Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Thermometer calibration is a critical task to ensure that cooking and low-temperature storage, are done safely.
An accurate food thermometer plays a significant role in maintaining food safety in any food establishment. Whether for low-temperature storage or thorough cooking, accurate temperature readings are significant.
Thermometers are very common kitchen equipment where they are used almost every day during service. With frequent use, thermometers lose their accuracy over time and must be calibrated. As such, thermometer calibration must be regularly performed.
In this article, learn about the different ways how to calibrate your thermometer and why it is important to do so.
With an inaccurate reading, the purpose of these operations becomes insignificant and defeated. Food safety hazards, particularly pathogens, may survive and continue to grow if the target temperature reading is off by a few degrees. Such reasons make thermometer calibration an important part of food safety operations. No need to worry because this task is easy and does not take too long.
WHAT WE'LL COVER:
Thermometer calibration refers to the process of reconfiguring a thermometer for it to produce accurate readings.
Thermometers, like other equipment, fall out of their standard specifications due to frequent use or time. Inaccurate thermometers can result in misleading results.
These results can cause over or under-processing, which can be significant for the safety or the quality of the food product.
Food safety operations such as chilling, cooking, and holding are temperature-dependent. For example, different types of meat require a particular target internal temperature that will make the final product safe from food safety threats.
These target internal temperatures are based on the most effective temperature in eliminating pathogens and ensuring food safety. They can only be effective if reached accordingly with the help of a thermometer. A few degrees below the target temperature will increase the risk of causing foodborne illnesses.
It is important to note that the calibration process can differ for every type of thermometer. Manufacturers and distributors often provide calibration instructions and kits to food businesses.
Regardless of the type of thermometer, calibration is a must to produce reliable and accurate temperature readings.
Use FoodDocs' smart Food Safety Management System with a digital Calibration Log. Record all calibration readings and maintain comprehensive records as proof that your instruments are regularly maintained. Using our smart solution, you can ensure that every food handler knows how to calibrate a thermometer. Our Calibration Log comes with clear step-by-step instructions on how to perform approved calibration methods.
To calibrate a thermometer, the device is compared against a known temperature reference and adjusted to match that reference as closely as possible.
In food operations, calibration is most commonly performed using:
The appropriate method depends on:
Calibration should always be documented, including the date, method used, results, and any corrective action taken if the thermometer is found to be inaccurate.
The significance of thermometer calibration in the food industry goes beyond food safety. This operation helps your food business maintain stable operations, increase efficiency, and address food-related issues.
When done regularly, thermometer calibration can save your team time and continuously grow your market by gaining consumer confidence in your food safety practices and services.
Specifically, thermometer calibration can help you achieve the following advantages:
Regularly monitoring thermometer calibration is an integral part of a food safety management system. Monitoring forms for this operation must be available and include information such as date, time, frequency, and results.
It can help food businesses achieve compliance with significant food safety laws concerning any thermometer calibration standard. It can also create a seamless and uninterrupted flow of work operations for everyday services.


Thank you for downloading free template!
Want to get a customizable HACCP template?
Or set up your food safety system in 15 minutes?
There are different types of thermometers depending on their application. In the food industry, all thermometers are required to be food-safe and can withstand high heat or very low temperatures. This means that thermometers, such as mercury thermometers, are not allowed in the kitchen.
Digital thermometers use electronic sensors to measure temperature. The temperature reading is then displayed on a digital readout screen. Most digital thermometers used in the food industry are instant-read. This type of thermometer requires only a few seconds to stabilize and is preferred since changes to foods can occur in split seconds.
Digital thermometers can be wireless or attached to an appliance. They can be used for both hot and cold foods.
