Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Inadequate food safety practices can cause foodborne illnesses and other related food hardships.
There are a lot more requirements to keep a food business running than just serving quality food. Customers must make repeat purchases and food business owners must make connections with them to ensure continuous patronage. If a customer leaves a bad review about your services, it would be very bad for your operations.
To keep customers coming back and protect them from any foodborne illnesses, you want them to feel satisfied and safe with the food and service you provide. Food safety practices are the main key to achieving this. Adequate food safety practices lead to less hospitalizations.
Key takeaways
Food safety practices are crucial operations within the food supply chain designed to control hazards and prevent food product contamination.
These practices range from basic personal hygiene to cooking foods to safe internal temperatures to prevent foodborne illnesses.
Implementing robust food safety practices can significantly reduce foodborne illness hospitalizations and enhance consumer trust and safety.
Food safety practices are essential for maintaining public health and ensuring continuous business growth by preventing productivity loss due to illness and ensuring food security.
Regular monitoring and proper implementation of food safety practices are required to maintain compliance and protect against food safety hazards.
Effective food safety practices lead to fewer customer complaints and reduced risk of foodborne illness, fostering a safer dining and purchasing environment.
FoodDocs offers tools such as free templates and digital solutions to help businesses implement and manage their food safety practices more efficiently.
Adherence to food safety practices not only protects customers but also enhances the reputation and operational success of food businesses.
Different food businesses require specific food safety practices. These sets of practices range from basic procedures to technical ones that are highly specific. They help reduce the occurrences of foodborne illnesses that cause almost 128,000 Americans to undergo hospitalization every year. Protecting public health from these foodborne diseases must be the top priority of food businesses. This objective also contributes to the continuous potential for growth of the economy as it lessens the loss of productivity due to hospitalizations and ensures food security.
In this article, learn about which food safety practices are essential for food businesses and the problems that can occur from the lack of these practices.

Food safety practices are routine methods in preparing, processing, storing, and delivering food items safely to consumers. These practices are meant to prevent contamination of produce and food hazards that can cause significant effects on public health such as foodborne illnesses and related injuries. Food safety practices can be very simple tasks such as regularly washing your hands or very specific ones including processing different types of food to the correct internal temperature. They help prevent the release of unsafe food into the market.
Food safety agencies such as the Food and Drug Administration have established minimum requirements for these food safety practices and are normally included in prerequisite programs such as Good Manufacturing Practices, Good Postharvest Activities, and Sanitation Standard Operating Procedures. These standard safety practices protect food businesses from complaints and potential hazards that can cause foodborne illnesses.
To help you understand what are food safety practices, here are common questions asked by consumers:
Food safety refers to any activity related to preparing food in the most hygienic way to prevent foodborne illnesses from occurring. This concept is applied in all areas of food production, from the harvest of raw materials to the tables of consumers.

Food safety protects consumers from foodborne diseases and other related injuries. Food safety hazards such as contamination of food cause at least 600 million foodborne diseases per year worldwide, and these practices help reduce this number.
Any food safety handling activity helps prevent the spread of physical, biological, and chemical contamination in food service establishments or any processing plant and causes foodborne illnesses. They also help reduce costs by addressing food safety issues such as food waste, hospitalizations, recalls, lawsuits, and other food hardships.
When proper and adequate food safety practices are implemented, less hospitalizations due to foodborne illnesses occur. These foodborne illnesses can very much be avoided by properly handling and preparing food. Consumers, especially the high-risk groups, are susceptible to foodborne illnesses, especially since they do not have enough knowledge of how your food products are being prepared in your food business.
As a food business owner, it is your responsibility to oversee and ensure that all food safety practices are regularly being implemented. These practices involve learning about the importance of food safety and what could be the result of improperly implementing them. Additionally, food employees can be trained to acquaint them with basic and advanced food safety practices related to your operations. Training and certification programs for these food safety practices are widely available in the food industry.
Safe food practices comprise many different procedures. In an attempt to acquaint both food processors and consumers with which food safety practices are most important, food agencies such as the World Health Organization have established 10 basic food safety guidelines for safer food processing.
