Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Biological hazards contribute most to the reported 48 million cases of foodborne illnesses worldwide every year.
Most foodborne illnesses reported in food safety news are often caused by one major type of food safety hazard - biological hazards. One of the most significant tasks of food handlers is to control biological hazards in foods and protect consumers from their effects.
Food safety and biological hazards co-exist in the food industry as most raw ingredients are organic. Biological hazards in food are practically invisible to humans, making them very hard to remove from a food facility. They can enter at any point in the distribution of food.
Maintaining food safe from biological hazards requires preventive controls and strict monitoring. The effects of biological hazards, when consumed by customers, can cause severe health risks and economic loss to your food business. Every food handler is responsible for learning and understanding how to prevent biological hazards in food to protect public safety. This is one of the major requirements for food safety compliance.
WHAT WE'LL COVER:
Biological hazards in food are pathogenic organisms or their products that can cause health problems when ingested, such as foodborne illnesses or food poisoning. It is one of the major types of hazards. Biological hazards are a significant concern in the food industry. In fact, major biological hazards caused most of the foodborne illness outbreaks recorded in history.
Because of poor food safety practices, biological hazards become dangerous to public health when they enter the food chain system. This type of foodborne hazard causes symptoms such as watery diarrhea and abdominal cramps. Some cases of foodborne illnesses caused by biological hazards can even lead to death when left untreated.
The organisms considered biological hazards can either cause infection or intoxication in humans. Human infection refers to the case when the organism itself enters the host and causes the illness. In contrast, intoxication occurs when the by-product of the organism causes the illness.
The effects of biological hazards may differ depending on the contaminating organism, environmental factors, and the level of food safety approach applied by a food business.
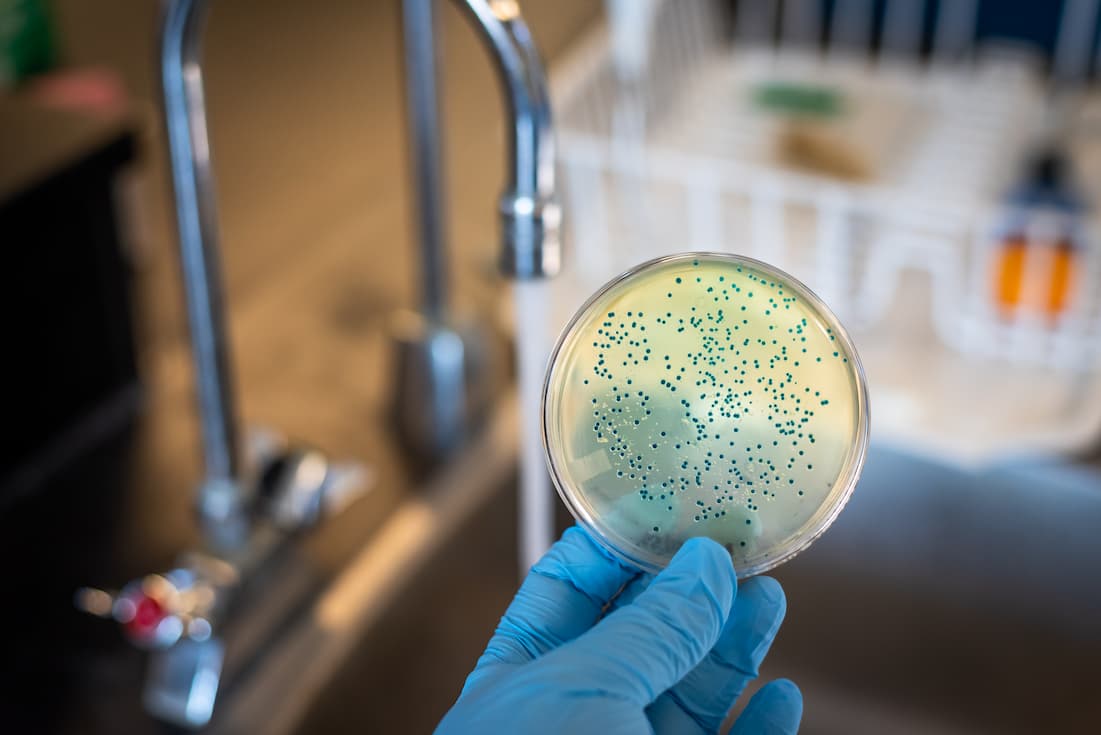
Biological hazard refers to the organism that causes foodborne illnesses and other risk factors to human health. On the other hand, biological contamination is when pathogenic hazards enter the food chain. Biological contamination is caused by foodborne hazards such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, which are all collectively known as biological hazards that make food unsafe for consumption.