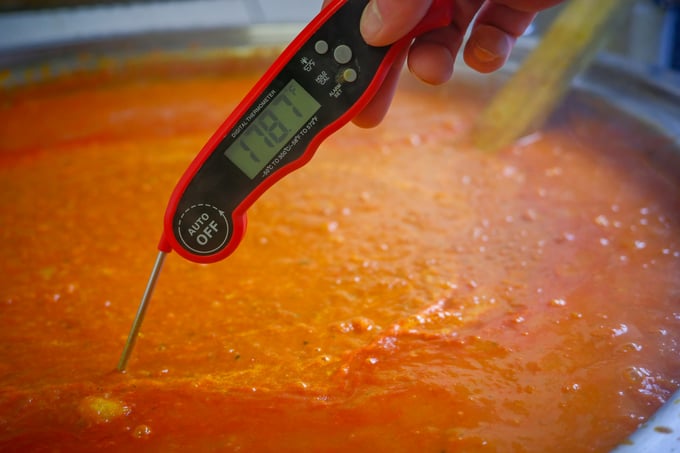

Calibrating a digital thermometer may greatly vary depending on the manufacturer's instructions. Calibrating a digital thermometer involves comparing its readings to a known and accurate reference temperature.
...depending on the thermometer's intended use. You can use a designated reference thermometer to check if the readings are correct.
Calibrating a digital thermometer often involves a reset button that is set to recalibrate the temperature reading to a particular range.
Probe thermometers come with a pointed probe used for inserting into foods and can determine the internal temperature. Probe thermometers are often used for measuring the internal temperatures of meat for its level of doneness. This type of thermometer is common and a conventional food thermometer in any kitchen.
The thermometer's read-out is presented by a display dial that contains the temperature reading. This thermometer is also otherwise known as the common dial food thermometer.
This type of thermometer can be used for measuring the safe temperature of meat inside the oven. As it is made of metal, it can withstand extremely high temperatures.
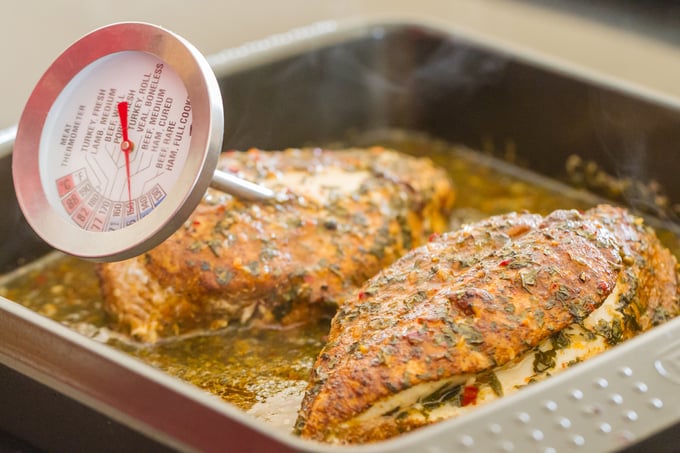

Calibrating a regular meat thermometer involves adjusting a nut with a specialized wrench that often comes with the thermometer. This process will require a reference thermometer.
Since meat thermometers are often used for measuring the internal temperature of food during cooking, such as for hamburger patties, the best calibration method is the boiling point method.
A bimetal food thermometer uses a strip made of two different metals bonded together. The strip bends with temperature changes, causing a pointer to move on a scale to indicate the temperature.
A bimetallic stem thermometer presents the temperature reading through a dial display. Calibrating requires a wrench to turn the nut and recalibrate the reading.
Calibrating bimetallic thermometers can be a bit more challenging compared to other types of thermometers due to their mechanical nature. This type of thermometer can be calibrated using the freezing point method or the boiling point method.
During calibration, the thermometer is submerged in boiling or very cold water, and the nut is turned to recalibrate the reading, similar to the reference thermometer.
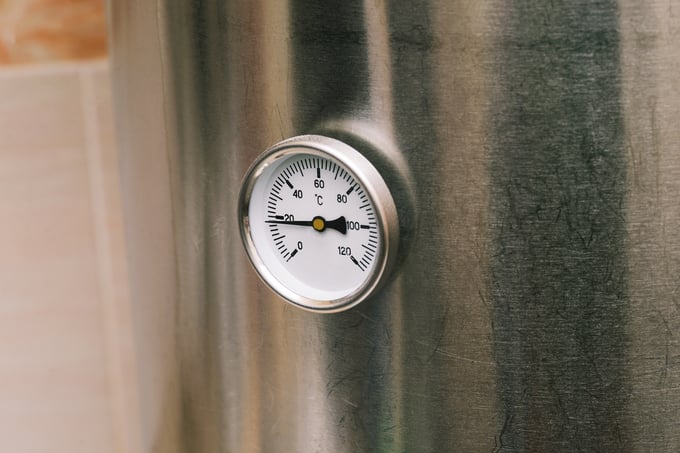

Calibrating a bimetal thermometer is important to ensure accurate temperature measurements, especially in applications where temperature accuracy is critical, such as ensuring proper internal temperature. Here are key times when a bimetal thermometer should be calibrated:
Infrared thermometers are non-contact appliances. This means that the thermometer will not touch the food. Temperature readings are executed by detecting the infrared radiation emitted by the food.
