Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Today, consumers have started to become more and more aware of the importance of food safety. This topic has become a major deciding factor for consumers to dine in a food establishment. Whether it is a newfound awareness or not, food safety is an obligation of food business owners.
Poor food safety is the source of many different foodborne illnesses that endanger the lives of consumers and your food business. If this is the case, then what is the best way to prevent poor food safety?
Poor food safety can be prevented by having enough knowledge about proper food safety practices and proper hygiene. These practices promote a clean working environment and help control food safety hazards to prevent their spread. Food handling practices can be applied anywhere within the distribution chain and do not have to be very technical to become very effective.
Here are a few best practices in preventing poor food safety:
This food safety practice, although very simple, is one of the most effective proactive steps to prevent the spread of foodborne illnesses. The hands of food handlers can pick up hazards anywhere in the kitchen and can easily spread them around. Not to mention, some harmful microorganisms such as Staphylococcus aureus live as commensal on the skin. Proper handwashing removes the majority of the food safety hazards on hands and prevents their spread.
Handwashing needs to be done correctly to become effective. It is advised to use warm water or soapy water and perform the operation for at least 20 seconds. The advised duration of a handwashing procedure should be as long as one Happy Birthday song. The contact time of the soap with the pathogens increases the effectiveness of the operation.
To guide your team with the simple steps of proper handwashing, use this handwashing food safety poster from our food safety template hub.
Cross-contamination is the travel of a food safety hazard from one place to another. The potential hazard can come from humans, equipment, or food and be transferred into any food item being prepared. This perhaps is the fastest route to spreading food safety hazards. The contamination of foods can be prevented through several operations including:
Cross-contamination can easily occur when food handlers have little knowledge about this hazard. Washing raw produce and then proceeding to handle other products that will be minimally processed such as fresh fruits and vegetables is a sure source of cross-contamination. Preventing this event can be achieved by first orienting food handlers on what it is and how can it occur in their everyday operations.

The temperature danger zone refers to the range of temperature at which most food pathogens optimally thrive. This danger zone is anywhere between 40°F and 140°F (5°C and 60°C, respectively). As a rule of thumb, foods must not stay in this zone for more than 2 to 4 hours depending on the risk level of the food product. Keeping food in this temperature range longer than the advised time can increase the risk of causing foodborne illnesses.
To prevent this from happening, apply hot-holding for foods that need to be displayed before consumption. This case is usually what happens in cafeterias. Food in this scenario must be held above 140°F (60°C). On the contrary, if foods are to be consumed at a later time, they must be stored at proper refrigerator temperature to slow down the growth of microorganisms.
In keeping food outside the temperature danger zone, proper and constant monitoring of temperature is important.
In addition to proper storage temperature, storing foods properly also means grouping like products together. This process minimizes the risk of cross-contamination. As an example, dried condiments such as herbs and spices must be kept in air-tight containers or bottles and shelves away from too much moisture. Keeping them too close to wet food ingredients may cause them to absorb moisture and increase the risk of spoilage.
Additionally, storage in a refrigerator must also be considered. With a multi-level refrigerator with adjustable shelves, ready-to-eat foods such as cooked meats must be placed at the topmost portion as these will no longer be processed. Raw products such as raw meat, poultry, and fish are placed at the lowest shelves because they require the most processing.
Learn how to store food properly in the fridge.
One of the best ways to prevent poor food safety is properly cooking foods and identifying proper temperature controls for them. Microorganisms such as bacteria in food are very natural. Some are pathogenic, whereas some are just common non-beneficial microorganisms. This means that food, especially meats, must be cooked to become safe for consumption.
Foods such as meat have commonly associated pathogens such as Salmonella for poultry and Trichinella spiralis for pork. In addition to these known pathogens, food can easily get bacterial contamination as a result of poor food safety. Different internal safe temperatures are established by the concerned regulatory authority specifically for targeting these pathogens. Cooking food thoroughly can help bring out the best flavors of the food while maintaining food safety.
