Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Contamination and foodborne illnesses do not necessarily equate to foodborne pathogens and their effects alone. Other types of contaminations can also harm consumers. Physical contamination is a very alarming and potentially dangerous type of contamination in the food industry.
Although some examples of physical contamination are more easily detected and excluded from the food system, there are physical contaminants that can quickly go undetected and cause significant problems.
WHAT WE'LL COVER:
The term physical contamination refers to the presence of any physical hazard in a product or the food production system that is not intended to occur.
Physical contamination is a significant food safety concern as it can lead to food-related injuries that involve choking, cuts, tooth damage, and difficulty in breathing. Depending on their origin, they can be physical objects made out of organic or non-organic material.
This physical contamination definition similarly describes the two categories of contaminants in food manufacturing based on FDA guidelines. According to the food safety agency, physical contamination can be caused by choking hazards such as rocks and seeds, and hard or sharp hazards including glass and hard plastics.
The occurrence of physical contamination is possible anywhere along the farm-to-table process and may imply different levels of risk. Depending on the type of physical contamination, other types of food contamination may follow.
An example of this scenario is the contamination of foods with pest droppings. This physical contamination potentially carries foodborne illness-causing pathogens that can spoil food and negatively affect customers. Symptoms of foodborne illness can exhibit as a result of physical contamination.
Just look at its presence in the news over the years.
Physical contamination is more common than a regular customer would think. In 2018, physical contamination from foreign materials in food was declared the top cause of food recalls in the US. This report showed that physical contamination is even more common than undeclared allergenic food items.
And that information only reflects the detected cases of physical contamination. This type of contamination can easily go undetected within the whole food processing line.
Thankfully, FDA food recalls in 2023 revealed that foreign materials (i.e., physical contaminants) were among the least common recall reasons. But even then, the end of 2024 saw another instance of MadeGood granola bars recalled over possible metal contamination.
To help food business owners and food handlers alike address physical contamination concerns, we've compiled some of the most essential information about physical contamination below.
As mentioned, physical contamination can occur at any point in the entire food processing chain. There can be a number of sources that can introduce physical contaminants to the food. Some sources can even be a mandatory component of the production process such as raw materials and a piece of equipment used for processing.
Objects such as leaves and bones are naturally part of fruits and meat raw materials, respectively. Similarly, plastic paddles in mixers can become sources of physical contamination.
To give you examples of how physical contamination can happen and be introduced to the food being prepared, here are a few common sources of physical hazards:
Food handlers. Although food handlers are supposed to be responsible for keeping physical contamination outside the production, they can actually become sources of the hazard. Any foreign material such as nail clippings, hair strands, and personal items such as jewelry can come from food handlers that do not follow food hygiene practices. In addition to the mentioned foreign contaminants, food handlers can also become carriers of physical contaminants such as papers, pen caps, and soil from dirty uniforms. Food handlers are known to be the most common route for cross-contamination to occur in a food service kitchen.
Equipment. Physical contaminants such as metal, plastic, and glass can sometimes come from the equipment used in the preparation of food. When the equipment used in your kitchen is not regularly maintained or is too old, the chances of chipped metal pieces or glass shards becoming mixed into the food are increased. Any equipment that is used with a certain amount of stress can wear down its material. An example of this is when your blender or meat slicer is too old. Using it may cause the blades to chip and the shards may mix into the food.
Raw materials. With low-quality raw materials, the chances of detecting physical contaminants are higher. Agricultural produce such as unwashed fruit, vegetable, and crop can carry soil, stones, or sand from harvesting and delivery. In addition, raw materials are natural sources of physical contaminants. Fresh materials such are fruits have seeds and leaves which can unintentionally be incorporated into the products. Such is also the case for raw meats. Bone-in raw meat materials have the health risk of mixing bone fragments into the food item and can seriously injure unsuspecting consumers.
Pest. There is a reason why food service and pests don't go well together. A pest management plan is a must for every food establishment. Animals can contribute physical contaminants such as hair, feather, skin, limbs, or other debris from pests such as droppings. Not only can these physical contaminants cause injury or choking but they can also further cause other types of contaminations. Pests are known carriers of common pathogens including foodborne illness-causing bacteria and viruses.
