Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
The Codex Alimentarius aims to provide a sound reference to promote fair trade and consumer health.
With the rise of food globalization, standards for international food trade have never been so important as today. Opening a country's food system to the world means increased risks and potential hazards to harm the public.
As such, international food industries all over the world must be harmonized in terms of which standards to follow for strict food handling.
WHAT WE'LL COVER:
The Codex Alimentarius is a compilation of internationally recognized standards for food crafted through a global perspective application. The guidelines, standards, and codes of practice published in the Codex Alimentarius are intended for food safety legislators, manufacturers, traders, food handlers, and consumers.
Codex Alimentarius literally translates to "Food Code" in Latin. The compilation serves as an international basis for food safety concerns. Every standard and guideline published in the Codex Alimentarius is based on sound evidence from scientific research and is often provided by international bodies conducting risk assessments.
The international guideline also provides standards to allow sound international trade among countries. It is currently being used as the main standard reference for international trade as agreed by the World Trade Organization's Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary measures.
The standards published under the Codex Alimentarius apply to "principal foods," including raw, processed, and semi-processed foods.
Although the Codex standards act as a national reference for food handling practices, the document is not considered a direct substitute for a country's national legislation.
The Codex Alimentarius was created to fulfill the following objectives of the commission:
As all guidelines and standards in the Codex are based on scientific research and findings from food safety experts, it provides a sound reference for other practitioners in the food industry. The establishment of the Codex came as a response to the need for a wide-ranging harmonization and common ground for all food businesses.
Before the creation of the Codex Alimentarius, concerns about trade barriers as a result of conflicting standards and the use of food additives with unequal knowledge of food technology were widespread.
In an effort to resolve disputes in international trade and food safety regulations, international organizations for food safety created the Codex Alimentarius.
The Codex Alimentarius was established by the joint efforts of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO). Both organizations make up the Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC), which is responsible for reviewing and establishing the guidelines for the food industry.
All 189 Codex Members contribute to the information released by the CAC. These members consist of 188 countries and 1 member organization, The European Union. In addition to the participating countries, other international intergovernmental and nongovernmental organizations influence the decisions and information disseminated by the Commission.

The Codex Alimentarius Commission was first established in 1963. This year was when the first session and gathering of participating bodies occurred, which was held in Rome. As of writing, the CAC has held 44 sessions since its establishment.
Codex standards are important as they create a common ground for international food standards and help resolve conflicts in trade barriers. As food safety standards all over the world may greatly differ, Codex standards provide reliable references for creating safe resolutions while prioritizing the consumer's health.
The establishment of Codex standards came as a resolution to the long-standing differences in societal disciplines and perceptions. Concerned regulators, legislators, and scientists, therefore, collected internationally useful standards.
These industry representatives then created a commission that provides identification of terms for uniform understanding. It also provides elaboration for vague topics supported by scientific evidence.
The presented Codex standards all aim to protect consumers from food handling malpractice and promote a harmonious relationship among traders. They also help ensure that all food products placed in every establishment are safe, wholesome, unadulterated, and properly labeled.
With globalization at hand, food industries all over the world are expected to open their markets to neighboring locations. Codex standards ensure that every market, despite different barriers, sees each trade through the same lens.
For food businesses, compliance with Codex-based standards can increase the chances of having your products approved for international trade.
Test how well your food employees understand food safety standards using our free Food Safety Quiz.
The Codex Alimentarius guidelines, standards, and codes of practice are otherwise known as Codex texts. These texts are established considering all products and product categories.
All established Codex texts deal with the following areas of food production:

The regulations and standards established under the Codex Alimentarius are all considered voluntary and will require the discretion of a nation's government regulatory agencies to adapt.
Codex texts are categorized into two types:
Recently, the Commission has focused more on producing general standards or standards that are applicable to food groups rather than one specific food product only.
Compliance with these standards must be consistent. You can ensure safe food trade by implementing a comprehensive food safety management system. To help you manage food safety effortlessly, use our digital Food Safety Management System, which gives you intuitive solutions using a digital platform for monitoring food safety standards at all times.
Every established standard in the Codex undergoes a series of reviews and approvals by the commission. Proposals for new guidelines or revisions to existing standards are submitted by government representatives through a discussion paper that outlines the recommended actions.
The process of submitting documents and getting a proposal approved is described in three steps.