In case your food business offers rare-cooked foods such as veal and beef, even stricter food handling practices must be applied. In addition, a consumer advisory must always be present to inform consumers of the risks of eating undercooked foods.

Food hygiene refers to the way food safety practices are carried out in the cleanest and safest way possible. This process promotes cleanliness both in handling foods and in the everyday behavior of food handlers. Food hygiene includes operations such as properly washing foods before use as well as how food handlers present themselves. It includes personal hygiene such as the proper wearing of uniform, tidy hair, clean nails, and good health.
Unhygienic conditions attract food contaminants such as pests and microorganisms. These then can cause foodborne illnesses and unwanted food safety issues.
Food safety practices need to be constantly monitored to ensure that they are being applied and that their objectives are being met. In the food industry, there are several ways for food businesses to do this. In addition, programs that help reduce poor food safety and improve other management systems are present.
Knowledge about these systems can help your team improve their food safety performance. Here are a few systems that your team can implement:
An FSMS is a useful systematic program that helps ensure that food safety operations are always in place through constant monitoring. Several types of FSMS are used to manage food business operations. They can be written documents that describe how to maintain food safety and proper verification procedures to ensure their effectiveness.
Most countries mandate the implementation of an FSMS based on the preventive nature of the Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point system. A comprehensive FSMS covers monitoring operations from sourcing raw materials and validating suppliers up to the distribution of finished products to the consumers.
These programs are sets of procedures that help create a sanitary and compliant environment to minimize the presence of food safety hazards. Prerequisite programs are basic food safety principles and are the foundation of higher food safety systems including HACCP.
These prerequisite programs make a more conducive environment that has very minimal food safety hazards. They include most of the operations mentioned above and where applicable can be used to control hazards in the following business operations:
Some of the most widely known prerequisite programs are the following:
Perhaps one of the most widely known tools in preventing poor food safety in any food business is the HACCP program. HACCP or Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point is a systematic approach to food safety that aims to prevent and control the spread of food safety hazards before they even cause further damage. This program is composed of 7 major principles that lay out how to properly control and address any particular food safety risk in a food business.
The HACCP system analyses the whole food chain and identifies all potential food safety hazards. These hazards are then evaluated and assigned particular critical control points with critical limits to monitor their progression and ensure that they are well under control. All food businesses in some countries are required to implement a HACCP plan or a risk-based preventive plan to prevent foodborne illnesses from occurring.
These tools were all designed to prevent the spread of any foodborne infection. They were systematically conceptualized to address hazards before they spread to critical levels. Any best way to prevent poor food safety is covered by these tools with proper monitoring procedures.
At FoodDocs, we offer the most intuitive and easy-to-use system to help you create a digital food safety management system fit for your daily operations. We know how leaving the traditional process and shifting to a digital platform can be daunting for some. That is why we have simplified the process of creating a digital FSMS using artificial intelligence.
In just an average of 15 minutes, you can get a digital FSMS complete with the necessary digital monitoring forms and other features that can help you remain compliant with food safety regulations. The process only involves answering basic questions about your food business operations and our system will do the rest.
