving one and we must strive to keep learning.”
You can use digital food safety solutions such as FoodDocs to implement and fully customize your monitoring, traceability, and HACCP tasks and documents to easily stay compliant.
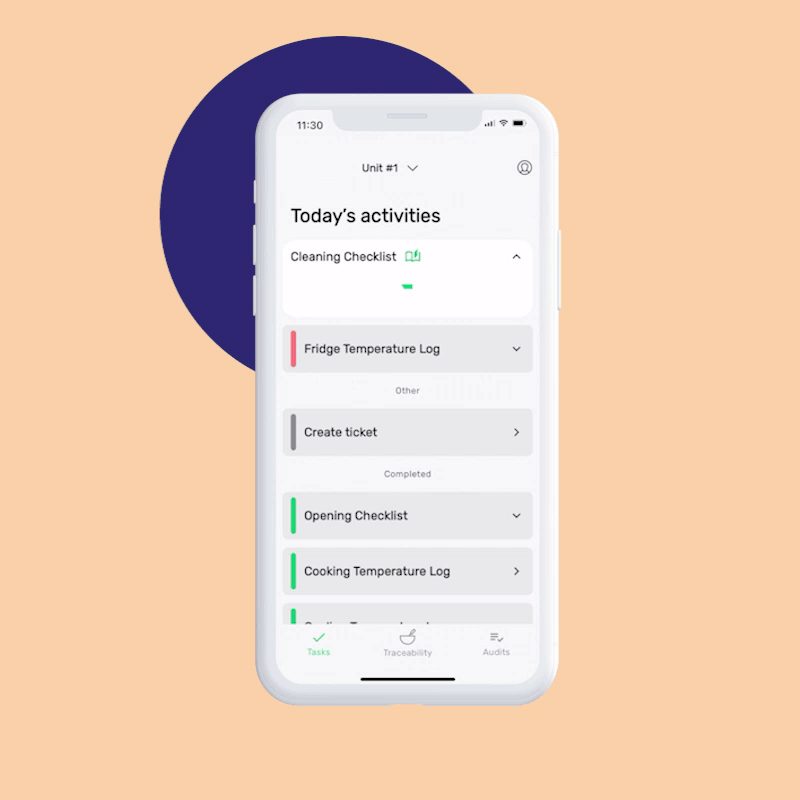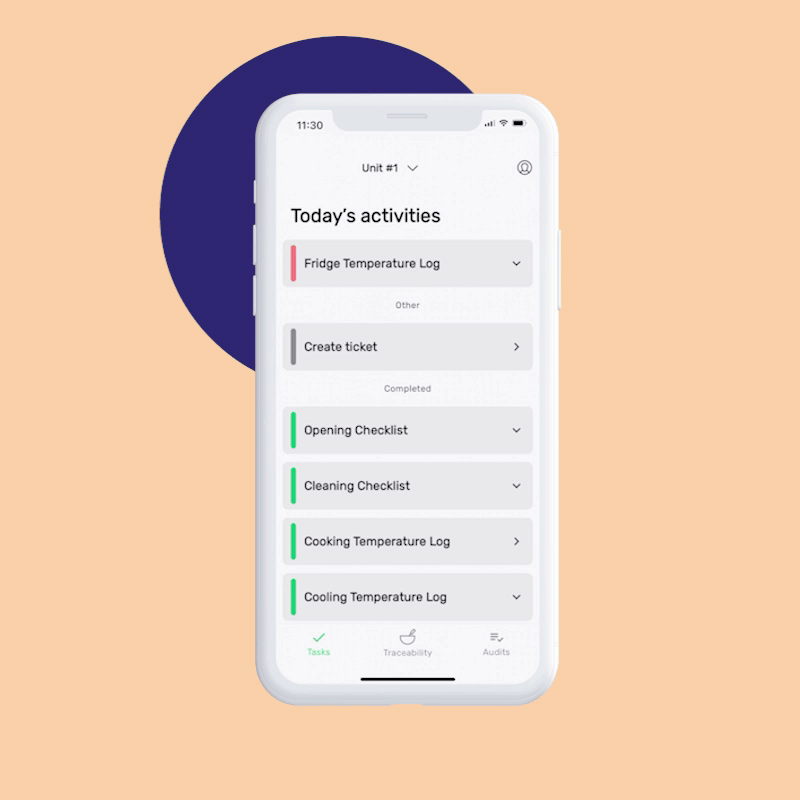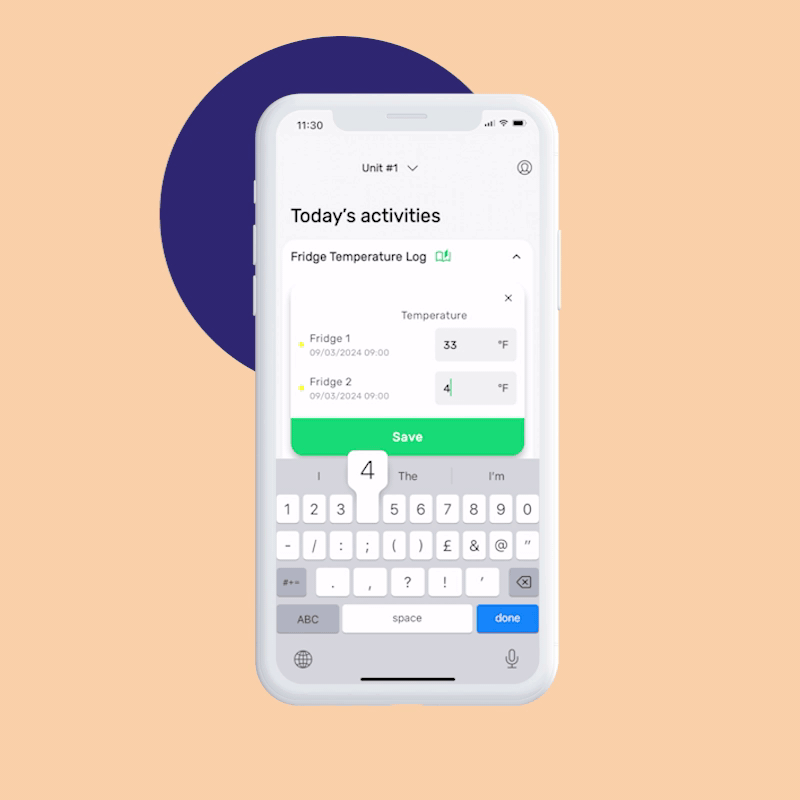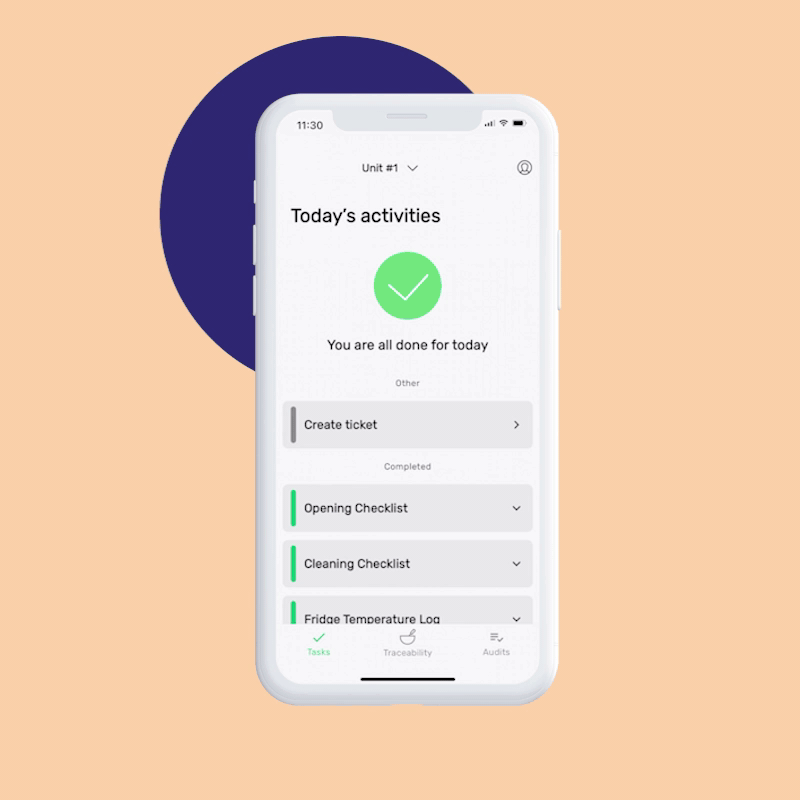
The FSMA Final Rule for Preventive Controls for Human Food states that your facilities registered with the FDA must have and implement a written food safety plan that includes:
Our AI-powered HACCP software helps you create a HACCP Plan to meet legal requirements in less than 1 hour.
After answering a few questions about your business, our system will compile the essential HACCP documents you need for compliance. All documents are fully customizable according to your company's needs at any time.

