Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
If you can nail the 4'Cs of food safety, you'll have a much easier time achieving and maintaining compliance.
The 4 C’s of food safety are a simple framework used to reduce food safety risks by focusing on Cleaning, Cooking, Cross-Contamination, and Chilling throughout food handling and preparation.
While numerous food safety practices are being taught in the food industry, these practices revolve around a few basic principles. In what is known as the 4 C's of food safety, the foundation of more technical food safety practices can be covered.
The components of this concept can significantly protect every customer from foodborne illnesses and other risks of food hazards. If done correctly, these methods can effectively achieve compliance with most food safety laws and regulations.
Key takeaways
In the food industry, food safety practices can be implemented throughout the whole food supply chain. These practices can become very technical especially when they are used for a critical control point.
Whether basic or technical, food safety practices are used to control food safety hazards that can lead to damaging events. These hazards can either be biological, physical, or chemical and can cause significant problems for any food business.
Most food safety practices are based on four basic tasks. The 4 C's of food safety are as follows:
These are based on the main principles of how to address different kinds of food safety hazards and several other food safety practices can be derived from them. They are always part of the different prerequisite programmes for higher food safety management systems.

This food safety operation can be applied in many different ways. It can be applied with raw ingredients, food contact surfaces, facilities, equipment, and employee hygiene.
Cleaning may mean keeping food contact surfaces spotless and sanitised at all times. These food preparation surfaces can harbor microbiological hazards easily and can become a source of foodborne illnesses.
Especially in a kitchen with very limited space, both raw ingredients and cooked food can pass through a single preparation area. In such cases, constant cleaning and sanitation are a must.
In this aspect, cleaning can be applied to the floors, walls, windows, and doors of all the rooms in your food establishment. This includes using the proper cleaning solutions and materials for thorough cleaning. Use a cleaning schedule to ensure that proper timing and materials are being consistently applied.
Although the primary design of the facility and kitchen environment must be that they won't harbor physical hazards such as dust, constant cleaning must be done. Dust can easily contaminate food without being detected and can cause spoilage, especially for high-risk ingredients and products.
While raw materials will still be processed, cleaning them is also an essential task. Cleaning in this context can mean removing physical hazards such as excess soil on root crops, inspecting for debris, or isolating materials that are not wholesome. This reduces the chances of causing spoilage on the products and the risk of spreading any food safety hazards.
Being frequently used, any piece of kitchen equipment needs to be cleaned before and after use. Sanitizing is also a must, especially before operation. This step ensures that crevices and corners on the kitchen equipment would not have any leftover food material to attract harmful bacteria. Wash equipment and cooking utensils with soapy water and rinse well with warm water.
In this case, cleaning can be done by applying excellent food hygiene practices including handwashing before and after handling foods. Proper handwashing must be communicated to all food employees. It must be done correctly to be effective.
Steps such as doing it for at least 20 seconds and with soapy and hot water will ensure the elimination of foodborne bacteria. Learn more about proper handwashing and get your team an informational poster about the topic here. Personal hygiene may also include properly wearing a protective uniform, clean clothes, neatly tied hair, and regularly trimmed nails.
To keep foods such as raw meats, milk, and other dishes safe for consumption, cooking them is essential. This step reduces the initial microbial load of foods to acceptable levels and kills target pathogens. Food safety standards for cooking different types of food have been provided by several food safety authorities.
Things to remember when cooking:
The standards for cooking different foods have been established to make the food safe and enjoyable for everybody. To do this step correctly, the application of heat must be accurate and well-guided. Use a clean food thermometer and a cooking chart to help you make sure that you will be targeting the correct internal temperature for your food.
In combination with an accurate temperature reading, the heat treatment must also be applied for a specific amount of time. This ensures the efficacy of the cooking process. Additionally, a longer cooking time can be applied if you intend to cook foods at a lower temperature. As an example, while the generally prescribed temperature to cook chicken is 74°C (165°F), it can be cooked at 62.8°C (145°F) as long as this temperature is constantly held for 9.8 minutes.
In cooking food, it's important to hit the correct internal temperature. Doing this every time means that the food receives equal treatment and that the heat reaches the coldest part of the ingredient, otherwise known as cold spots.
In addition to proper cooking, foods must be kept hot if they are meant to be served moments after cooking. This step helps maintain the safety of the food being served. Keep food temperature at least 63°C (145°F) to prevent the growth of pathogenic microorganisms.