All of the listed items could be sources of biological health hazards. If you inhale, eat or come into skin contact with them bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi or mold, they pose a threat to human health and can result in food poisoning, tetanus, respiratory infections, parasite infection, and similar illnesses.
There are several biological food hazards recognized in the food industry. Some of them are known to cause severe health problems, whereas others are less common. Regardless of the risk that a biological hazard may have, they all prefer growing in moist and nutritious environments. This fact makes food their number one target.
There are major types of biological hazards that every food handler must be aware of, and these include the following:
Viruses are very resistant to intense conditions such as high acidity and heat and can be easily transferred from the food handler to the food being prepared.
Viruses are most commonly associated with contaminated water, seafood, vegetables, and food handlers. Some of the most common infectious diseases caused by viruses include gastroenteritis and hepatitis.
The types of foodborne bacteria vary greatly. Some can survive extreme conditions, whereas some bacteria can be eliminated easily and have minimal threats to human health. Some bacteria can stay inactive in the form of spores and multiply when the conditions are favorable again. This mechanism of bacteria makes them a major concern in food preparation.
Some of the most commonly known foodborne bacteria include the following:
Several fungi are known to produce toxins that are very hard to remove when they have contaminated foods. In such cases, prevention is a better approach to protecting human health. Some of the most common foodborne fungi include the following:
Other examples of foodborne parasites include:
Among the mentioned types of biological hazards, a few species are recognized to cause the most foodborne illness cases worldwide. The big 6 major pathogens include:

Other references include natural toxins produced by dangerous pathogens to be categorized as biological hazards.
Biological hazards significantly contribute to the average of 48 million cases of foodborne illnesses in the U.S. each year. At least $95.2 billion per year is lost in low- and middle-income countries in treating foodborne diseases and economic losses caused by biological hazards.
Use FoodDocs' digital HACCP plan builder and automatically get a detailed and customizable analysis of the most significant biological hazards in your food safety operations. With our digital solution, you can immediately establish critical controls and preventive measures to protect your customers.
Biological hazards in food are common, especially in food businesses with poor food safety management. Microorganisms considered biological hazards can contaminate a wide range of food products and produce very different outcomes.
Some biological hazard examples in food produce observable changes. Such is the case of molds on fruits. Molds produce a cotton-like formation on the surface of the contaminated food products. Other changes may be observed as bad smell, acidic taste, or softening of the food's surface.
Some biological hazards do not form noticeable changes until they significantly multiply. Despite this, they can still cause foodborne illnesses, even in low cell counts. A common example of this is Salmonella in raw poultry. This bacteria does not usually produce obvious changes and can still cause diseases when contaminated food is improperly processed.
Learning how to prevent biological hazards in food is one of the most significant tasks of every food handler. A part of training food service handlers is identifying the most common contaminants in a food service operation.
The following are examples of biological hazards in food service operations:
A restaurant facility provides a very hospitable location for biological hazards. That is why food handlers must be trained to handle foods to avoid introducing biological hazards properly.
You can use our free food safety quiz tool for training food handlers on the essential operations for controlling biological hazards in a restaurant.
Biological hazards are always around us, especially in food businesses. Since the main source of nutrition and energy for biological hazards are also food products, a restaurant kitchen or retail food store is a suitable environment for them to survive.
Below are some of the most common points where biological hazards can be found:
In addition, food handlers are the fastest way for biological hazards to travel. Through cross-contamination and the lack of food hygiene, common bacteria and viruses can quickly spread from one place to another.

Once your water system is contaminated, your entire food service area can easily become contaminated as well. Water is used in almost all operations inside a kitchen.
Preventing the spread of foodborne biological hazards can be an easy task if consistently done and monitored. A food business with a comprehensive food monitoring system based on a hazard analysis can significantly control the presence of biological agents.
Use FoodDocs' digital Food Monitoring System to get intuitive solutions for monitoring food safety practices. Our software features solutions that automatically generate monitoring logs with prefill solutions and a smart notification system to help ensure consistent food safety compliance.
