HACCP Plan for Restaurant Template: How to Create One (Free Sample PDF)
Get the exact steps to easily write a restaurant HACCP plan or download our free HACCP plan for restaurants template PDF and get compliant even...
Perhaps the most widely recognized approach to food safety management systems in the food industry is HACCP.
Perhaps the most widely recognized approach to food safety management systems in the food industry is HACCP: Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point. The systematic approach consists of seven elaborate steps that aim to address health hazards before they even occur or control them to a safe level as part of your commitment to food safety.
Each step requires a thorough understanding of your establishment profile for a more practical application. The whole HACCP system starts by performing a critical hazard analysis.
Key takeaways
Conducting a thorough hazard analysis is the foundational step in developing a HACCP plan to ensure food safety.
Hazard analysis involves detailed assessment of each potential hazard, including its type, severity, and likelihood of occurrence.
Proper hazard analysis is crucial for the successful implementation of a HACCP plan and to prevent foodborne illnesses.
The HACCP system is a systematic approach that begins with hazard analysis to address health hazards before they become a threat.
Understanding your food business operations thoroughly is essential for effective hazard analysis and critical control point identification.
Engaging a knowledgeable HACCP team is vital for identifying potential hazards and analyzing them effectively.
Comprehensive hazard analysis sets the stage for establishing critical control points and ensuring food safety throughout the production process.
Regular updates and validations of the hazard analysis are necessary to adapt to changes in production processes or new hazard information.
Utilizing digital tools like FoodDocs can simplify the hazard analysis process, making it quicker and more efficient.
FoodDocs' AI-powered HACCP Plan software generates a detailed hazard analysis and a complete HACCP plan in just one hour, enhancing compliance and food safety management.
The safety of consumers and your food supply from potential risks significantly depends on whether your HACCP team can perform hazard identification in your operations and adequately analyze them for critical control point assignment.
The first step in developing a HACCP plan is accurately identifying foreseeable hazards and their analysis. Your HACCP system team performs the process of analyzing a potential hazard which is an essential legal requirement for the success of your HACCP implementation. It is an important prerequisite to performing all other basic principles of the HACCP system.
After conducting the five preparatory steps to making a HACCP plan, your team needs to thoroughly analyze potential hazards before establishing any preventive measures. The objective of this step is to properly analyze the entire food system related to producing your food items.
This analysis includes product formulation control, receiving raw materials, end-product testing, food supply storage methods, packing activity, and the delivery of your products to consumers.

The hazard analysis step of the HACCP plan refers to the process of evaluating the information of potentially present hazards in your operation and deciding which ones require critical control measures. To do this step, food handlers must have extensive knowledge of both their operations and existing information about food safety hazards.
Hazard analysis can be streamlined to become more manageable by consulting the following resources:
Proper hazard analysis is the prerequisite to establishing critical control points in your coherent plan for food safety.
Regulatory standards from agencies such as the United States Food and Drug Administration can offer extensive information about food safety risks. These resources may give you adequate ideas on which hazards can be found in your operations. They may also provide information on the basic conditions and applicable requirements that may encourage the presence of potential hazards and how to control them.
However, the information may take a lot of time to interpret and is often difficult to understand. Do not worry, at the end of this article, you will know how FoodDocs can help you with everything and make the process easier.
Hazard analysis must be performed first because all other HACCP principles depend on its results. Critical control points, monitoring procedures, and corrective actions can only be defined after hazards have been properly identified and evaluated.
Conducting hazard analysis at the beginning ensures that food safety controls are:
Without a thorough hazard analysis, a HACCP plan may overlook significant risks, leading to ineffective controls and increased food safety incidents.
Hazard analysis is performed to identify all potential food safety hazards, whether biological, physical, or chemical hazards, for the production of safe products. The considered hazards in your HACCP plan are prioritized for establishing critical control measures, appropriate monitoring procedures, and subsequent validation activities.
The first step of a HACCP system is ultimately used to minimize the unacceptable health risk of causing any foodborne illness to consumers due to consuming your products.
Health risks may arise from unsafe operating conditions or inadequate sanitary conditions because your hazard analysis was not thorough enough. An incomplete hazard analysis may allow unforeseen hazards to pass a sequence of observations and harm customers because of non-compliant products.
Before conducting a hazard analysis for control of product safety, your food safety team will need to have a detailed map of your whole processing system and any additional activities. Your team will need an accurate process flow chart describing your design process.