During the HACCP plan creation period, you’ll get:
All of which are very time-consuming to complete manually, even with the support of a consultant. These documents are critical to ensure consistency in daily operations and clearly communicate good food safety practices.

You can set up your Food Safety Management System in minutes by answering a few simple questions about your business. Our AI creates your first monitoring tasks automatically, and you can start monitoring right after finishing your signup, or customize the tasks as necessary.
The digital checks in FoodDocs’ Monitoring system include corrective actions. If a task is out of range, a prompt will guide your team on how to respond, ensuring food safety and saving time on training. You can use our pre-set actions or create your own.
And for completed monitoring tasks, whether you’re on-site or remote, you can choose to verify them by assigning the finished ones to yourself or a supervising team member.
This feature ensures that your staff completes their activities according to food safety requirements. This feature is essential for companies that apply very high food safety standards.

FoodDocs allows you to complete traceability logs and attach monitoring tasks to the same product batch right away. Just log important quality checks like the cooking temperature to the prepared batch during the preparation process.
This ensures necessary traceability and visibility in case of a recall or customer complaint and will help you ensure high-quality food safety.
If you ever need to access essential recall data quickly, you can search by product, batches, ingredient, or expiry date. Since all your traceability records are digital, they’re always secured and easily found to prove compliance.
When taking in shipments and filling receiving logs, you can quickly complete a traceability log with three clicks. Select the product by searching for it manually or using a built-in mobile scanner to make the process faster thanks to EAN/QR codes.
In addition to easily accessing recall data, the FoodDocs Traceability system also calculates shelf-life dates for your products automatically in your digital recipe book. This is especially true in the wake of FSMA 204 if you manufacture items on the food traceability list.

Using digital food safety management software will help you get there much easier, faster, and cheaper than a paper-based food safety system.
Try FoodDocs’ 14-day free trial today and see how easy food safety management can be. Or book a demo to get a personalized look at how FoodDocs can support your business’s GMP compliance.
The difference between cGMP and GMP is in their emphasis on technology and standards, even though they both set guidelines for manufacturing. GMP offers broad, regularly updated guidelines allowing manufacturers some flexibility in compliance, whereas cGMP mandates the use of the latest technologies and standards, requiring continual updates to manufacturing processes to ensure that products are produced using the most current procedures available.
This ongoing evolution in cGMP ensures that compliance is dynamic, reflecting the latest advancements in the food, medical, and pharmaceutical industries.
GMP experience involves understanding and applying Good Manufacturing Practices, a set of regulations designed to guarantee that products are produced reliably and safely. You can develop this expertise through formal education, practical training, and direct work experience in relevant industries.
GMP certified indicates that a product has been manufactured in a facility adhering to Good Manufacturing Practices, a system of quality assurance standards designed to ensure that products are consistently produced according to specified quality criteria. This certification reflects a commitment to reliable manufacturing processes and adherence to established quality standards.
A GMP facility is a manufacturing site that adheres to the guidelines set forth by the FDA for producing food, pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and supplements. These facilities are meticulously designed to ensure that products are consistently manufactured to meet rigorous quality standards.
As defined by the FDA, Good Manufacturing Practices are a set of regulations to ensure the quality and safety of various products, including food, drugs, and cosmetics. These guidelines govern the entire production process, encompassing manufacturing, processing, packaging, labeling, and storage, to set uniform standards for quality and safety.
In a food quality quiz, the following is not true of good manufacturing practices: it should be used as a guide to establish a food safety program.
Here’s a timeline of GMP development in the United States:
|
Date |
Milestone |
|
1906 |
The Bureau of Chemistry passes the 1906 Pure Food and Drugs Act, prohibiting interstate commerce in misbranded and adulterated foods, drinks, and drugs |
|
1933 |
FDA recommends revising the 1906 Pure Food and Drugs Act |
|
1938 |
FDA passes the 1938 Federal Food, Drugs, and Cosmetics Act, which provides identity and quality standards for food |
|
Mid 1960s |
FDA decides to clarify the FDCA through GMP regulations |
|
1968 |
FDA proposes food GMP regulations |
|
1969 |
FDA finalizes food GMP regulations |
|
Early 1970s |
FDA considers promulgating industry-specific regulations |
|
Late-1970s |
FDA decides to revise the general GMPs rather than adopting industry-specific GMPs |
|
1986 |
FDA publishes revised food GMPs |
|
2002 |
FDA forms Food GMP Modernization Working Group |
|
2004 |
FDA announces effort to modernize food GMPs |
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...