The effects of biological hazards can range from a simple abdominal cramp to more serious cases that can lead to life-threatening diseases or death. Depending on the causative agent, the degree of contamination, and the overall health of the consumer.
When customers consume foods contaminated with biological hazards, the effects can include the following:
In consumers with weak immune systems, the results of consuming contaminated foods can have more adverse effects. These consumers include pregnant women, the elderly, and children under the age of five. When uncontrolled, the effects of biological agents can spread and affect more consumers, leading to a foodborne outbreak. In such cases, food businesses are tasked to cooperate with food safety inspectors during outbreak investigations to control the situation.
Using a preventive approach to control biological hazards is proven to be most effective in reducing unnecessary costs and damages. Simple food handling practices and personal hygiene can significantly contribute to reducing food safety issues from foodborne pathogens.
To help food handlers prevent biological hazards and public health risks, follow these tips and guidelines:
Proper controls and monitoring procedures must be set in place to ensure that these common practices are always followed. With consistent performance, your food business can become free from public health risk factors of foodborne hazards. This makes your business compliant with food safety regulations.
You can use our free food safety tools and templates to guide food handlers in preventing contamination by biological hazards. Use our free food storage chart and free sanitation standard operating procedures template to ensure proper storage conditions and a clean working facility at all times. We also provide all cooking temperature charts for ensuring proper cooking and processing of foods.
Use more intuitive solutions to help your employees control bacterial hazards and other infectious pathogens in your food business. Using FoodDocs' digital Food Safety Management System, food handlers can smoothly monitor food safety tasks. They can use prefill solutions that automatically input data on monitoring sheets based on previously inserted data. All that is left to do is to verify if the data is correct. In addition, our digital solutions make it less likely for food handlers to forget tasks through a smart notification system.
Read more about our smart software in detail in the next chapter!
Biological hazards include a great food safety risk for both the consumers and your food business. Causing a single foodborne illness outbreak not only puts public health at risk, but your business also becomes at risk of losing customer loyalty.
Despite their potential adverse effects, biological risks can be effectively controlled with very simple steps. All you need to do is analyze the hazards, set preventive measures, and then establish a consistent monitoring procedure to ensure compliance with preventive measures.
Do all of these steps in just 1 hour with our digital solutions at FoodDocs!
Hazard analysis is a critical task, especially for creating risk-based food safety plans. Biological hazard assessments involve identifying the following
This information will determine the appropriate approach and preventive measures needed to control biological hazards.
Identifying and analyzing biological hazards is the first step in any food safety plan. Your team must manually list all potential biological hazards related to your food business and analyze them one by one. This step can be supported by analytical methods conducted to evaluate your products. You can use our free HACCP Hazard Analysis Template to get a detailed guide in analyzing foodborne hazards.
In controlling biological and other types of hazards, the sooner you identify and analyze them, the faster you can create preventive solutions and protect consumers from the risk of hazards.
At FoodDocs, you can automatically have a comprehensive list of biological, physical, and chemical hazards related to your food business. As a critical part of our customizable digital HACCP plan builder, our software generates a thorough, smart hazard analysis table complete with essential information about the hazards.

What makes our software more flexible is that you can customize the information analysis with easily editable fields and preselected levels of severity and likelihood of occurrence. You can further improve the analysis and tailor-fit the descriptions and justifications according to your business needs.
The hazard analysis part is just the first of many features of our digital HACCP plan builder! In a total of 1 hour, you can get a complete and customizable digital HACCP plan by just answering a few basic questions about your business. Through the help of artificial intelligence and a machine-learning program, our software can generate a comprehensive HACCP plan template with detailed information related to your business operations.
Get the most essential parts of a HACCP plan, such as:
.jpg?width=680&height=590&name=HACCP_template%20(1).jpg)
Our software is a great alternative method that significantly shortens the common amount of time you need to spend on making a HACCP plan with the traditional method. In just approximately 1 hour, you can take control of your food safety and start serving safe food.
As we have mentioned, a key part of controlling biological hazards after their analysis is consistently monitoring the established preventive methods. At FoodDocs, you can get all the necessary tasks done to completely control biological hazards.