Once you have ensured that your food safety team has considered every food operation in your flow chart steps or simple schematic diagram, you're ready to perform your hazard analysis.
Below are the critical steps in conducting a hazard analysis:
Using your detailed block-type flow diagram and existing literature, list all potentially existing food safety hazards in your production process. Categorize hazards based on which point of your actual production process are they likely to occur. This will also help determine the classification of activities needed to control them.
After listing all food safety hazards, start the hazard analysis by describing each hazard based on its category. The common categories of hazards include
In addition, the description must include whether a condition induces the hazard or if it is naturally present in the process step. The description step for hazard analysis must be thorough enough for the HACCP food safety team members to understand the significance of a hazard.
During the previous stage, your team may come up with a very long list of hazards. Note that not all of these hazards will require critical control. Prerequisite programs or standard operating procedures may address some of them. Your team must describe their severity to select only the significant food safety hazards.
The severity of the effects of a hazard can be categorized into five different levels:
Depending on what your HACCP system team and establishment management may agree on, the terminologies may be different as long as they represent the consequences of failure. The severity of a hazard must be based on expert opinion, personal experience, and existing literature on its effects.

In addition to the severity of the hazard's effect, describe how likely is a hazard to occur given the correct conditions of your food production process. This factor will help determine whether the hazard at hand requires critical attention or not. Use the following scale for accurate identification:
The likelihood of occurrence from your entire production process can also become the basis for monitoring frequency. Once all of the necessary information has been collected, you can use a risk assessment matrix to determine whether a hazard will require critical control or not.
Every step of the hazard analysis process is an important approach to food safety and quality control. Proper identification and analysis are essential to keep food production, manufacturing, and service safe. Any chance for product contamination can be properly prevented for consumer safety by analyzing their sources.
When hazards are correctly analyzed through the mentioned critical process, your production team can set up appropriate critical control measures and contingency plans. Continuous monitoring techniques are also essential to prevent loss of control of food safety and unsafe conditions. Likewise, hazard analysis may save your HACCP system team the time and business resources of preparing for a hazard that prerequisite programs and basic food safety practices can address.
Generally, comprehensive hazard analysis is the key to successfully implementing your HACCP system and producing safe food products. It is also essential to prevent foodborne illnesses from occurring by controlling hazards to an acceptable level. Basic safety conditions will help prevent food safety issues from dining in your restaurant or consuming your finished product from a retail food establishment.
A common misunderstanding is that assembling the HACCP team or creating a flow diagram is the first step of HACCP. While these activities are required preparatory tasks, they do not replace hazard analysis as the first official step of the HACCP system.
Regulatory authorities and auditors consistently evaluate hazard analysis as the starting point of HACCP implementation.
To help you visualize how a hazard analysis is conducted. Let us take a typical restaurant as an example. In a restaurant, raw material receiving, preparing, and cooking food for consumption are all essential processing methods. Below is a hazard analysis example of these food operations and manufacturing practices:
The hazard analysis sheet above is a typical hazard analysis summary for a restaurant business in a food chain. Of course, a complete analysis would show more defined hazard identification, including a complete description of how and at what environmental conditions these hazards occur.
Other workplace hazards and food safety risks such as the transmission of illness from unhealthy employees, cross-contact with allergens, unsafe food safety practices, and improper organization of food supply may be included.
To help facilitate hazard analysis and produce safe food, your HACCP system team can use numerical values to designate the likelihood and severity of the hazard. A 1-3 scoring system is used for narrower hazard analysis in other contexts. Use this scale to determine whether the hazard is significant enough to require critical control or not.
Fulfilling the principles of hazard analysis takes a great time in the HACCP food safety plan-making process. Not only does it require much expertise, but also a fundamental understanding of processing stages.
At FoodDocs, we offer the fastest way analyze your hazards. With our digital solution, you can get a complete hazard analysis and all other areas of a HACCP food safety plan in just an average of 1 hour.