Whether it is in a restaurant kitchen or home setup, leftovers are very common. These foods have already been exposed to external factors and may have already attracted an unalarming amount of pathogens. To ensure the safety of leftover foods when you intend to serve them again, thoroughly reheat them to 74°C (165°F).

This step refers to one of the fastest ways that promote the spread of pathogens and foodborne diseases. By definition, cross-contamination is a way of transferring food safety hazards from one area to another. This event can be classified into three different instances:
Cross-contamination poses a great risk for any food establishment. This occurs when food hygiene practices are not being applied and when a team's approach to food safety is not properly monitored. Without anyone knowing, hazards, especially pathogens, can be easily transmitted. Cross-contamination can be observed in the form of these situations:
The first key to preventing cross-contamination is knowing how and when it could happen. Through this, food handlers can be more aware and conscious of how they do things. In addition, proper food hygiene practices can be applied to help prevent cross-contamination from happening.
Chilling is a food safety practice that helps control food safety hazards. The main principle behind chilling is that the low temperature of a refrigerator slows down the reproduction of pathogens. This works both ways for cooked foods and raw materials. As such, the low temperature during chilling must be consistently maintained.
Here are a few important food safety things to remember during chilling:
Before chilling, foods must be cooled down as fast as possible. Preferably, the cooldown process must be achieved within the first two hours. This step prevents the overall temperature from falling to maintain its capacity to cool all foods inside. Chilling is the best way to extend the shelf life of food and to stock perishable raw materials for later use. As long as it is done correctly, foods can stay wholesome for an extended period.

The 4 C’s of food safety are often used as a foundational framework within broader food safety management systems.
Each “C” aligns with key system elements:
While the 4 C’s are not a complete food safety system on their own, they help translate food safety principles into everyday operational practices.
The four C's of food safety are not mere food handling practices that can be ignored. They are essential food safety tasks that help every food business maintain compliance. They also help protect customers from any foodborne disease. Quality of services and food items must always remain safe to be enjoyed by everyone.
There are five reasons why the 4 C's of food safety can help every food business achieve the following benefits:
When food services and products are made and served correctly, food businesses can reap their products without any additional costs. Problems such as product recall cost money, time, and effort from your side and will surely hurt your brand image.
The main objective of these major food safety practices is to control food safety. They were designed to reduce, if not eliminate, potential hazards that can cause food poisoning. They are general activities that may be considered most effective and can even amplify the effects of more sophisticated food safety management systems.
If a food business consistently displays thorough use of these food safety practices, customers can have more confidence in your business. They will be more likely to come back and even promote your services through word of the mouth.
Concerning foodborne diseases, this problem can easily escalate especially if it has caused more significant damage. In the case of grave events such as hospitalization or death of a customer, your food business can face lawsuits and product recalls. If the 4 C's of food safety are properly implemented and monitored, these problems can be avoided.
As part of improving the knowledge and skills of your food employees, the introduction of these practices can help them become more adept with everyday food operations. With specific instructions on how to properly perform the 4 C's of food safety, employees can unconsciously improve and apply them even when no one is looking.
One of the main things that any food business has to achieve to become successful is to prove to consumers and food safety authorities that they are capable of serving delicious and safe food. The occurrence of foodborne problems does not only affect personal living but other industries as well. Whenever consumers become sick, the burden for the health sector increases, whereas the manpower for other industries decreases.
The 4 C’s of food safety are designed to:
However, the 4 C’s are not:
The 4 C’s are most effective when used alongside structured food safety controls, monitoring, and ongoing review.
The implementation of food safety practices such as cleaning, cooking, cross-contamination avoidance, and chilling always be coupled with proper monitoring. The documents that become generated from monitoring these practices are proof of the quality and safety of your food products.
But establishing a strong food safety management system takes time. All steps and components we mentioned must be considered and assembled into a cohesive system.
To help solve this problem, use a smart, digital solution to produce a food safety and quality management system in just minutes.
