Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Bacterial contamination can come from many different sources, but it can always be avoided by proper food safety practices. Food and bacteria will always come together and as food handlers, what you can only do is to control their presence and make their environment inhabitable to produce safe food. Protecting your consumers from foodborne illnesses is a top priority for any food business.
Food products become unsafe for consumption when bacterial contamination occurs. Bacterial species such as Staphylococcus, Campylobacter, Clostridium, Listeria, E.coli., and Salmonella cause the majority of the infectious risk of foodborne illnesses around the world.
Strict food safety practices are crucial to avoid bacterial contamination in food products.
Bacterial growth is influenced by factors such as acidity, moisture, temperature, oxygen levels, and the initial microbial load.
Contamination can occur quickly, within 20 minutes to 2 hours under favorable conditions, making food unsafe for consumption.
Common bacterial pathogens like Staphylococcus, Campylobacter, and E.coli cause a significant portion of foodborne illnesses in the United States.
Proper food safety practices are key to preventing bacterial contamination and protecting public health.
Understanding the sources and conditions favorable for bacterial growth can help food business owners implement effective preventive measures.
Maintaining the correct food temperature and ensuring good personal hygiene are fundamental practices to reduce the risk of bacterial contamination.
Regular training and strict adherence to food safety protocols can significantly mitigate the risk of bacterial growth and foodborne illness.
Food safety agencies emphasize the importance of these practices to prevent foodborne diseases and ensure consumer safety.
Food business owners can use FoodDocs to make food safety management easy.
Scientists have estimated that at least 39% of foodborne illnesses in the United States are caused by bacteria, whereas the rest are caused by any viral contamination and parasites. These bacteria can travel from one food to another because of their close relationship with the food, food handler, and food contact surfaces.
As a food business owner, you can contribute to protecting public health and preventing food recalls by knowing what is the best way to avoid bacterial contamination.

Bacterial contamination is a type of biological contamination in which bacteria is unintentionally introduced into a food material and causes it to spoil. The presence of bacteria can cause foodborne illnesses to consumers especially for risk groups like pregnant women, children, the elderly, and individuals with autoimmune disease. Biological contamination can be divided into two major classifications: food intoxication and food infection.
Food intoxication is microbial contamination caused by bacteria that can multiply fast on food and produce bacterial toxins that cause the negative reaction of illnesses. It is the most commonly caused by Staphylococcus aureus, Clostridium perfringens, and Bacillus cereus. These bacteria are most associated with poultry meat products, low-acid canned foods, and foods rich in starch such as rice, respectively. Food intoxication causes symptoms that include upset stomach, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Contrary to food intoxication, food infection is caused by the bacteria themselves and does not produce toxins. These bacteria can cause foodborne illnesses once they greatly multiply on the food and are consumed by a customer. Bacteria that can cause food infection include Salmonella, Listeria, and Shigella.
The detection of bacteria and contamination in products can produce obvious changes in the food that they contaminate at a certain point. Contaminated food by kitchen germs can exhibit the following characteristics:
Although, you have to keep in mind that not all spoiled foods will show obvious signs right away. To avoid and control bacterial contamination and observe for any signs.
Bacteria double in number in a very short time, commonly around 4 to 20 minutes. The initial bacterial load of food materials can dictate the rate of spoilage especially around the temperature danger zone which is 40°F–140°F or 4°C–60°C. Depending on the surrounding environment, the contaminating bacteria, bacterial load, and the food material, bacterial contamination can occur to unsafe levels anywhere between 20 minutes to a day.
Here are other related questions you might be interested in:
Food can become contaminated once it comes in contact with previously contaminated food or any unsanitized food contact surfaces or if it stays in conditions that favor bacterial growth. Transmission of pathogens can occur upon contact or within 20 minutes, whereas spoilage can occur within the first 2 hours.
Under the right conditions, bacteria can double in number every 10 to 20 minutes. Imagine this, if you had 2 cells of a bacterium, you will have 4 cells after two minutes and 16 cells after an hour. This is the reason why pathogens can easily cause spoilage in a short time.
Some of the most common bacterial contaminations and outbreaks of infection are caused by the bacterial species Campylobacter, Staphylococcus, E.coli, Listeria, and Salmonella. The symptoms of foodborne illnesses caused by these microorganisms are almost the same with the most common symptoms being nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and stomach cramps. The degree of symptoms experienced by customers depends on the contamination level of food.