The entire process of creating and establishing a Codex guideline or standard often requires years of preparation. The previously mentioned outline steps are further elaborated by the Food and Agriculture Organization through 8 key step processes.
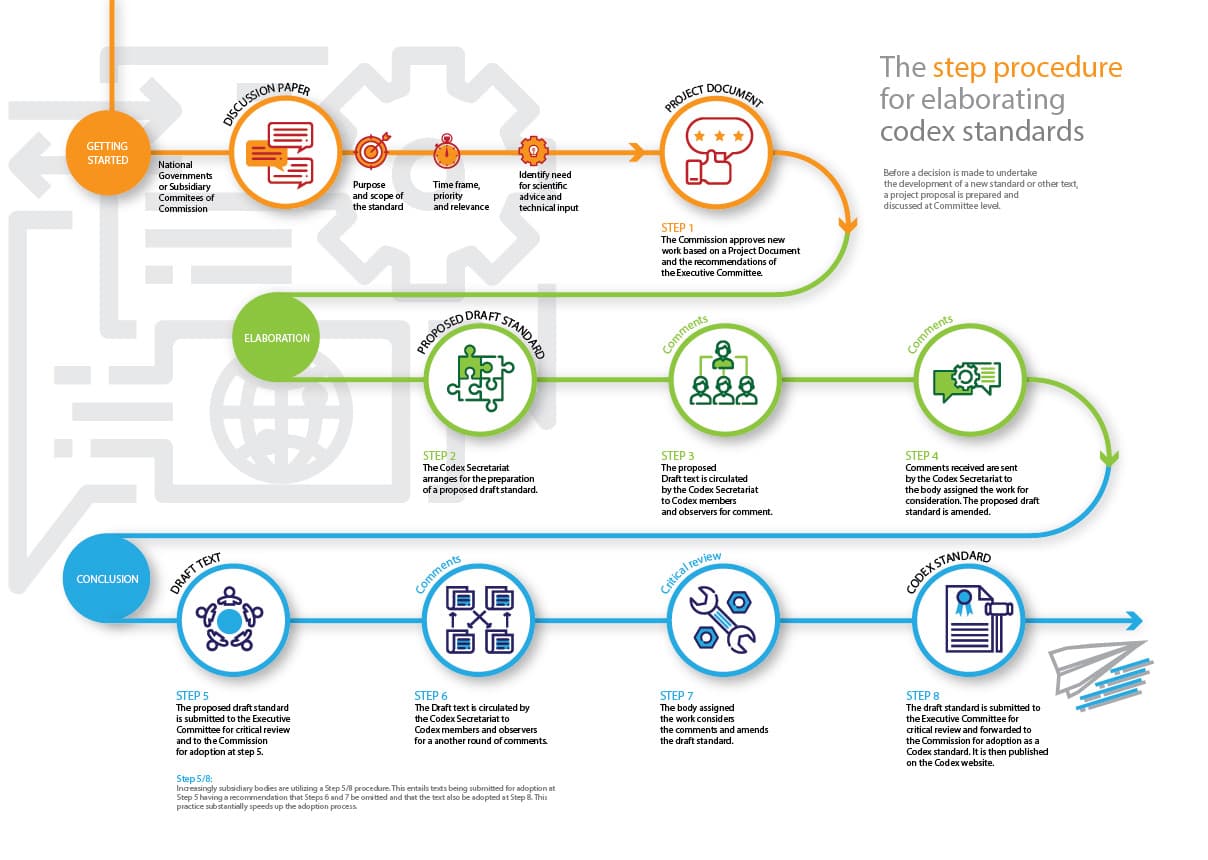
Food businesses receive the fully reviewed standards through the interpreted versions of their governments. Government review ensures that the standards from the Codex become fit to the norms and practices of a country.
The Codex Alimentarius Commission provided HACCP guidelines for small and/or less developed businesses globally. The Committee agreed during its 35th session that the guidelines would be created by the FAO and WHO.
The Codex HACCP identifies the 7 principles of HACCP and 5 preliminary steps to establishing a HACCP plan. Under the guidelines produced by the CAC, it also provided a general decision tree for establishing critical control points, which was recently updated in the Codex Alimentarius HACCP 2020.