The 10 basic food safety rules include:
This food safety practice is involved with refraining from consuming minimally processed or raw foods that can affect health. All food materials normally contain contaminants such as microorganisms on them. Especially for foods that are grown in direct contact with soil, contamination of produce is highly likely. That is a very natural thing. Although, foods such as any fruit or vegetables can be eaten safely without processing. On the other hand, processing foods such as meat reduces the risk of food safety hazards such as microbial contamination from causing any harm. Additionally, adequate food safety practices lead to fewer hospitalizations especially when you properly cook your foods. Undercooked foods can still cause foodborne illnesses, especially in high-risk groups of consumers.
Concerning the previous rule, this food safety practice specifies the need to reach the recommended internal temperatures of different kinds of food products based on a target pathogen. Raw materials such as beef and poultry vary in terms of the required internal temperature to become safe. Beef can sometimes be served rare to medium-rare which is slightly undercooked, and can be achieved by cooking the meat to at least 52°C to 60°C (125°F to 140°F). On the other hand, poultry meat must always be cooked at 74°C (or 165°F). Processing them less would significantly increase the chances of causing foodborne illnesses. Serve only acceptable foods to consumers.
Any food contains nutrients that are attractive to spoilage microorganisms. Especially for high-risk foods such as those with a low acid content, consumers are advised to eat these foods immediately after cooking to prevent microbial contamination. These kinds of foods are more likely to become contaminated in a short time.
If you plan on saving food for later, make sure to keep your food out of the temperature danger zone, which is 40°F to 140°F (5°C to 60°C). At this temperature, microbial growth is significantly increased at very fast rates. Store foods that will be consumed later at refrigerated or freezing temperatures.
When storing foods in the refrigerator, the risk of contaminating the food increases. Although bacterial growth is slowed during refrigeration, it can multiply as soon as the food returns to room temperature. As such, make sure to reheat foods at least at 70°C or 158°F.
This food safety practice deals with minimizing cross-contamination. Cooked, ready-to-eat foods and fresh produce are expected to be consumed soonest or stored for later, such as fresh fruits and salad mixes, whereas uncooked foods still need to undergo processing. Fresh-cut produce still has a high number of microbial contamination in them. Handling these foods close together may cause cross-contamination which is the leading cause of the spread of contaminants in the restaurant kitchen.
One of the fastest spreaders of cross-contamination, and therefore microbial pathogens is through inadequate washing of hands. Humans are considered a major contamination source. Any contact with produce may cause contamination. Aside from the fact that food handlers have human pathogens on their skin, handling food, utensils, and other kitchen materials without handwashing can easily spread food safety hazards, even any infectious disease. Regularly wash hands with warm water or soapy water during processing and especially after using the toilet.
Another potential source of contamination in the kitchen is dirty food contact surfaces. Food preparation tables can become reservoirs for bacteria and other microbial pathogens if improperly cleaned and sanitized in between use. All types of food will pass through preparation tables or surfaces and crumbs or pieces may fall and encourage microbial growth. These can attract biological contaminants and become sources of foodborne illnesses. Additionally, avoid using toxic chemicals to clean surfaces.
Pests such as insects and other wild animals are attracted to food. Where there is food, the possibility of having pests is very high. Even domestic animals should be kept away from the kitchen. Additionally, animal feces can cause microbial contamination, and their hair, nails, or severed parts are considered physical hazards. As such, throw away food waste which can serve as their resources for food, and regularly empty trash cans to prevent pests from accumulating. Any contact with an animal in a kitchen setup can be considered a contamination source.
Some microbial pathogens such as E.coli can cause contamination of water. Use safe water for preparing dishes, cleaning, and drinking. Once contaminated water comes into direct contact with foods and utensils, the contamination can easily spread throughout the preparation area. Ensure the supply of adequate quality water in your establishment or processing plant.
These rules are just some of the most common food safety practices but build up the most basic food safety programs. They are vital for everyday operations to prevent any foodborne disease from occurring and are part of the basic principles of higher food safety programs. In addition to these rules, activities such as wearing only clean clothes, reporting any sickness, and observing proper personal hygiene are all important food safety practices as well.

The following four simple steps are correct food safety practices: clean, separate, cook, and chill.
Washing and cleaning both hands and surfaces frequently will help prevent biological hazards because soapy water and regular handwashing dislodge pathogens from the hands. You should separate raw meats from other types of food when handling them in the same shift.
In addition to the pathogens that live on the skin of humans, they can come from simply touching an unsanitized knife. As such, regular cleaning and sanitizing are important parts of everyday food safety practices. Implement this practice along with other food safety practices as mentioned above.