Packaging. Physical contaminants such as a piece of plastic wrap, cartons, wood chips, Styrofoam, and sometimes glass can come from packaging materials. Any packaging items with low integrity can easily be torn or broken and can become incorporated into the product. Packaging comes in contact with food directly and they are the last external objects that will be introduced with the product before serving to consumers. As such, the detection of physical contamination from packaging can be a bit more challenging than others.
Because of the nature of any physical contamination of being able to enter the production process at any point, proper monitoring procedures, corrective actions, and operational prerequisite programs must be in place.
To help you stay on top of everything that concerns physical contamination, use our digital Food Safety Management System. Our system has a waste management plan and pest management audit features that can help your team manage physical contamination.
Perhaps the best answer to the question "What is an example of physical contamination in food?" would be one that is very common and can occur in every food business. A contaminant that fits this description would be hair. Whether the hair would come from the food handler or an animal, hair strands in restaurants are a big offense.
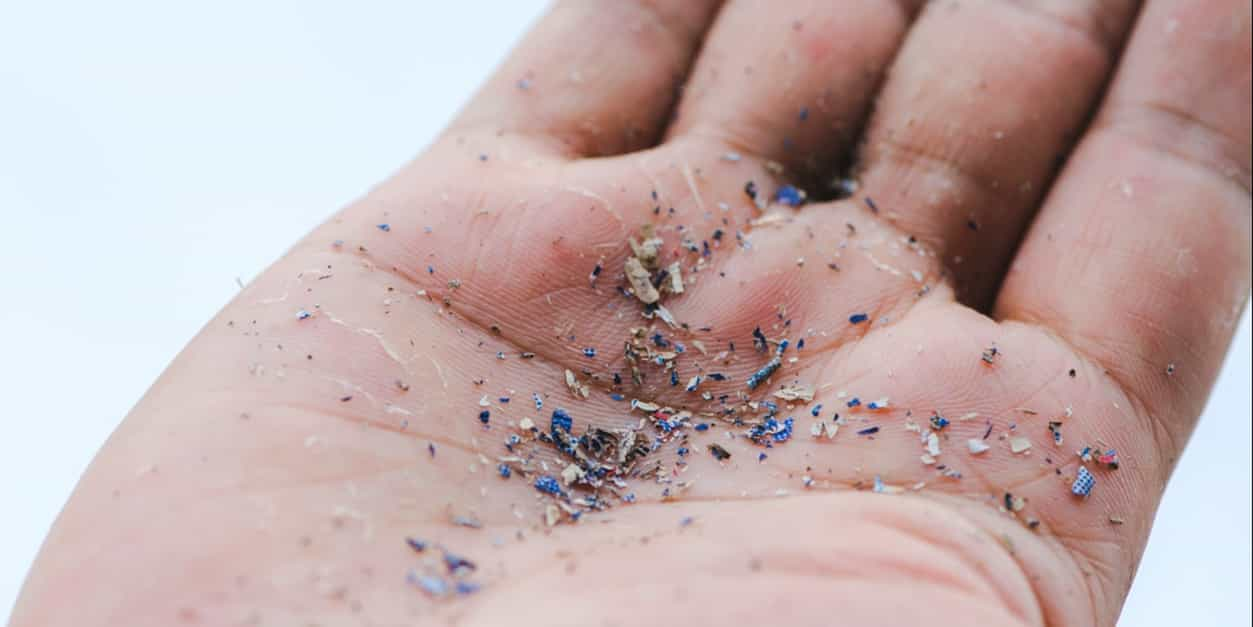

Any foreign, tangible object can be considered a physical contaminant. The premise of a physical contaminant is that it is an object that has been introduced into food and can cause harm to consumers.
Remember that food safety exam question:
Stones, hair, metal, rubber, and insects are all considered potential physical contaminants.
Plastic. This type of physical contaminant can come from food packaging, plastic paddles, as well as utensils. Although sturdy, plastics are not resistant to strain and can be easily cut by sharp objects. Plastics are serious choking hazards especially when they are of significant size. Plastic contaminants were reported to be the top foreign material to have caused recalls in 2018.
Metal. Most equipment and tools used in the kitchen are made of metal. Knives, preparation tables, meat slicers, bimetallic thermometers, and other cutleries are commonly made of metal. In addition, loose screws, joints, nuts, and bolts from machines can also become sources of physical contamination in food. Depending on the shape and size of this contaminant, they can cause injuries, choking, and even cuts to consumers.
