Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Chemical contamination of food is described as the presence of an unwanted chemical substance.
Chemical contamination of food is one of the major food safety hazards in the food industry. This type of contamination poses a great health risk to consumers as it can cause both immediate and long-term effects. The first step to preventing foodborne illness and food poisoning caused by chemical contamination is understanding which contaminants are under this category.
In a recent food and health survey published in 2021, consumers ranked the presence of chemicals in food as a top food safety concern. This survey shows that the lack of common information on chemical ingredients may be a big problem for consumers.
In this article, we discuss in detail the nature of chemical contamination, its sources, and how to control them in a food business setting.
Chemical contamination is the presence of unwanted chemical substances in food or feed. These substances can be synthetic or naturally occurring and can cause negative effects on human health when ingested.
The unintentional presence of generally considered safe chemicals in food is considered a form of contamination. Chemical contamination can be indicative of the food processes applied to raw materials.
For example, the presence of exceedingly high contamination levels of contaminants, such as pesticides and other dangerous chemicals, on food ingredients can indicate malpractice or non-compliance to approved food safety regulations during the growing periods.
While not all chemical contamination poses an immediate threat to human health, some chemical hazards in food can accumulate in the body and cause long-term adverse effects.
Learn more about the two other types of food contamination, biological and physical, from our Food Safety Blog.
Chemical contaminants are inorganic or organic compounds that are toxic to humans and can cause harm when present in foods.
This type of contaminant is one of the main food safety hazards that can make food unsafe for consumption.
Chemicals that can be considered food contaminants are common in any commercial kitchen. Cleaning chemicals, common additives, and preservatives can come in contact with food through cross - contamination and result in foodborne illnesses. Chemical contaminants can also be sometimes found as drinking water contaminants, which pose a significant threat to your food business.
Some chemical contaminants may be naturally present in foods for human consumption and can be removed through processing. Chemical contaminants can be non-harmful at low levels. Examples of these natural contaminants include the antinutrients in soybeans and glycoalkaloids in potatoes.
The example can be removed by simply soaking and peeling the soybeans, whereas glycoalkaloids can be removed through adequate cooking enough to achieve safety but maintain food quality.
In contrast to removing chemical contaminants through processing, some examples of chemical contamination in food are produced through over-processing. Toxic chemical substances, such as acrylamide, are formed when high-protein foods are exposed to extreme heat for a prolonged time.
This process contamination commonly occurs in overprocessing fried foods such as french fries, potato chips, and processed meats. Food processing contaminants are common when overprocessing and unregulated operations are present.
Any chemical, whether organic or inorganic, that is unintentionally present in a food product is considered a chemical contaminant.
Some of the most common chemical food contaminant examples include:
Although chemical contamination can have vital outcomes for consumers, not all chemicals are bad. Chemicals help preserve food safety, prolong shelf life, and reinforce a clean environment for processing food products. Some food-safe chemicals can also be considered contaminants when improperly used.
In some countries, contamination by chemicals is permitted if the level of contamination is within the approved limit. The threshold level may vary among developed and underdeveloped countries depending on their daily intake.
An example of this case is the allowed level of nitrate in drinking water. In the U.S., a maximum level of 10 mg/L of nitrate in water is considered safe. On the other hand, the U.K. government allows 50 mg/L of nitrate in water. Exceeding established thresholds makes these chemicals toxic contaminants and can manifest dietary implications.
Not all chemical contaminants pose a significant food safety risk in small levels in food. For example, human exposure or direct contact with very low heavy metal concentrations may not have rapid potential health effects or cause mild gastroenteritis. Despite this, accumulation through aggregate exposures to food contaminants can cause adverse health effects.
Some of the mentioned chemical food contaminants, such as cleaning solutions, flame retardants, and preservatives, are common items in a food business facility. Food safety plans consisting of proper handling and regular monitoring are needed to prevent these harmful substances from contaminating food.
Using comprehensive food safety plans, sources of food contamination can be immediately identified and addressed, and critical control points can be established accordingly.
Not sure how to analyze food safety hazards in your business? Use our free hazard analysis template as a guide.