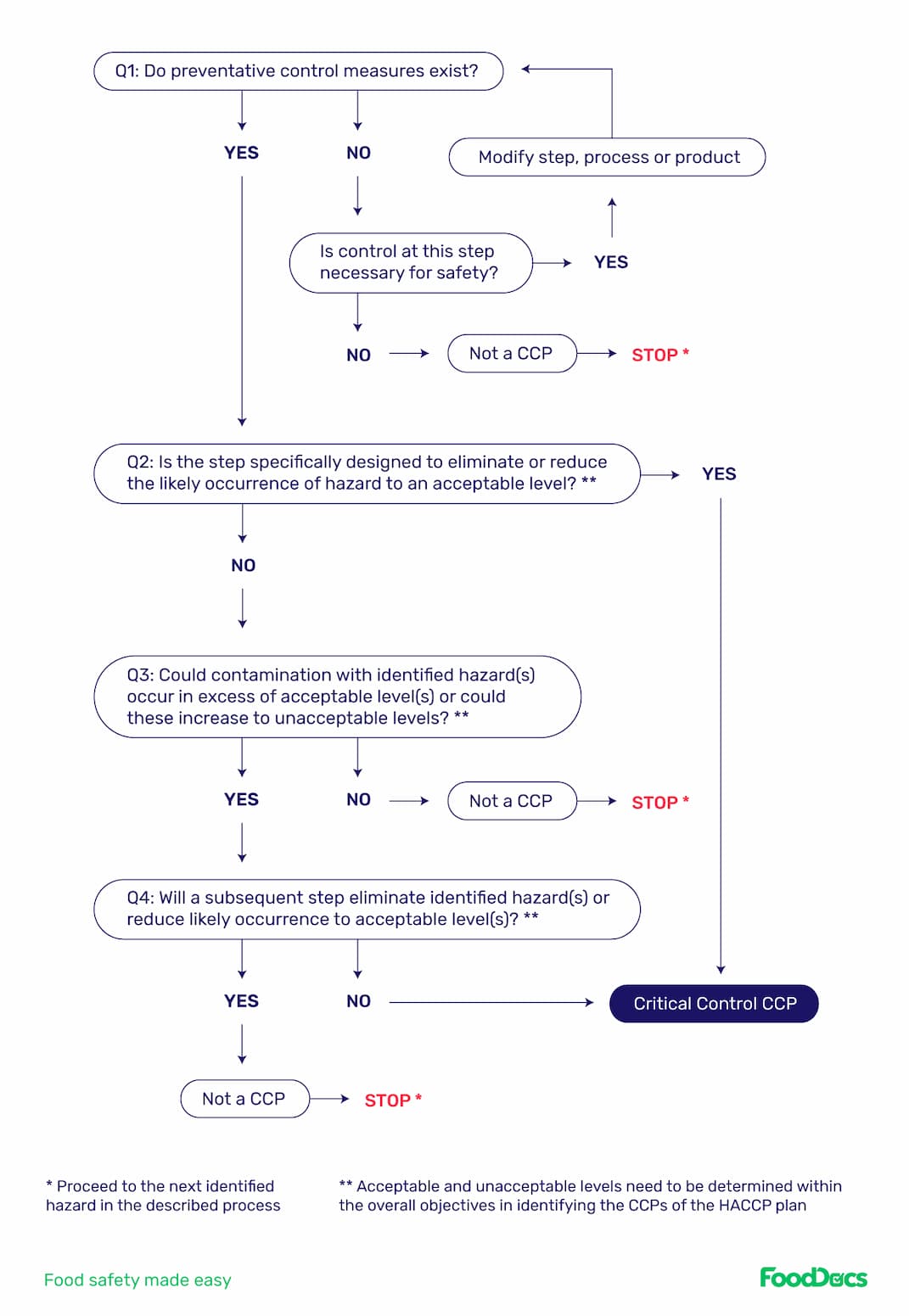
Codex Alimentarius HACCP decision tree
The general guideline for building a custom decision tree is that it must be flexible for different types of operation, and it must be able to discern between a critical control point and other types of operation controls.
The most recent significant change in the Codex guidelines is the revisions to the Codex HACCP. Some of the most notable changes from the old version include the following:

While the Food and Drug Administration Food Code has the same premise as the Codex Alimentarius, it is not synonymous with the latter collection of food safety guidelines. The FDA Food Code can be considered as the interpretation of the U.S. government agency on the guidelines provided by the Codex.
Both documents are collections of essential food safety guidelines for food businesses and are considered voluntary. They also similarly aim to protect public health from the risk of food safety hazards.