Hands down, the best way to avoid bacterial contamination is to always observe food safety practices as part of your food safety program. As we have mentioned, the presence of bacteria on food and the risk of bacterial contamination will always be present. Therefore, the best way to keep producing safe food and protecting your consumers' health is to prevent pathogenic bacteria from further multiplying to a point when it can cause severe effects.
Kitchen germs such as bacteria can come from a mobile sources such as food handlers, cooking utensils, equipment, food contact surfaces, and other food materials. A food handler can control the spread and growth of bacteria with very simple practices and an effective food safety program. Some of these food safety practices include the following:
The first step in avoiding bacterial contamination and producing safe food is to know how it happens and have a better appreciation of its potential effects. Simple bacterial contamination can cause widespread outbreaks of infection and can even kill consumers. The most potent food poisoning that can cause a fatal outcome is known to be caused by Clostridium botulinum. It only takes 1 to 2 cases of foodborne illnesses caused by this bacteria to declare outbreaks of infection.
Most foodborne illness-causing bacteria are found in soil as it is a common source of microbial contamination. As such, raw food such as raw meat, root crops, and other agricultural products are most likely to have a high bacterial count. Choose a supplier that also applies strict food safety standards such as in terms of storage conditions, processing, and delivery to only produce safe food.
Transmission of pathogens can occur at any point in the food supply chain. During storage, any food unit can get contaminated by improperly joining any cooked or ready-to-eat food and those that will require more extensive cooking on a single shelf. While it is true that cooking treatment will reduce bacterial contamination, if a food unit that will only be processed lightly gets contaminated, the contaminating bacteria will have more chances to survive. Similarly, ready-to-eat foods would only need reheating. Contamination after cooking can make further processing less effective. Storage conditions such as applying the wrong storage temperatures can encourage the unwanted growth of bacteria. Make sure that you store your foods in either a refrigerator unit or freezing conditions. Maintain a storage condition with consistently low temperature and prevent cold food from thawing which will encourage bacterial growth.
The presence of bacteria can be minimized when the kitchen staff practices good personal hygiene options. Bacteria can come from dirty fingernails, soiled clothes, or untidy hair. Make sure to regularly instruct kitchen staff to observe and control proper personal hygiene options. This instruction includes reporting any potential sickness among the kitchen staff which can cause viral contamination or the spread of the virus among food workers.
Within the kitchen, train kitchen staff to be aware of their surroundings to prevent transmission of harmful bacteria from cross-contamination. Use separate utensils, cutting boards, and gloves to handle raw and cooked foods to avoid cross-contamination. Regularly clean food contact surfaces with hot water or soapy water and a clean cloth. Observe proper handwashing before and after food service operations. Use soapy water to wash down any kitchen germs on your hands.
Food wastes are a great culture medium for bacterial growth as well as attractants for pests. Their presence increases the risk of food poisoning. Pests can carry bacteria from wastes and then to food contact surfaces or foods and spread the contamination risk. They are also capable of bringing other pathogens such as a virus and spreading it within the service area. Make sure to regularly remove trash bins and food waste from the kitchen area.
One of the last lines of defense in terms of minimizing the presence of bacteria is properly cooking your food. Standard cooking temperatures established by food agencies such as the Food and Drug Administration in the United States are based on the most effective time and temperature combinations to inactivate kitchen germs.
Despite this, a food handler must not be complacent that the foods will be processed and that the risk of food poisoning will be completely removed. Toxins produced by some bacteria cannot be removed by heating. However, if the bacterial count or contamination level is already too high, the cooking process may become ineffective.
Similar to the principle of avoiding any gastrointestinal illness, prevention is always better than cure. Any foodborne illness caused by kitchen germs can be easily avoided with proper knowledge and strict food safety practices. As a food business owner, ensure that your food workers are well oriented when it comes to these practices.
Additionally, implement a food safety program, that efficiently and effectively monitors all food service operations. A monitoring system will help ensure that all conditions are met regarding food safety compliance. At FoodDocs, we have taken this step to another level. Now, you can get an intuitive digital Food Safety Management System with automatically generated monitoring logs. Learn more about it at the end of this reading.
Here are a few related questions you can use to further understand this section:
Properly training staff with the correct food safety processes and orienting them with the significance of food safety and contamination can ensure the prevention of cross contamination in a food business. When food employees understand what they are dealing with and what they are trying to prevent, they would have a better appreciation of the practices and apply them meticulously.
To prevent food poisoning, practice the basic food safety practices which include the following:
For customers, you can minimize restaurant risks by reviewing the establishment's reviews, checking for a food safety permit, and observing the establishment prior to dining.
For food business owners, the best way to minimize restaurant risks is to implement a comprehensive food safety management system.