As mentioned, chemical contaminants can either be inorganic or organic contaminants. In addition to this classification, there are other approaches to classifying chemical contaminations of food. Each classification consists of a wide range of chemical contaminant examples and can cause a wide range of human health effects.

The most general classification of chemical contamination in foods is based on their sources within the food chain cycle.
Contamination with respect to environmental conditions involves chemical pollutants found in drinking water sources, air, or soil that may have resulted naturally or through environmental issues. Environmental pollutants, such as lead and other metals in agricultural soil, cadmium in rice crops, microplastics in the marine environment, agricultural chemicals in farms, and even radioactive elements, are widespread.
Natural chemical contaminants originate from the food ingredient or are naturally produced. This type of contamination includes naturally occurring toxic contaminants in plant materials, such as alkaloids, and toxins from microbiological contaminants that can produce adverse human health effects. A common example is legumes, which have to be always handled carefully and processed thoroughly because of their inclusion of natural contaminants.
Heavy meta contamination in the environment can be easily transferred into the food we use for human consumption when improperly regulated. Environmental contaminants can be sourced from agricultural processes and industrial chemicals such as pesticides, fertilizers, and water treatment operations that contaminate fresh produce or cause contamination in drinking water and soil.
Chemical contamination can also be created by processing food. For example, when frying potato chips or french fries, by-products named acrylamide and furan are produced. Acrylamide is a known carcinogenic food contaminant and can be used as an indicator of overprocessing food products.
Adulterants are chemical compounds that are intentionally added to the food product to replace a missing substance or improve the overall food quality or shelf life of food. These unwanted chemical compounds are undeclared and are considered a violation of food labeling laws.
The mentioned major types of chemical contamination can enter the food production chain at any point. Chemical contaminations are also often categorized as intentional or unintentional. Intentional contamination includes unwanted chemical compounds added to the food as a form of terrorism or to mask an unwanted character. On the other hand, unintentional chemical contaminations are those that are introduced through the environment of the food.
While some types of chemical contamination are hard to eliminate or avoid in foods completely, regulatory measures for the minimum and maximum contaminant levels are set to protect the health of consumers from adverse health effects.
Chemical contamination in food may occur from raw sources of food materials, processing methods, food packaging products, and agricultural products.
There are 5 common sources of chemical contamination in food that enter the food supply through the following sources:
An example is an alkaloid produced by some plants, such as potatoes, which can induce digestive, neural, and immune system problems when consumed excessively. This substance is part of the defense mechanism of plants to protect themselves from herbivores. Dietary exposure factors to some of these toxic compounds can cause serious problems.
These can become environmental pollutants and cause a wide range of food safety issues. Some plants can act collect toxic chemicals, heavy metals, or antimicrobial residues from contaminated soil and water. As such, monitoring and ensuring that your food supply follows food safety regulations is a must to avoid contamination of foods.
The water and soil used to produce food supply must be regulated and monitored to ensure they are within food safety standards and contaminant levels are low.
In the same light, food chemical contamination can also occur due to improperly removed cleaning solutions or food contact chemicals on equipment and surfaces.
Additionally, food can also be contaminated by chemical by-products produced during processing. The FDA summarized some of the most common process contaminants in foods resulting from heating and fermentation.
The design of food processing lines must consider critical limits and maximum levels to avoid producing toxic by-products and similarly ensure a hygienic design for cleaning and sanitizing surfaces.
When unregulated, chemical compounds from food containers, such as metals, aromatic hydrocarbons, melamine, and food contact plastics, can migrate into the food being held. Although migration from food contact packaging is uncommon, some studies show the iron migration of compounds from cans into foodstuff during storage. Frequent or daily exposure to chemicals in food packaging can cause cumulative human health effects.

Another type of intentional adulteration is when food handlers deliberately add extenders, preservatives, or food additives and contaminants to increase bulk size or improve food quality without declaring the additional ingredient.
Some chemical contamination or toxic compounds may produce immediate potential health risks for consumers, whereas others don't.
When designing a chemical storage area for a commercial food business, food safety and the safety of the employees should be the top priority.
While there are several features to consider for a good chemical storage area, food business owners must first consider a good ventilation system.