They are commonly used for quick, non-contact temperature measurements in industrial, medical, and culinary applications. They are very useful for big batches of food and when it is physically impossible to insert a probe into the food, such as in big production establishments.
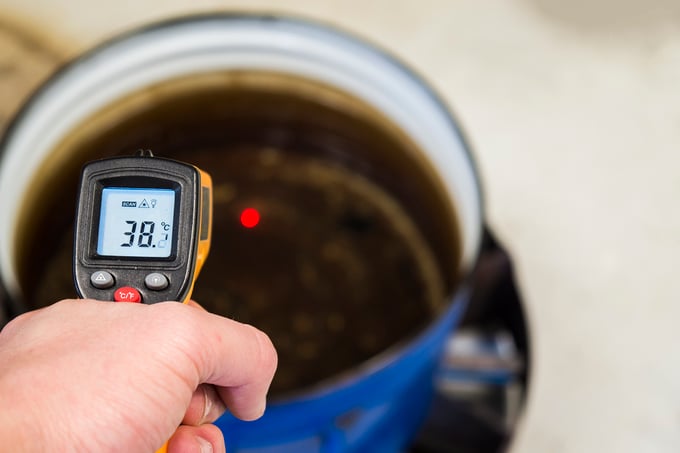

Calibrating an infrared thermometer can be a bit different from the other methods. The method also uses verification of the temperature reading from a reference.
Both freezing and boiling point methods can be calibrated but with slight differences.
During calibration, the infrared thermometer must be turned on and pointed toward a boiling or very cold ice-water mixture within a specified distance. The temperature reading will then be compared with a reference thermometer submerged in boiling or very cold water.
If inaccurate, the thermometer will then be reprogrammed. Some infrared thermometers offer adjustment settings to account for calibration differences. Consult the infrared thermometer manufacturer's instructions to determine if adjustments are possible and how to perform them.
Infrared thermometers have a very different mechanism from other manual and digital thermometers. As such, the frequency of calibration may be very different depending on the manufacturer's instructions.
In general, an infrared thermometer must be calibrated in the following cases:
Some infrared thermometers require very technical calibration. In this case, the manufacturer will request that your business send them to the unit, and they will perform the calibration for you. In this case, the calibration effect can last longer than normal.
Thermometer calibration methods depend on the type of thermometer you use. Some thermometers come with a special kit used specifically to calibrate them, whereas some can be calibrated using general methods.
More technical calibrations are often done by thermometer manufacturers themselves. They can either send a calibration expert to perform the calibration on-site or return the thermometer to their calibration laboratory for custom thermometer calibration services.
Here are two of the most common methods for thermometer calibration that you can perform for common thermometer types.
Otherwise known as the ice point method or ice-water method, this technique is commonly performed for thermometers that measure low temperatures. This method is performed as follows:
Thermometers used for refrigerated storage or cold-holding foods would require this calibration.
Freezing point calibration method
The boiling water method is used for thermometers to measure high temperatures, such as cooking and hot holding. This method is performed as follows:
Boiling point calibration method
For both calibration techniques, take note that the water to be used must be soft or distilled water. The impurities in hard water can significantly affect the accuracy of the thermometer reading. When the water is filled with impurities, the freezing and boiling point of water are relatively higher and lower, respectively. Additionally, a reference or comparison thermometer can also be used for the freezing point method.
The two calibration methods can be used along with a reference thermometer to calibrate non-adjustable thermometers. Reference thermometers are preferably NIST-certified (National Institute of Standards and Technology).