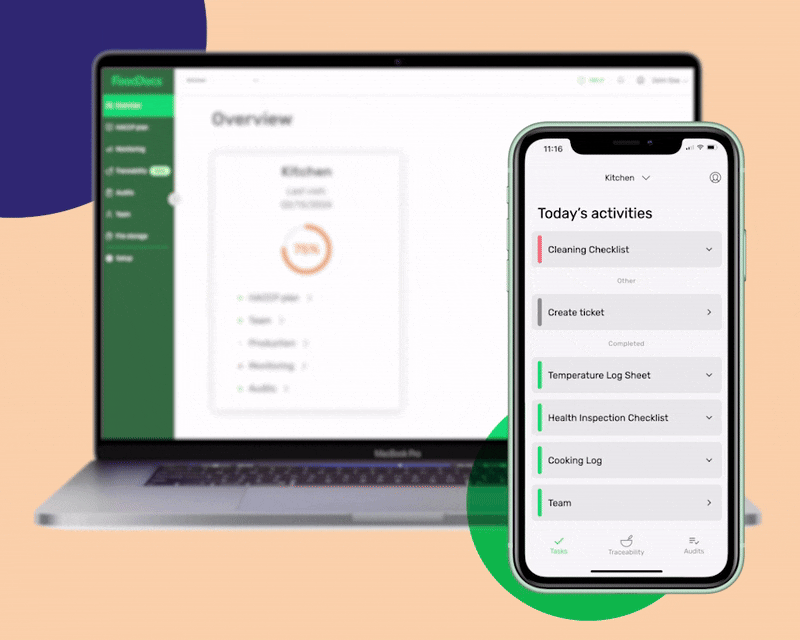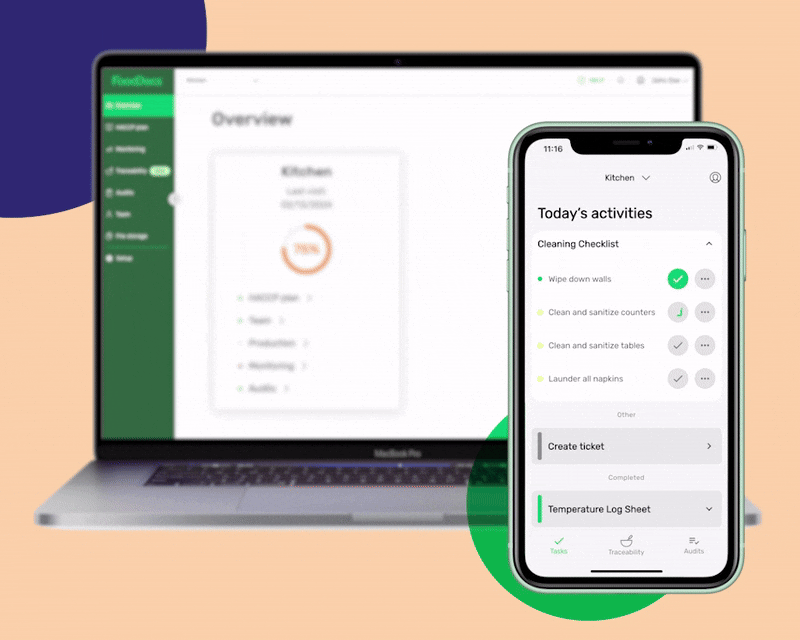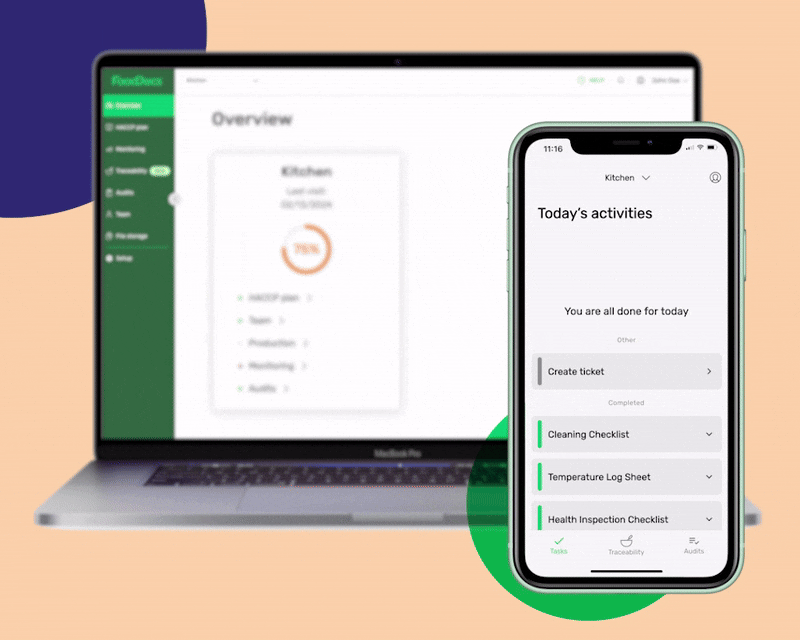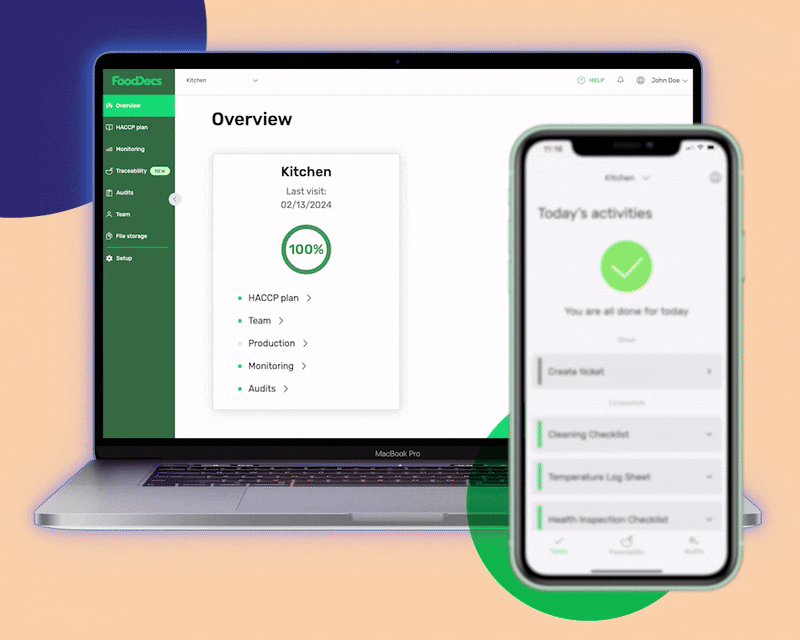
Using our digital Food Safety System Software, you will gain access to the following benefits:
One of the essential features of our software is a smart notification system that will help remind employees of tasks that need to be done.
The system will send intuitive alerts through our Food Safety App, reminding employees of a particular food safety task. With this feature, you can ensure that all controls in the food safety system will be followed efficiently.
The notification system can also help remind managers whenever certifications or training programs require renewal based on their effectivity dates.
Obtain a digital FSMS powered by AI and a machine-learning program, which generates monitoring logs automatically. All logs and checklists have step-by-step instructions to help the team perform tasks correctly and ensure compliance.
Use the instructions to train new employees or remind the team to monitor every control procedure.
By providing the team with accurate instructions, you can ensure consistent compliance with food safety regulations.
To accommodate the unique operations of every food business, our smart FSMS features customizable selections. Tailor the generated monitoring logs and checks to fit operations. Set any preferred standards and parameters to control. You can even build new detailed forms from scratch.
Add the option to upload your own educative instructions as photos or videos for a better understanding of the tasks. Make every control measure the best fit for operations with our customizable features.