A working ventilation system helps maintain a safe environment by preventing the accumulation of hazardous vapors, fumes, or gases. Adequate ventilation ensures that any potentially harmful substances are properly dispersed, reducing the risk of inhalation or exposure to chemical hazards.
A good ventilation system must have the following characteristics:
A proper ventilation system and a dedicated storage area are critical for any type of food business. This particular location will be used to store all non-food-related chemicals, such as cleaning agents, which could be harmful when they contaminate the food.
In addition, the storage area will also be used to house tools and equipment used for cleaning and chemical contamination prevention during accidents.
In addition to these two features, here are some more factors to consider when building a chemical storage area for food businesses:
Chemical contamination or toxic compound is more likely to occur when food handlers do not practice proper food handling procedures and the operations lack proper monitoring of food materials.
All food businesses must have appropriate food safety plans to control chemical contamination.
Excessive use of different types of food contact chemicals for cleaning and agricultural processes can lead to contamination of drinking water and food materials. In addition, incorrect food sanitation operations and schedules can increase the risk of chemical concentrations in water. Read more about the chemical contamination of water below.
Food handlers who are not practicing proper sanitation and hygiene can cross-contaminate food products and spread organic pollutants. Personal care products used by food handlers inside the food facility can contaminate the food supply when unregulated.
These cases can be significantly reduced if your food business uses a comprehensive food safety management system. At FoodDocs, we provide an intuitive monitoring solution to help your team reduce the likelihood of causing chemical contamination in your food business. Use digital Food Safety Management software to automatically generate your team's most important food safety monitoring logs and checklists.
Chemical contamination in food can cause a variety of foodborne illnesses. Some chemical contaminants can cause acute or rapid adverse health effects on affected individuals, whereas others may take time to manifest. Physiological effects on health may sometimes be very obvious.

Some symptoms and acute effects of foodborne infection from human exposure to chemical contamination may include:
Any of these symptoms will require medical attention to minimize the potential health risks.
Chronic effects of chemical contamination due to repeated human exposure and dietary intake can cause diseases such as cancer and renal, hepatic, and neurological syndromes.
The symptoms and toxic effects of chemical food contamination examples may vary depending on their origin and contaminant concentration. Chronic foodborne diseases are usually associated with the effects of pesticides and other toxic substances.
Water is one of the most widely used materials in any food business. It is used in almost all of the operations related to food preparation. As such, it is a very fast way to spread contamination in the workplace. Once contaminated with chemicals, the water system can cause a widespread problem.
Chemical contamination of water refers to the presence of toxic chemical substances in the water system. Contaminants in drinking water can cross-contaminate other areas and food materials during food preparation.
The concerns surrounding the contamination of water systems are critical and can be addressed by food businesses through regular water testing.
Concerned government agencies highly regulate chemical components of foods. Before a chemical compound is allowed to be used in food production, it undergoes several stages of screening.
To ensure that approved chemicals and present common chemical contaminants are always regulated, food safety and health agencies set up regulations.
Below, we discuss which agencies are responsible for regulating chemical contaminations in foods and their main tasks.
In the U.S., the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the U.S. Department of Agriculture are mainly in charge of food safety and regulating the U.S. food supply.
The health agency conducts safety determinations for the potential risks of chemicals of concern, establishes tolerance guidelines, and provides safety rules for food businesses.
In particular to chemical contaminations, the FDA monitors chemical contaminants and the application of pesticides in food.
Specifically, the FDA's task in controlling chemical contamination includes the following:
The assessment of chemicals is then communicated to food business owners.
The Food Standards Agency (FSA) in the U.K. assumes the responsibility of regulating chemicals in foods. The agency conducts research and monitoring to enhance controls over chemical contaminants.
In particular, the FSA's role in controlling chemical use and contamination in the food industry can be summarized into the following:
While food safety agencies play a critical role in regulating contaminants, businesses must also execute their responsibilities. Food manufacturers and business owners are individually responsible for following food safety regulations on chemical contamination.
On a federal level, the United States FDA and European Food Safety Authority regulate and monitor chemical contaminants in foods. The safety agencies employ monitoring programs and regulatory compliance for naturally occurring toxins, agricultural products, and other chemical contaminants to reduce the risk of human exposure to food contaminants and their potential dietary intake and adverse health outcomes.