Make sure that the reference thermometer is accurately and recently calibrated. Upon comparing the temperature readings, the non-adjustable thermometer can be labeled with an offset value of the degree difference to correct any temperature reading.
That is, if the reference thermometer reads 212°F (100°C) and the thermometer being calibrated reads 209°F (98°C), all temperature readings using the non-adjustable thermometer must be offset by 3°F or 2°C.
In addition to repeatedly recording temperatures using the calibrated thermometer, you can also use a previously calibrated thermometer as a reference.
Submerge both thermometers in either an ice bath or in boiling water. If their temperatures are almost or exactly similar, then the thermometer is accurate.
If a thermometer is used regularly to measure a particular range and it repeatedly shows readings out of this range, this may be a sign that the thermometer needs recalibration.
Ideally, thermometers must be calibrated every day before starting your operations. This ensures you work with an accurate thermometer that produces correct readings.
Generally, a thermometer reading must only have a ±1°F or ±0.5°C difference from a reference thermometer. Any higher or lower reading than this calibration temperature range can significantly affect the results of food safety operations.
Ideally, calibration must be performed during these instances:
During calibration, recordkeeping must always be practiced.
All temperature readings during calibration must be recorded as proof of the accuracy of the performed calibration, which can be used for a thermometer calibration report. This calibration document can be used to verify whether the problem with a critical control point concerns the temperature, and proper corrective actions may be applied.
Level up your calibration tasks with the help of FoodDocs' Food Safety Management System. Our software is compatible with major appliances with IoT sensors. Integrations with our software can help log calibration readings seamlessly. Keep all records organized and ensure proper calibration with FoodDocs.
Calibrating a thermometer is a technical operation that requires training. When improperly done, the calibration can be ineffective, leading to several safety problems when the thermometer is used.
Here are some common mistakes that you should avoid when calibrating a thermometer:
Provide proper training and clear references to your employees for thermometer calibration with the help of FoodDocs' smart Food Safety Management System. Our smart software provides clear, step-by-step instructions on thermometer calibration and our digital Calibration Log.
With the help of our intuitive digital solutions, you can ensure that all of the mentioned problems can be avoided significantly. Ensure accurate and effective food safety with FoodDocs.
During calibration training, you must consider a few things. These factors may make a significant difference, and knowing them will prepare your kitchen staff for uncommon situations during calibration.
Below are a few factors to consider when calibrating a thermometer:
Use the freezing point method for a thermometer to measure low temperatures and the boiling point for hot temperatures.
Learning to calibrate a food thermometer must be part of a food handler's training routine. This operation will need to be repeated many times to ensure food safety. In doing so, the mentioned factors and proper temperature measurement procedures must be highlighted during training.
Regarding choosing the type of thermometer to measure high or low temperatures, dial thermometers can do both low and high-temperature readings.
This type is flexible and durable, even if exposed to extreme temperatures. Digital thermometers are advisable for operations that will not expose the thermometer to high heat. You cannot leave a digital thermometer inside an oven, unlike a dial thermometer.
Proper and timely calibration of a thermometer is a significant preventive step toward controlling food safety hazards.
Use FoodDocs' smart Food Safety Management System to ensure thermometer calibration is covered and well-emphasized.
Switch to our innovative solutions for recording thermometer calibration data and training employees with clear instructions.
Get a digital Thermometer Calibration Log and other automatically generated monitoring logs that fit your daily operations. Using our AI-powered system, you can get this comprehensive log for a more efficient recording of thermometer calibration readings.
You will no longer need a pen and paper to record results. In addition, the Thermometer Calibration Log is equipped with a prefill solution that shows calibration values based on your previous data entries.
Save more time and ensure more accurate calibration records with the help of our digital solutions. Present clear and credible calibration results to inspectors as proof of your commitment to food safety.

With the help of our smart solutions, food managers can efficiently and effectively train food handlers on how to calibrate thermometers and read temperature measurements.
We understand how important it is to perform every calibration process step precisely.
All monitoring logs are equipped with detailed instructions that can serve as references. Use these instructions to teach your employees the proper boiling point or ice-point method steps.