Biological hazards are food contaminants that include pathogenic microorganisms such as bacteria, molds, yeasts, and viruses. These pathogens are known to cause some of the most widely occurring foodborne illnesses all over the world each year. Microbial contamination can occur everywhere. Since these hazards co-exist with foods in the kitchen, the best way to prevent them from causing problems and only produce acceptable foods is to regularly wash hands and sanitize the surroundings.
Adequate food safety practices lead to less hospitalizations. As such, improper application of these methods can potentially increase the risk of causing foodborne illnesses and other related problems. These outcomes can also damage the reputation of your food business which then can lead to a loss of customer confidence and profit.
Some of the most likely effects of poor food safety practices involve:
Food safety practices keep a food business and consumers alike safe from any unfavorable food situation and food hardships. As such, regular monitoring of all food safety practices with effective food safety plans is required for every operator in the food industry. These operators include fresh produce growers, delivery services, and food processors. At FoodDocs, we strive to provide the most efficient digital FSMS in the food industry. Get automatically generated food safety monitoring forms when you sign up with us.

Similar to food safety laws and regulations, food safety practices can be regularly updated for improvement. This can be achieved through several ways to ensure that your customers are far from any potential foodborne illnesses. Like food equipment, food workers can be calibrated to understand food safety better and get more efficient in performing their jobs.
Here are a few steps you can do in your food business to improve any food safety practice:
In improving food safety practices, food handlers and food processors need to understand the importance of what they are doing. Through this, they can have a better appreciation of maintaining food safety and motivate them to consistently shift their attention to food handling. Additionally, commitment to serving consumers with safe food shows your concern for public health.
To help you monitor all food safety practices in your food business and maintain compliance with food safety regulations with minimal effort, switch to our digital food safety management system at FoodDocs.