The detection of chemical contamination is often the task of food manufacturers. Suppliers of raw foods to food businesses are required to declare the results of their chemical analyses upon the delivery of their products for official control purposes.
Detection of chemical contamination in food is mostly done through analytical methods, which give precise and accurate detection levels based on a standard.
Other detection procedures that yield immediate results include testing kits and smart devices. These procedures can help food businesses identify if food is contaminated and can be further analyzed through more thorough procedures in a laboratory.
Contamination measurements in drinking water are done through rapid methods and kits, such as test strips with known standards. Although very general, such tests can give food handlers an idea if there are contaminating products in drinking water.
Food handlers play a great role in preventing the risk of causing chemical contamination of food. Proper food sanitation and handling can significantly reduce the occurrence of chemical contamination.
Here are some common food safety guidelines that you can do to prevent causing chemical contamination or control the implications of food contamination in your food business:
Several factors affect the portability of water. Chemical contaminations can work their way into any water system in different ways.
Any of the following sources can contaminate your water system:
Water testing and monitoring are critical for any food business. It allows them to consistently ensure that the water used inside the kitchen operations will not contaminate other areas or ingredients inside the facility.
Integrate your Water Testing Logs into our smart Food Safety Monitoring System. Using our smart solution, you can get an automatically generated Water Testing Log which you can use to input test information from third-party laboratory analyses.
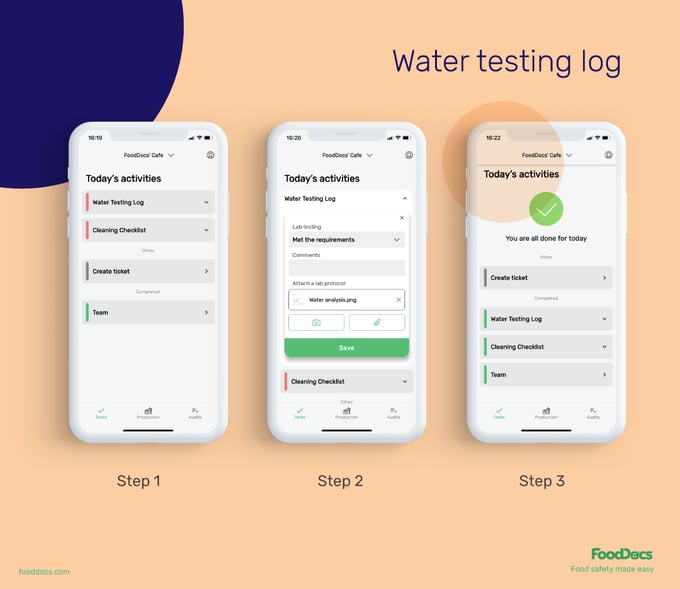
Water testing log from FoodDocs
The effects of chemical contamination on drinking water may depend on the nature of the contaminant, the level of exposure, and the amount of chemical contamination.
Consuming dangerous levels of organic chemical contaminants can cause acute effects, which include vomiting, diarrhea, and headaches. It can also cause long-term effects that could lead to reproductive problems, cancer development, and immune system diseases.
In addition to health issues, chemical contaminants can significantly change the taste, smell, and appearance of foods. This contamination can be offensive to customers and make consumer products unacceptable.
The presence of chemical contamination in food has remained a top concern among consumers. The human health effects of chemical contamination can lead to serious food contamination incidents and be very costly for your food business.
The key to avoiding such food safety issues is ensuring that chemical contaminations are controlled or eliminated from the source of food contamination.
The best solution to address chemical contamination of food and all other food safety concerns is to use a digital solution that offers intuitive features for your operations. At FoodDocs, this solution is exactly what we provide to food businesses.
You can get a digital Food Safety Management System to help control operations related to monitoring chemical contaminations in just 15 minutes. With our digital solution, you can get the most important monitoring logs and other intuitive features that will help you improve efficiency.