After establishing your HACCP food safety plan, use our digital Food Safety Management System to automatically generate all essential monitoring logs to make monitoring tasks easier. With our digital solution, you can get useful and intuitive features such as the following:
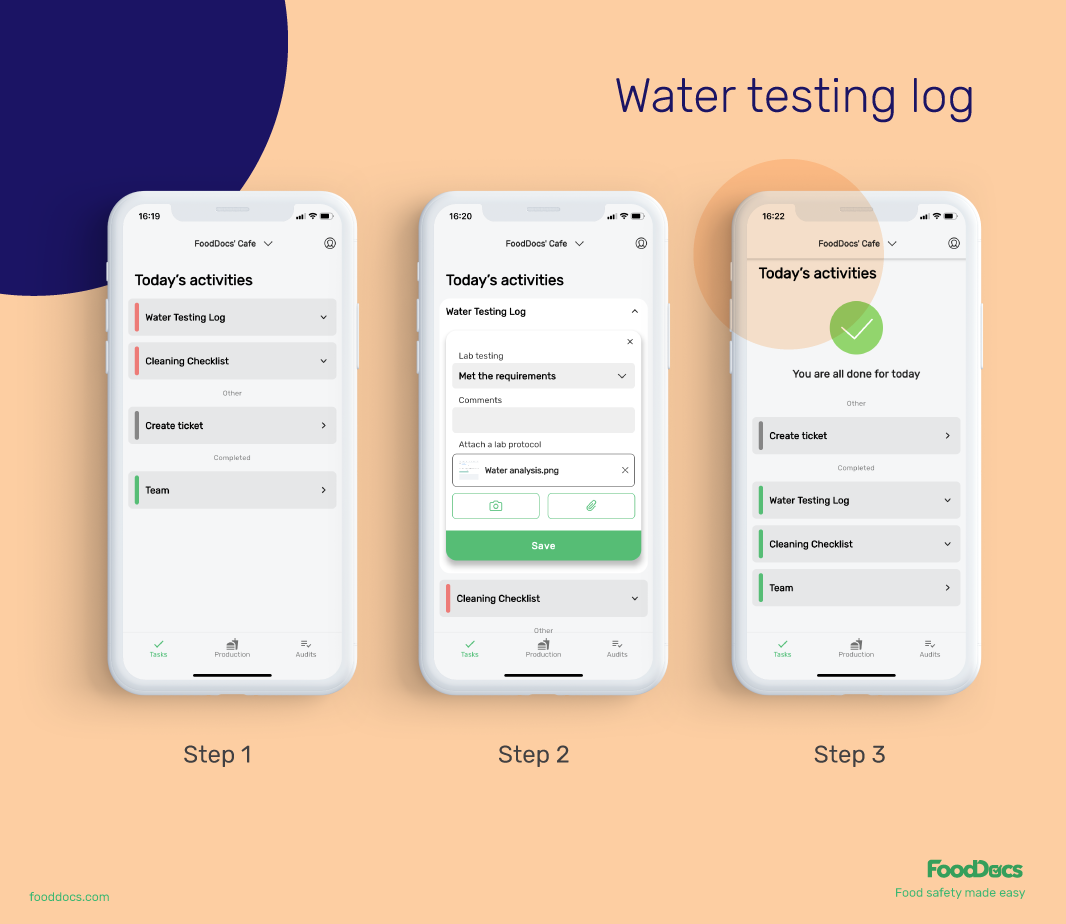
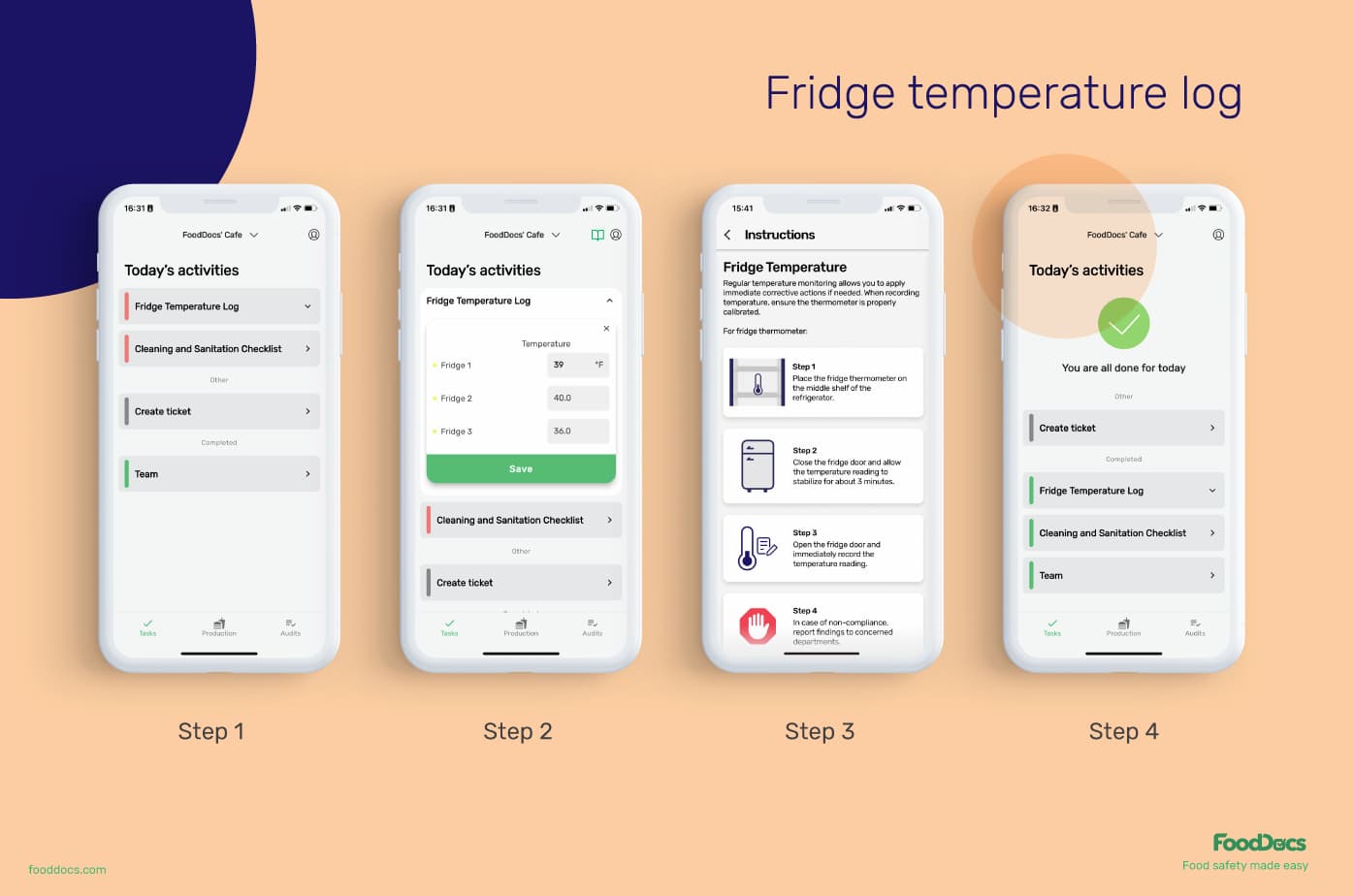
All monitoring logs and checklists are equipped with detailed instructions to guide food handlers in performing and monitoring the tasks. With this feature, you can ensure that your employees are correctly controlling biological hazards.
Our digital Food Safety Management System was built to make consistent food safety compliance easier and more accessible for food business owners.
to become compliant
Maintain compliance using our digital Food Safety Management System and effortlessly ensure that your business is free from the risks of biological hazards at all times.
Start monitoring your operations using our free 14-day trial and experience the efficiency of our software solutions.
Do you need more information on controlling biological hazards? Here are some of the most useful and relevant questions regarding biological hazards in the food industry.
The most effective food handling practice for preventing the contamination of food by biological hazards is to practice proper handwashing consistently. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention suggests that up to 50% of the risk of infections and deaths from diarrheal diseases could be prevented with proper handwashing.
Establishing a Critical Control Point depends on the severity of the risk of infection and the likelihood of occurrence of a food safety hazard. If a biological hazard has a very high potential severity and is very likely to occur, then a critical control point may be established for its control. Learn more from our comprehensive article about critical control points.
All pathogenic bacteria are identified as biological hazards. This includes bacterial agents that can cause acute effects on humans when consumed through contaminated food.
Bacteria and viruses account for the majority of the identified foodborne illness-causing hazards in the food industry.
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...