Our software's monitoring system can be easily customized and improved to fit audit findings or when changes in food safety legislation are announced.
Save at least 20% of the time dedicated to supervising using our real-time dashboard. Using the instant overview, you can get a clear picture of your entire operations and easily perform evaluations and verifications of your FSMS. Monitor the company's food safety compliance and immediately address any concerns about food safety operations.
This overview shows the status of all your food company branches and gives you the necessary information to make informed decisions.
When you use our digital FSMS, you not only become more efficient, but you also become more sustainable. With our food safety software, you can ditch the pen-and-paper system and use a completely digital food safety system. No more piles of papers for your team while your business is contributing to saving trees.
Using a digital platform can sometimes be overwhelming. That is why at FoodDocs, we made everything easier for managers and employees alike. We've set up our system with multiple guides, and easy-to-understand instructions to help food workers become more adept with the digital FSMS.
Experience the benefits of our digital Food Safety Management System first-hand by using our free 14-day trial.
Our impressive system does not only create a digital FSMS monitoring program for you. We also feature a built-in HACCP plan template builder that can create a complete HACCP plan within 1 hour. Get a comprehensive HACCP plan based on the key principles of the food safety program.
Want to experience the benefits of our software and get compliant now? Use our free 14-day trial and build your Food Safety Management System today.
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...