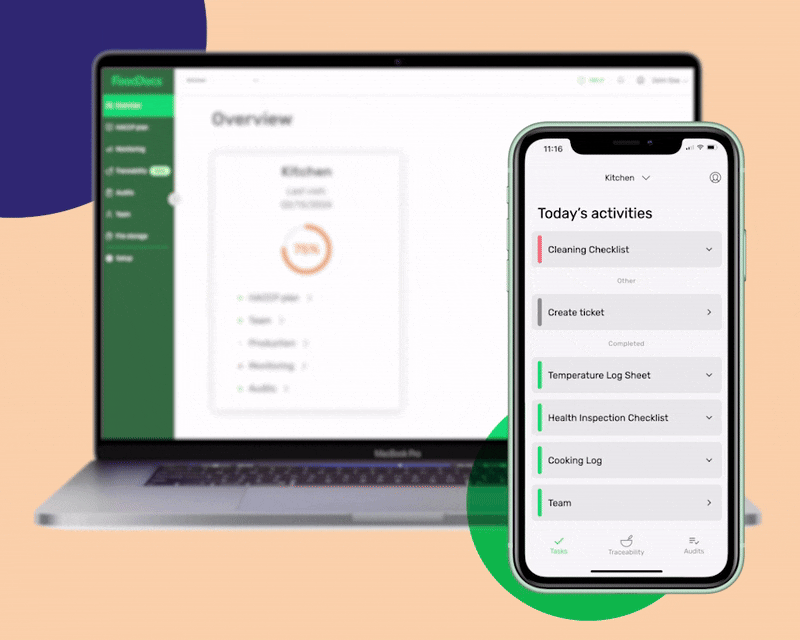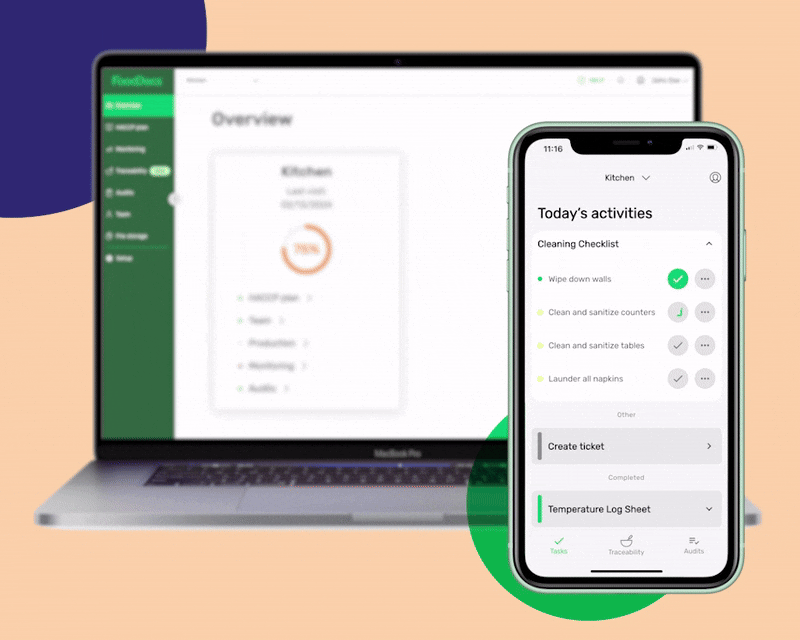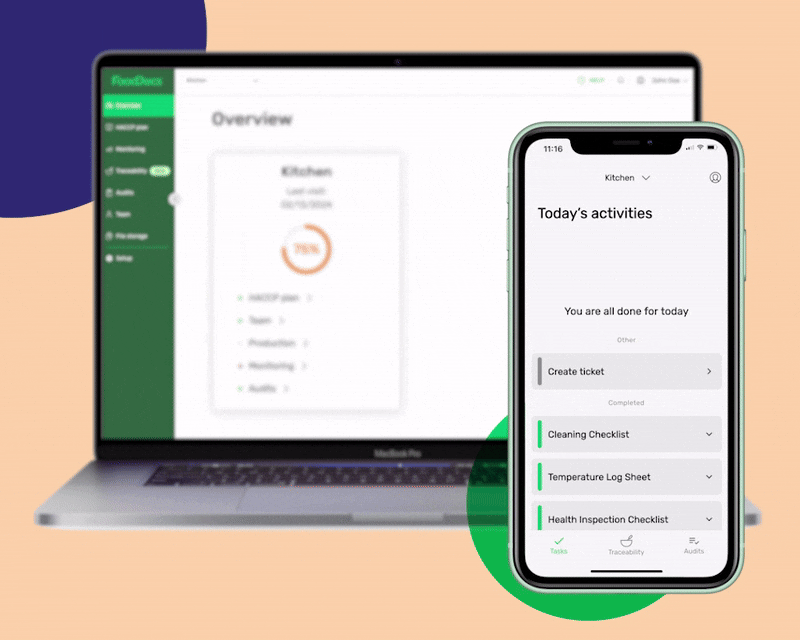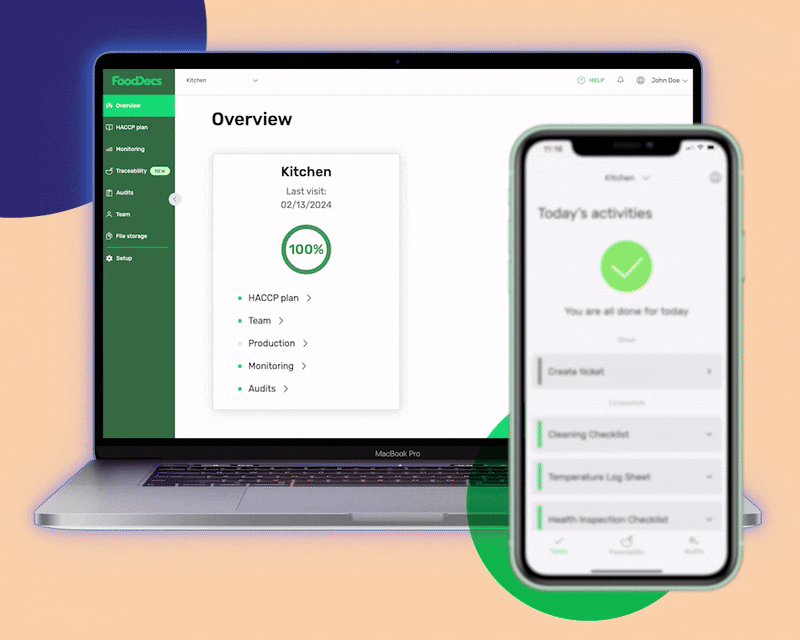
Our smart system can automatically generate intuitive, digital monitoring forms that can be further customized for additional operations. We call them intuitive as you can set them to be automatically filled based on your previous data entries. This feature can help your employees save time and just perform verification.
Never miss a food safety task and perform them on time with our smart notification features using our mobile application. Compatible with any major device, our system sends out notifications if any food safety tasks are due. You can also use this feature to manage training and certificate renewal due dates.
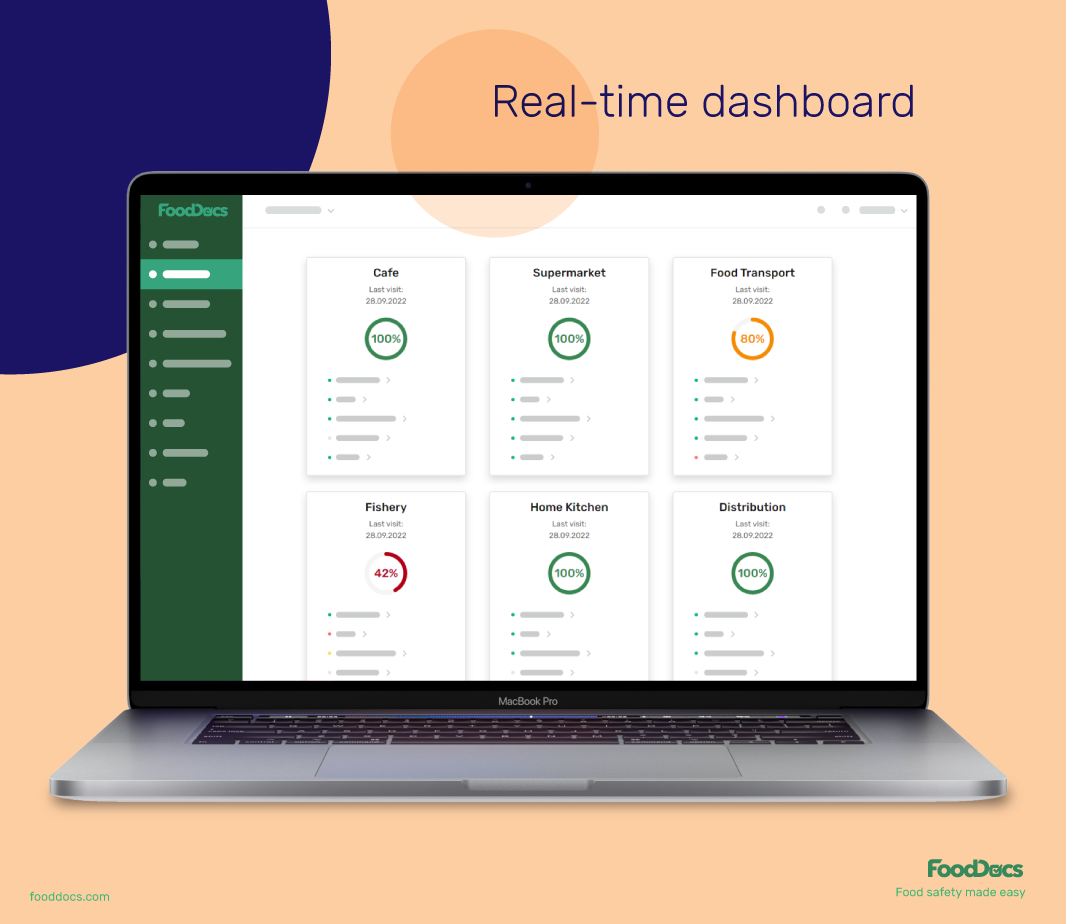
Review your whole operations and save 20% of your time from micromanaging them using your real-time digital dashboard. This feature reflects all of your daily tasks across your locations and can help you identify which areas need more attention.
With our digital FSMS software, you can become more sustainable as you can get cloud storage. Store, organize, and access all digital documents from a single location with ease and save space.