Here are some of the most significant features that can help you control chemical contamination in your operations:
Master Sanitation Schedule from FoodDocs software
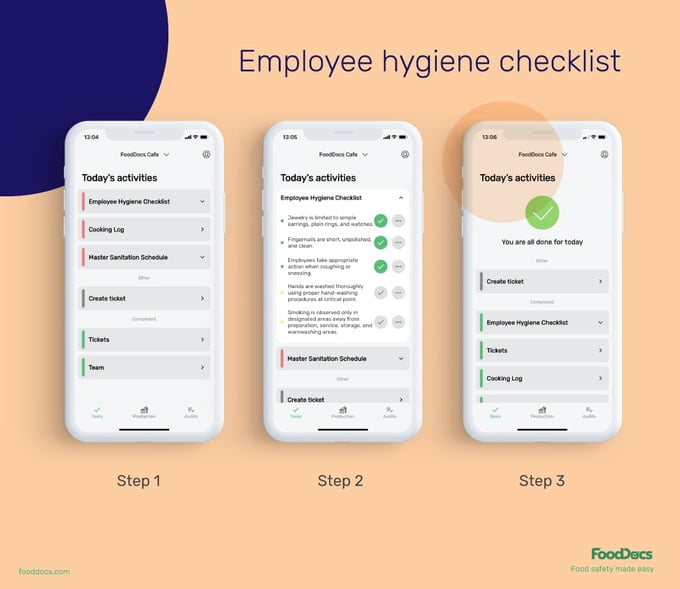
Employee hygiene checklist from FoodDocs software

Water testing log from FoodDocs
In addition to features that will help food handlers control monitoring procedures, our digital solution also offers features that can improve the efficiency of managing food safety operations.
In addition to the quick generation of a comprehensive digital Food Safety Management System, opting for a food safety solution in a digital platform can be your first step to becoming more sustainable. With FoodDocs, you can consistently improve food safety compliance while positively impacting the environment by switching to a paperless system.
Our digital solution complies with all food safety regulations and provides references to the most applicable standards based on your operations and location. What makes our system flexible is that you can customize monitoring logs to improve or tailor them to your operations better.
Discover and experience more of our features and services using our free 14-day trial and become one of the 30,000 customers enjoying food safety compliance using our digital solutions.
Need more information about chemical contaminants in food? Here are some of the most frequently asked questions about this topic.
Chemical contamination is a major type of food contamination characterized by the presence of harmful chemicals in food that can cause health problems when consumed.
Some chemical contamination examples in water include the following:
Chemical contaminant sources can include the following:
Any unwanted and unintended chemical substance that is present in food or in excess of application in products is considered a chemical contaminant.
How can food service establishments minimize chemical contamination?
Food service establishments can implement simple organizational operations to help control chemical contamination:
Some of the most harmful chemicals that may contaminate food include the following:
Foods are made up of chemicals. Some of the common chemicals that are completely safe for consumption and are found in foods include the following:
Remember that not all chemicals are bad for you. Even potentially harmful chemicals can be safe in very low amounts.
Here is a list of harmful chemicals in food that should be avoided in exceedingly elevated concentrations as they may cause health problems:
Remember that all foods are made up of chemicals. Some foods are added with other food chemical substances to improve their flavor and shelf life. Some of the foods that may have more levels of chemicals than others include processed meats, soft drinks, ready-to-drink fruit juices, and canned foods.
While not all chemicals in food are harmful, some can cause negative direct effects on health when present in large quantities or consumed over a long period.
Exposure to contaminants in food can be harmful if they are toxic at high exposure levels, affect bodily functions, cause food poisoning, cause chronic illnesses, behavioural effects, or cause developmental problems. They can also have ecological effects when uncontrolled properly.
Consumers with weakened immune systems are more prone to negative health effects from chemicals. Exposure to food additives may trigger allergic reactions.
It's important to note that some chemicals only become harmful when added in high amounts, breaching maximum levels, or exposed to unwanted conditions. Always consult reliable sources regarding the safety of chemicals.
All sanitizing chemicals must be stored away from the food preparation area. A dedicated storage area for cleaning materials must be present in any food business. Avoid storing hazardous chemicals in compartments higher than foods, and ensure that the area is well-ventilated. Only authorized food workers must be given access to the storage area.
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...