The rate at which kitchen germs grow and multiply is not the same all the time. It can vary depending on the conditions at the time of contamination. In knowing what is the best way to avoid bacterial contamination, these risk factors can play a great part. Some of the most prominent factors that affect the growth of bacteria include:
The infectious risk of food poisoning and food recalls increases when multiple favorable conditions are present. As such, food safety practices must be designed based on the food service operations and food products in a food establishment. This is what our machine-learning system at FoodDocs prides itself in. You get an automatically generated digital FSMS tailored to your food business in mere minutes.
This is what our Food Safety Management System at FoodDocs is all about. Based on the information about your food business that you provide us, our software automatically creates a digital FSMS that fits your operations. All generated documents and operations will be designed to control bacterial contamination and other food safety hazards in your food establishment.
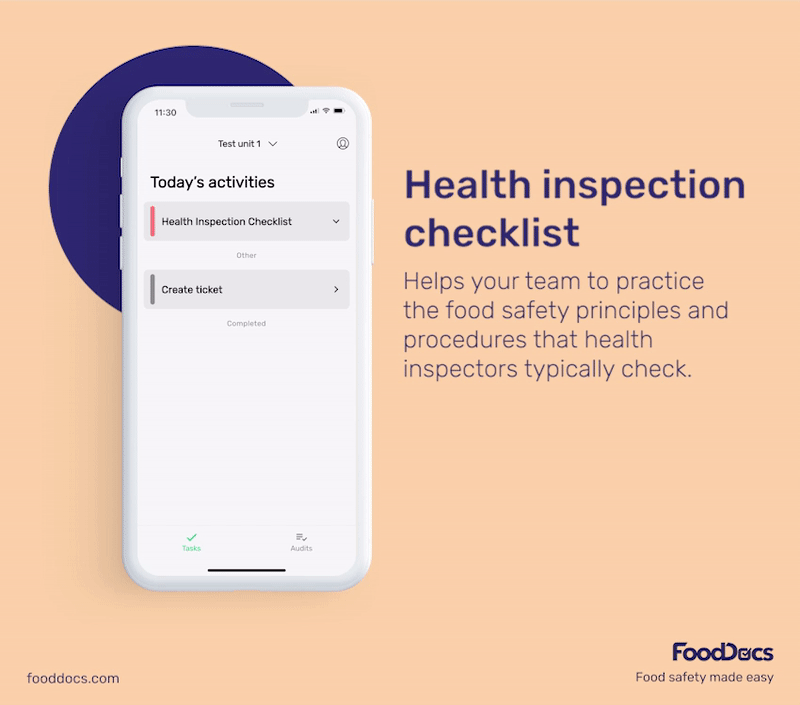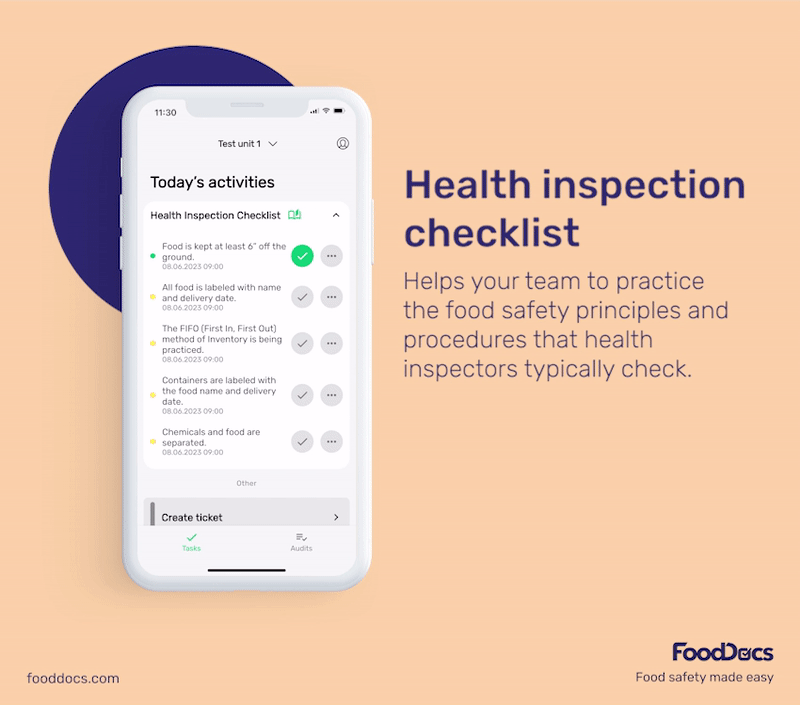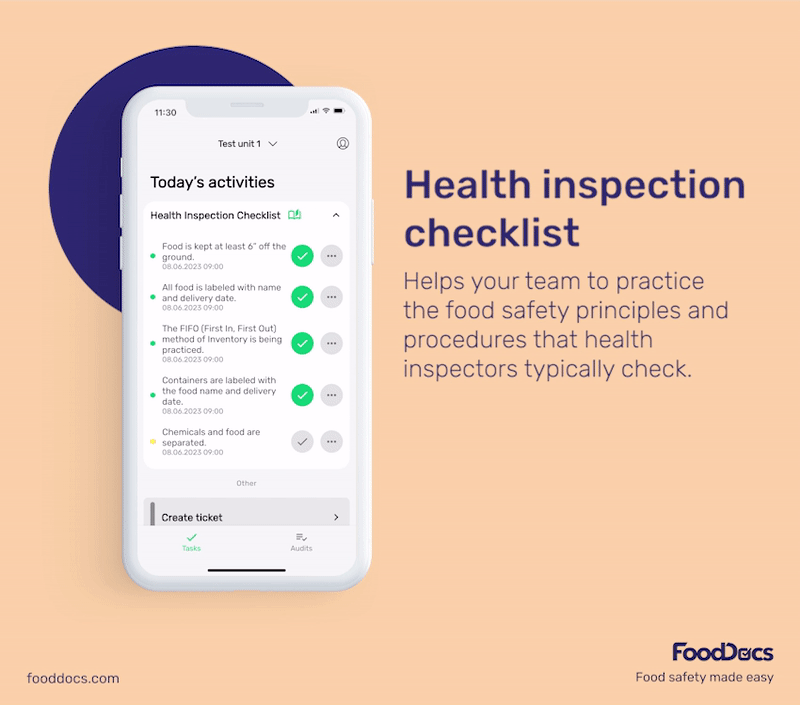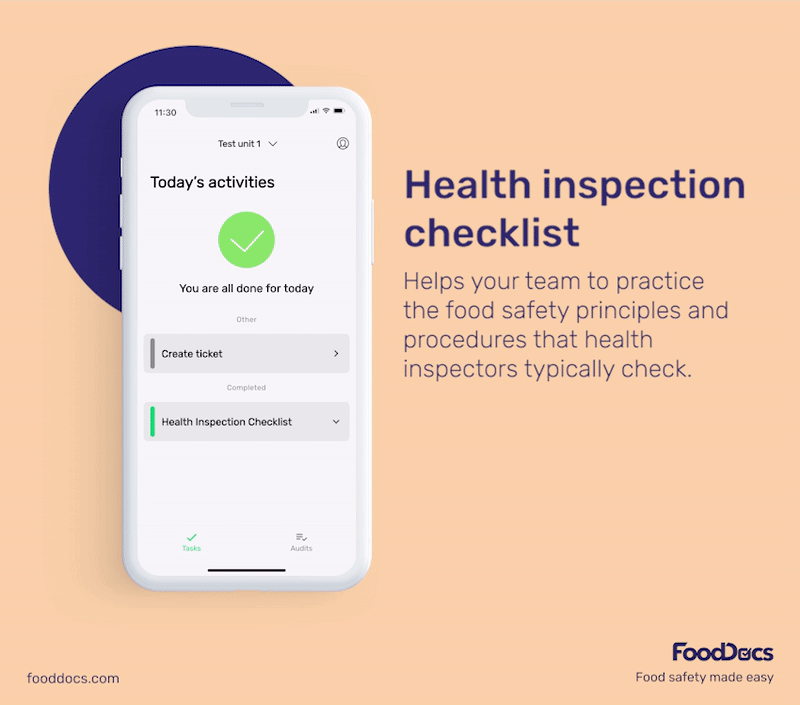
To get a better idea of what our food safety software offers, here are some benefits you will get once you join us at FoodDocs:
These monitoring logs can help you prevent and control the multiplication of bacteria more efficiently. To help food handlers, each monitoring log is equipped with detailed instructions on how to perform and monitor the task more efficiently.

Did we mention that switching to our Food Safety Management System will only take 15 minutes? That's right! In just an average of 15 minutes, you can complete and comprehensive digital FSMS for your food business.
Control the growth and spread of harmful bacteria and other food safety hazards in your food business with our digital food safety management system. Become an addition to our more than 10,000 satisfied customers and build a more efficient food business. Try our software free for 14-days and make all your food safe to eat.
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...