Monitor your operations and prevent the occurrence of poor food safety using our digital FSMS features. Try FoodDocs for free with a 14-day trial and get your digital FSMS in just 15 minutes.
As a summary and to help you understand these topics, here are some of the most frequently asked questions about food safety with simple answers:
Food safety helps control the spread of food hazards within the food supply chain. If left unmonitored, poor food safety can contribute to the growing number of foodborne illnesses and can potentially lead to an outbreak. Food safety involves basic hygienic manufacturing practices that can be applied throughout the distribution system.
Food safety issues and health concerns do not only affect your food business. It can contribute to the productivity loss of a country as a result of a reduced workforce from foodborne illnesses. The World Bank in 2018 estimated that at least $110 billion per year is lost in low- and middle-income countries as a result of foodborne illnesses. An undisrupted workforce and a safe food supply are keys to sustainable community living. Food business owners hold a big responsibility in ensuring that customers are protected from food safety hazards and that food employees are well-equipped with the necessary knowledge on food safety.
Poor food safety pertains to inappropriate or inadequate practices within the food supply chain and contributes to the spread of food safety hazards. This concept includes ineffective preventive controls, poor food hygiene, unsanitary food preparation, and unsafe water and air sources.
The four most effective ways of keeping food clean and safe include (1) cleaning the food preparation area, (2) separating raw and processed foods, (3) properly cooking foods to the correct internal temperature, and (4) chilling foods that are meant to be consumed at a later time.
Food handlers must keep food safe for consumption to prevent any problems such as foodborne illnesses or food-related injuries that can severely harm public health.
The CDC conducts studies and surveys to provide the link between major foodborne illnesses and the behavior of the community. They also find more effective ways of implementing food safety systems to prevent the spread and for the early detection of foodborne illness outbreaks.
All foods that are meant to be consumed at a later time are suggested to be put in an air-tight container and kept in refrigerated conditions. Low temperature helps slow down and control the growth of bacteria.
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...