Using our HACCP plan builder, we can automatically generate a credible hazard analysis document of all your food processes. It satisfies all requirements for hazard analysis, including:
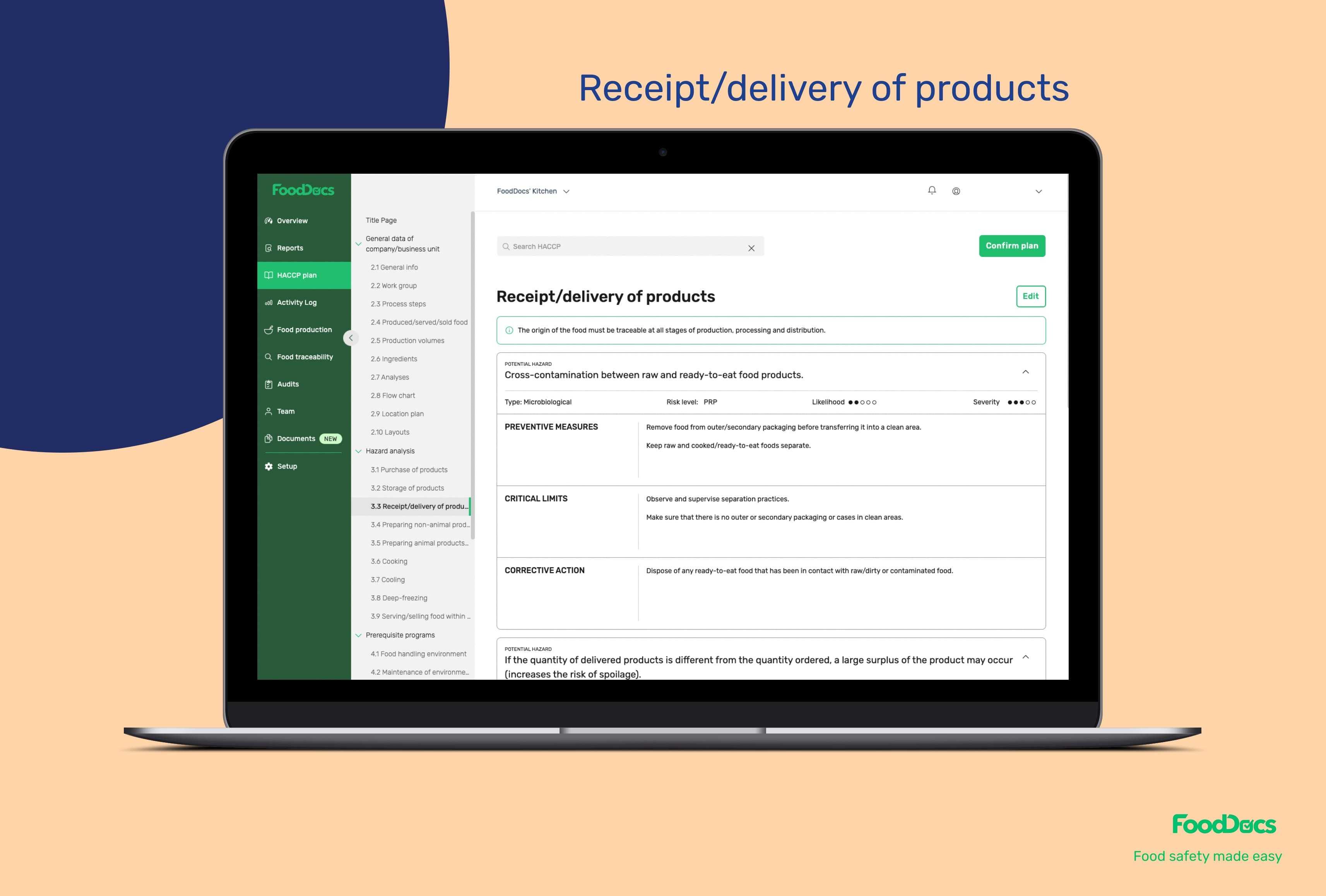
In addition, to complete the identification of hazards and hazard analysis, our digital solution also covers the following HACCP food safety plan critical stages:
Powered by artificial intelligence and a machine learning program, our built-in HACCP plan builder uses information from our data bank and builds a complete food safety plan for you. All you need to do is answer a few questions describing your operations to us, and our system will compile the HACCP Plan document. With our digital solution, you can focus on your other business activities.
Our team understands how some operations and documents are unique, and the likelihood of occurrence may vary from one business to another. As such, our digital solution can accommodate customization.
Can't find a particular hazard analysis document from the HACCP food safety plan our system generated? You can easily set up potential hazard analyses using our solution with just a few clicks.
Get the exact steps to easily write a restaurant HACCP plan or download our free HACCP plan for restaurants template PDF and get compliant even...
Get a clear and complete breakdown of the most common Critical Control Point examples in HACCP for biological, chemical, and physical hazards.
The HACCP allergen control program is one of the crucial prerequisite programs of an HACCP plan. These are the key components and goals of using one.