The FDA Food Code can be considered the American translation of the Codex Alimentarius guidelines. The guidelines published under the FDA Food Code use both the information from the Codex Alimentarius and the established U.S. food regulations and laws for national measures.
With the diversity of food safety standards all over the world, it is quite hard to find a food safety management system template that will fit your operations. Endless consultations with food safety experts for standards and guidelines will use up the time you could be spending on managing your food business.
At FoodDocs, we can provide you with an intuitive and versatile digital solution that can help you adapt to the essential standards for your food business. We offer software that can automatically generate a digital Food Safety Management System in just 15 minutes and can help you ensure consistent compliance with food safety standards.
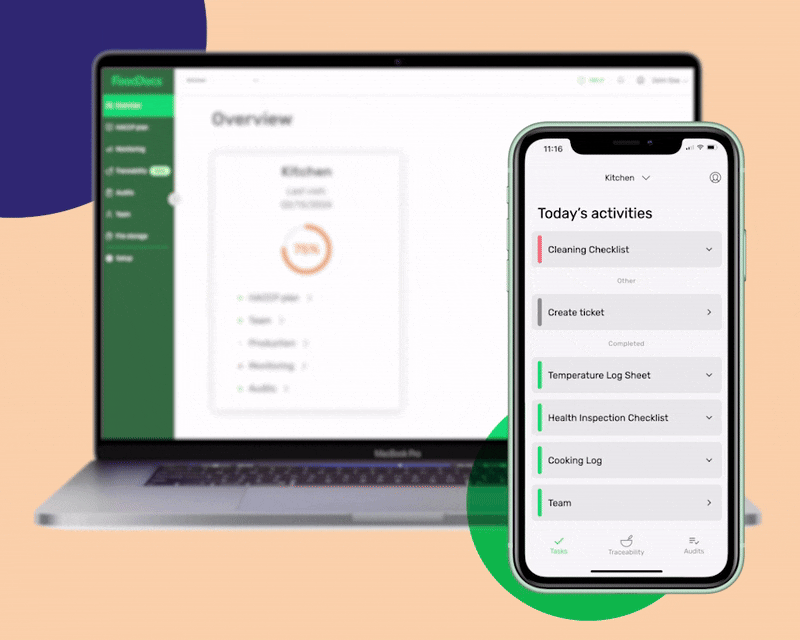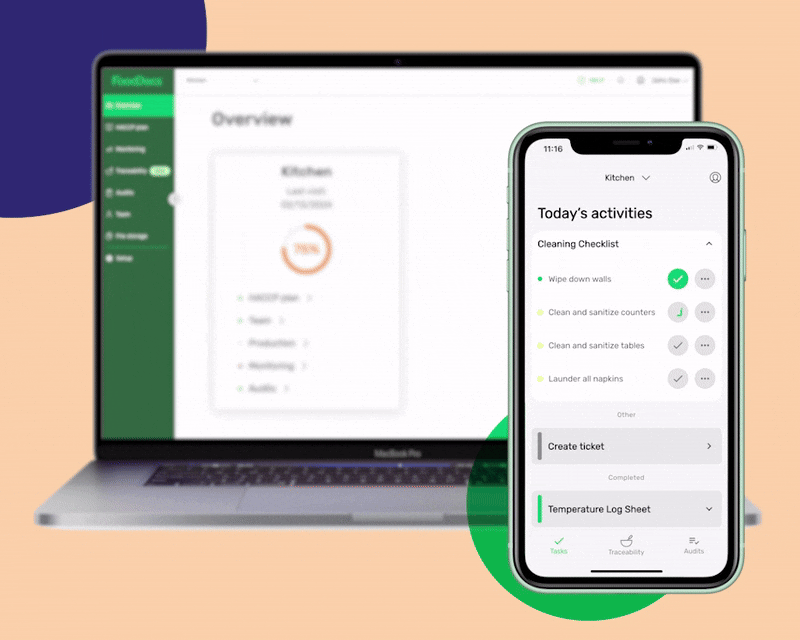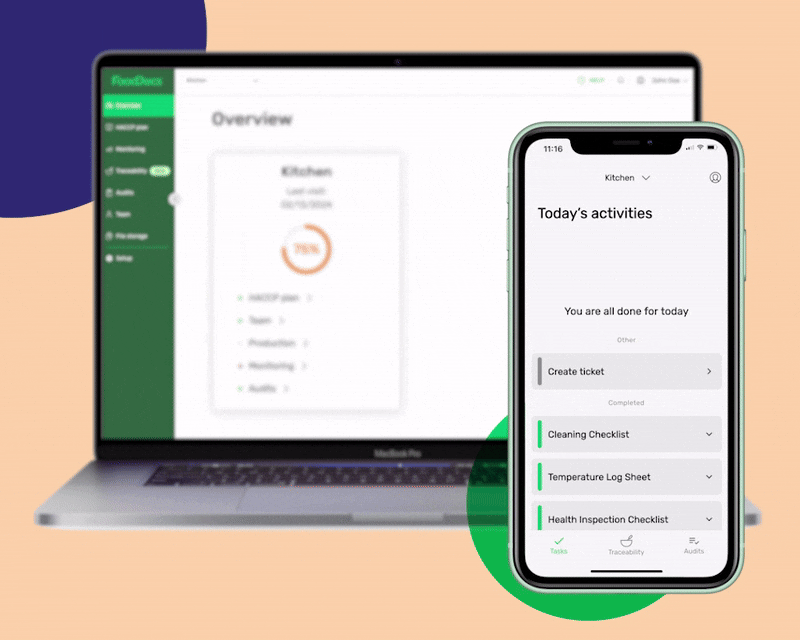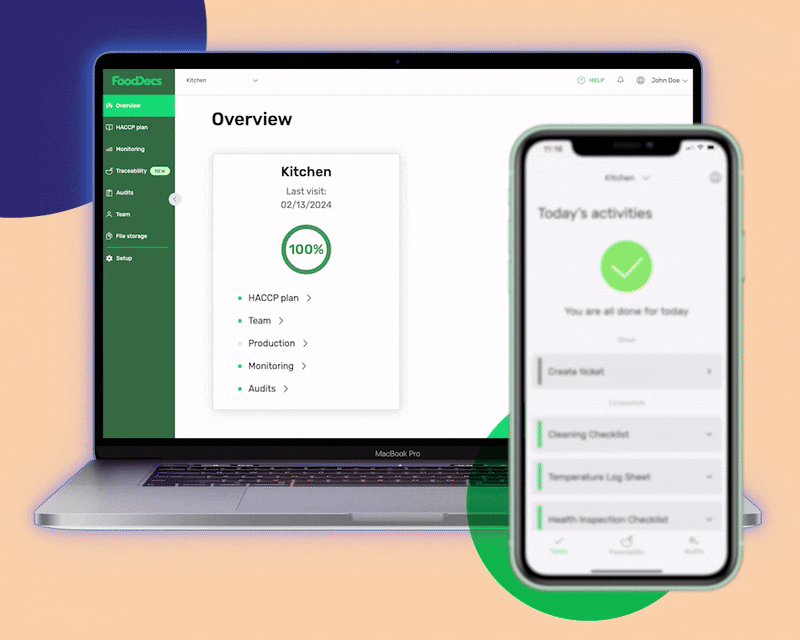
Our software system can provide you with the following benefits:
In addition to ensuring consistent food safety compliance, our system also offers benefits for improving food safety management for business owners:
What is even better is that you can get this comprehensive digital Food Safety Management System in just 15 minutes. With the power of artificial intelligence and machine-learning program, our system can match and generate which food safety documents you need and which standards are most applicable to your operations.
You can also continuously improve your digital monitoring logs as they are customizable. Incorporate your unique operations into the system and ensure that they comply with food safety standards.
Choose our efficient and intuitive digital solution to maintain compliance with food safety standards. Try using our features and experience the ease of compliance by using our free 14-day trial.
Here are more frequently asked questions regarding the Codex Alimentarius.
FAO stands for Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
The Codex Alimentarius was built to create internationally sound standards, guidelines, and codes of practice to ensure food safety by protecting the health of consumers from food malpractice and regulating fair practices for food trade.
The Codex Alimentarius contains a wide-ranging set of international standards, food safety guidelines, and codes of practice for handling food. The Codex provides an international reference for different food safety organizations in establishing their own guidelines.
The Codex is a set of international standards recommended for regulating food safety in different countries. On the other hand, ISO standards are voluntary guidelines that focus on improving food safety management systems.
To date, the Codex Alimentarius Commission consists of 188 member countries, the European Union, and 240 intergovernmental and international nongovernmental observer organizations.
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...