You can also upload your versions of the instructions as images of videos. Make learning more personalized to your unique operations with the help of our digital solutions.
Apply improvements from inspections and customize your monitoring logs and checklists according to your business needs. All sections of our digital monitoring system can be tailored to your requirements.
In no time, you can get a monitoring system that fits like a glove. Add monitoring parameters and recording fields to your tasks to capture more information for a more credible system.
If you have a unique operation to monitor, you can also make monitoring tasks from scratch using our system. Make switching to a completely digital system more seamless with the help of our solutions.
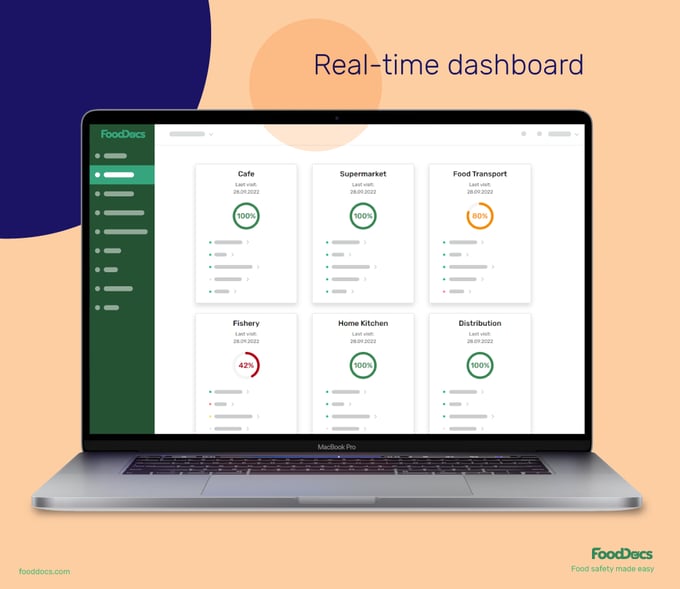
Quickly identify areas that can cause problems with the help of our real-time dashboard. This feature gives you a quick overview and informative insight into areas that need more attention across your brands.
You can quickly detect thermometers that require calibration with the help of our dashboard. In addition, you can also easily spot calibration processes with problems. Address the situation as it happens to minimize any further complications.
Save at least 20% of your time supervising your team manually with the help of our real-time dashboard.
With the help of our digital Food Safety System, you can ensure that every calibration process you perform is accurate and precise. We can help you secure temperature readings throughout your branches.
Our team of food safety experts aims to make food safety and compliance with food laws and regulations accessible to every business. With this digital FSMS with a built-in digital HACCP plan maker, food businesses can easily achieve compliance compared to the traditional process.
Book a free one-on-one call with our team to learn more about how can FoodDocs help your food business stay compliant.
Need more information about food handlers' tests and training? Here are some frequently asked questions about the topic.
Both boiling point and freezing point methods of calibration can be used to calibrate a digital meat thermometer. The only difference is that most digital thermometers have a calibration reset button and a digital display to reenter the correct temperature reading when compared with analog thermometers. Additionally, digital thermometers need to have their batteries checked and replaced.
A set of exhausted batteries will most likely produce inaccurate or unclear temperature readings. More sophisticated digital thermometers may need to be sent to their manufacturers for a scheduled thermometer calibration.
To check the thermometer calibration, the chosen method must be performed two to three times and gain the same temperature reading. Only very small differences between calibration results are allowed to ensure the effectiveness of the calibration method.
The best way to know if your thermometer is accurate is to compare its reading with a calibrated reference thermometer.
One effective way to calibrate a thermometer is by using a reference standard thermometer with known and traceable accuracy. Compare the readings of the thermometer being calibrated with the reference thermometer at multiple calibration points within its intended temperature range.
The temperature at which a bimetallic stemmed or digital thermometer should be calibrated depends on its intended use and operating range. Generally, calibration points should cover the thermometer's expected temperature range, including lower, middle, and upper values.
A bimetallic stemmed, or digital thermometer should be calibrated regularly, typically based on the manufacturer's recommendations and the specific application. It's important to calibrate whenever there are significant environmental changes if accuracy is in doubt or according to a predetermined schedule to ensure accurate and reliable temperature measurements.
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...