Our system automatically creates a digital FSMS built specifically for your food operations, complete with monitoring documents for your food safety practices. This digital FSMS is based on your answers to our basic questions involving the nature of your operations.
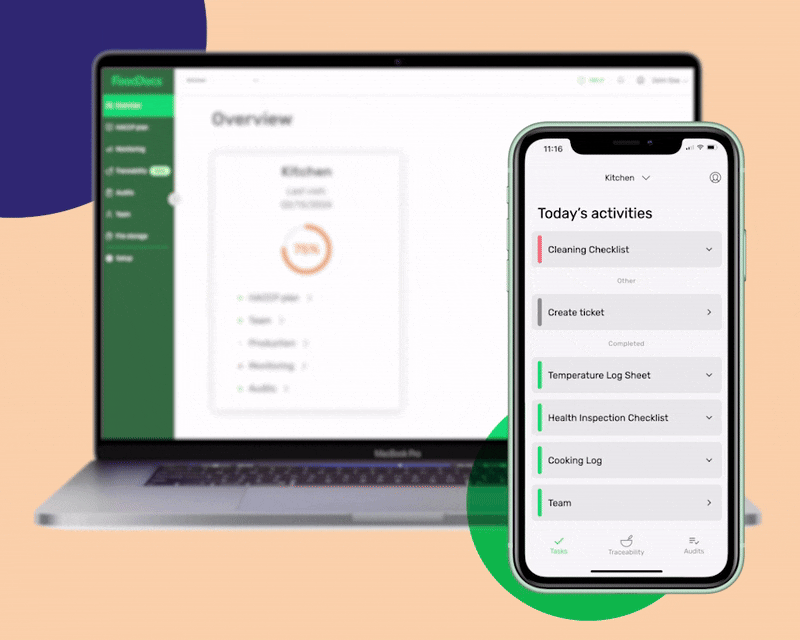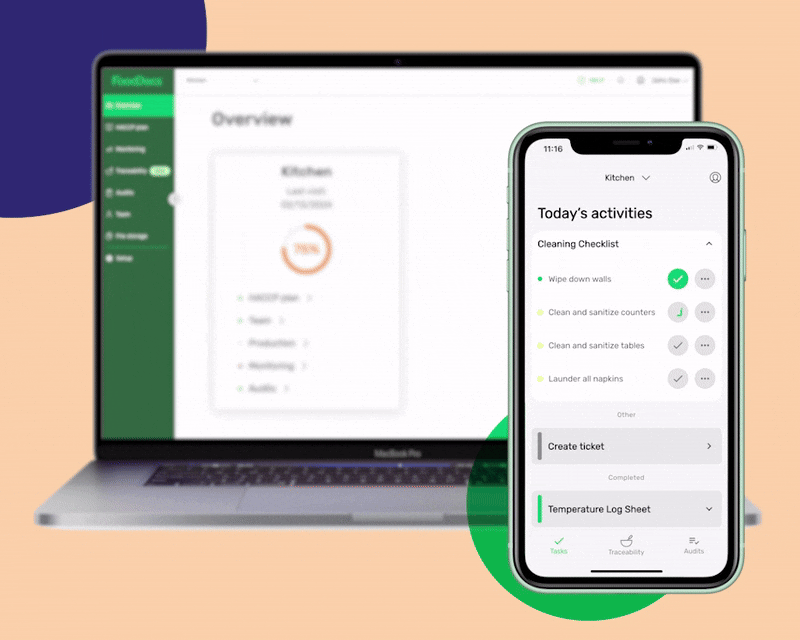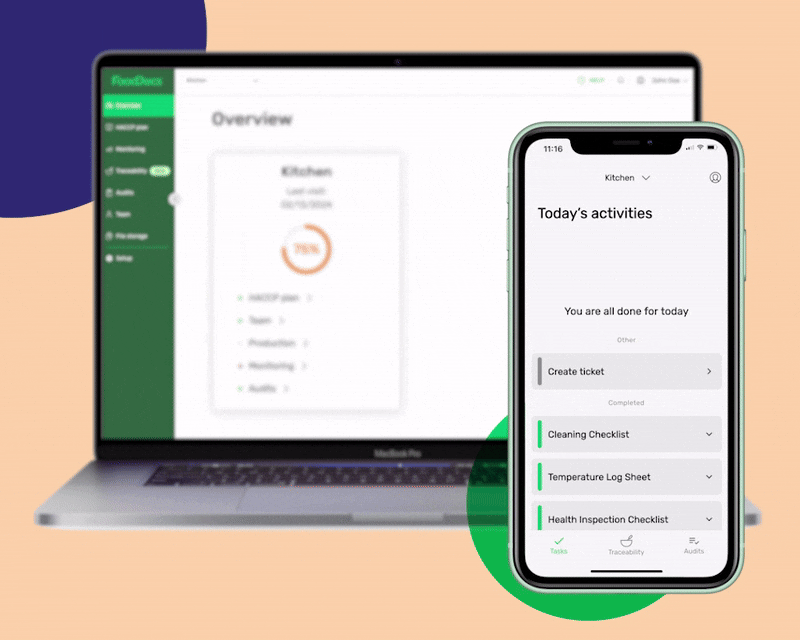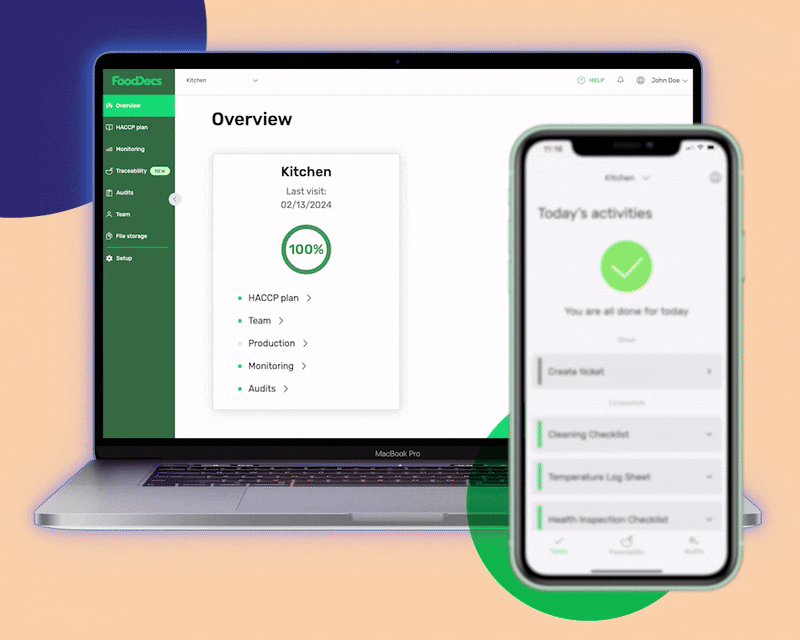
To help you decide with this big switch to the digital platform, here are some benefits that our system offers:
Some of the most important monitoring logs that our system can generate to help your business control food safety include:
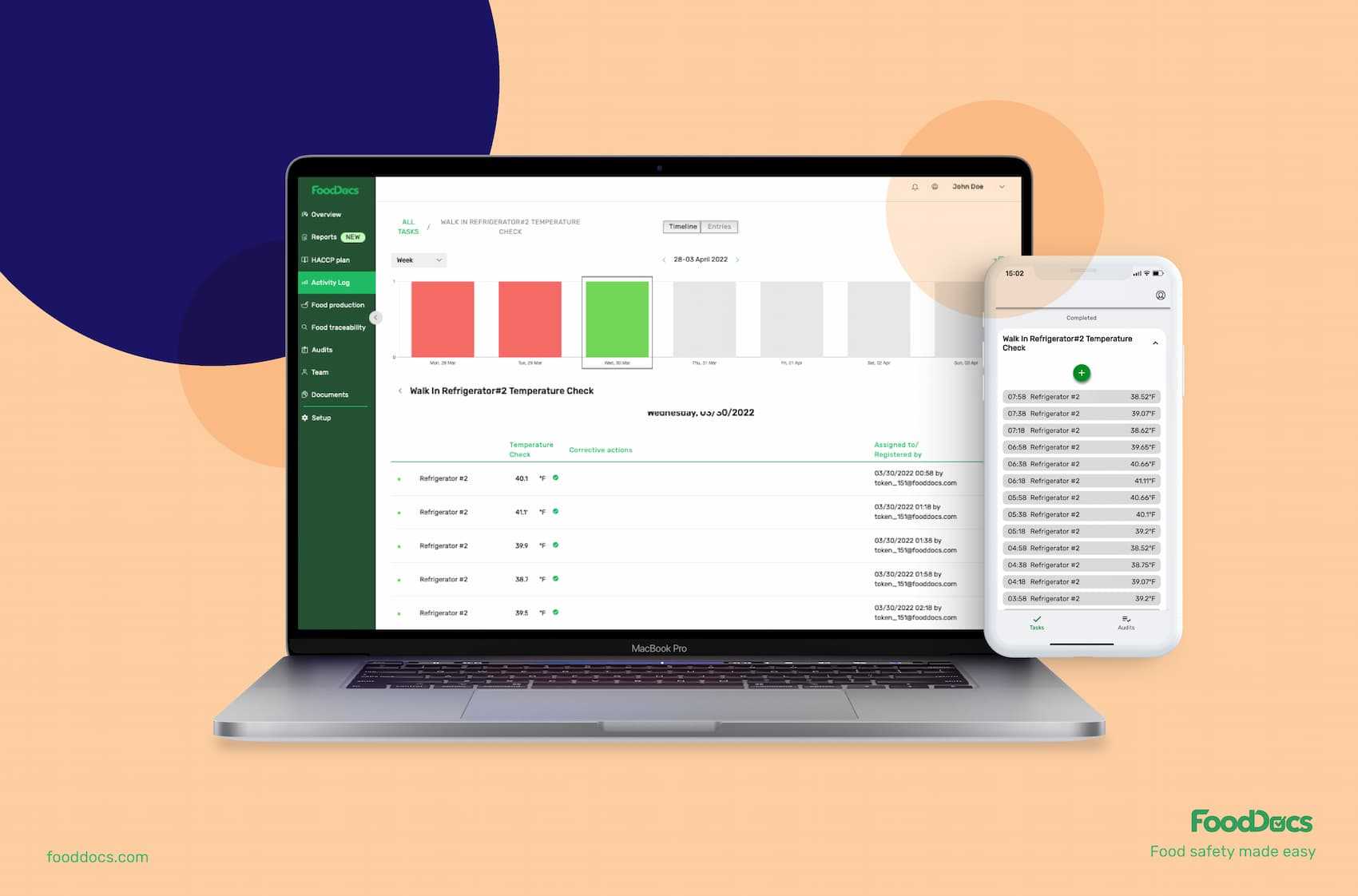
Gone are the days of using paper-based monitoring forms to make sure that your food safety practices are all implemented. In just 15 minutes, you can have your digital FSMS with all the necessary elements of an efficient and effective system. Complete our questions and try our services with a free 14-day day trial and continue maintaining compliance by availing of our services.
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...