Glass. This physical contaminant can come from glass containers and fixtures near the processing area. Even in restaurant setups, foods such as sauces and preserved products can be packed in glass containers. These containers can potentially break and fragments can work their way into the food being prepared. What is dangerous about glass is that even a small shard of this contaminant can cause serious injuries and cuts in consumers.
Rubber. Although not many materials in the kitchen are made of rubber, they still contribute to a large number of foreign material contamination in the food industry. Gaskets and seals which are used to prevent leakages in machine joints and pipes can sometimes snap and chip.
Bone. This type of physical contaminant is naturally occurring in foods. Unlike the previously mentioned physical contaminants, bones are part of food materials such as meat and poultry. Although true, fragments of bones are commonly excluded in finished products because they are choking hazards and can cause cuts. Only big bones with definitive shapes such as in steaks are considered to be part of a dish.
It's important to understand that some physical contaminations do not necessarily look dangerous at first sight such as a sharp glass or metal shard. Harmless foreign materials such as seeds or twigs can also be considered physical contaminants as long as they are not intended to be included in the product formulation.
Because pests are known to harbor different diseases, they can actually cause both physical and biological contaminations. The living conditions and behavior of pests such as mice, birds, and insects make them a source of microbial contamination from pathogens such as bacteria and viruses.
Even if pests do not get into direct contact with the food being prepared, their mere body parts can cause biological contamination. Rodent hair strands and cut pest bodies of insects can easily go undetected during preparation and contaminate foods.
Use a pest control checklist to monitor and ensure that all areas of your food establishment are free from pests.
Physical contaminations vary in degree of potential damage depending on their type and size. Their detection is a very crucial step in controlling food safety and must consistently be monitored. Over the years, detection of physical contamination has become more innovative and smarter.
Manual observation. During sorting, larger physical contamination can be detected and removed. For example, when sorting fruits, food handlers can remove twigs, leaves, or seeds. In addition, receiving materials such as flour often apply manual inspection of representative batches. Fine raw materials including flour, sugar, and starches are often passed through a sifter to determine if there is any significant amount of physical contamination.
Metal detector. Specific for metal contaminants, this machine is an effective control operation for physical contaminations. Food metal detectors can sense the presence of metal even if they are buried under a pile of products. The drawback with this machine is that it cannot detect other types of physical contaminations. A metal detector can be very useful for sorting raw materials where metals are known as frequent contaminants.
X-ray inspection. X-ray machines differentiate contaminations from their density and that of the products'. It can detect physical contaminants including metal, glass, steel, and others. When using an x-ray, the higher density materials look darker, whereas lighter ones have a lower density. The majority of the product would look uniform and contaminants can be easily detected. This type of inspection is more appropriate for products in their raw food state rather than those with complex components that have different densities.
AI-assisted inspection. With the recent application of artificial intelligence (AI) in the food industry, inspection has become easier and more intuitive. When using AI, a data library with images and descriptions of how anticipated physical contaminants are installed into the system, which is then analyzed and used to detect similarly-described foreign objects.
Detection is the first step to preventing physical contamination and its potential health effects. While very small physical contaminations are less likely to be detected, food handlers must still practice vigilance and always consistently apply monitoring techniques to the food processing system.
The potential health hazard that physical contaminations have is the fact that they can choke, cut, or injure the consumers and even break their teeth. Most physical contaminants are hard and irregularly shaped such as pieces of glass, rocks, and hard plastics.
When accidentally consumed, contaminants such as rubber, plastic, and bones choke customers and can be life-threatening when unaddressed. For physical contaminants such as hair, insect parts, and animal droppings, other health hazards may arise. The mentioned potential hazards can carry harmful biological contaminants including pathogens that may cause foodborne illnesses to customers and potentially start an outbreak.
Physical contamination can come from a number of sources. Raw materials, equipment, and even food handlers can contribute to the presence of physical contamination.
Included in a prevention and control management plan are the following steps to address physical contamination (all of which are covered in FoodDocs' Food Safety Management System):
Regular maintenance of equipment. Old equipment, whether plastic, metal, or glass, has a higher risk of breaking and contaminating foods. Regularly schedule maintenance. This operation must be an integral part of a food safety management system.
Pest control management. This management plan must contain ways how to prevent pests from taking shelter in your food premises. Operations may involve limiting access to foods, regular cleaning, and destruction of visible pests.
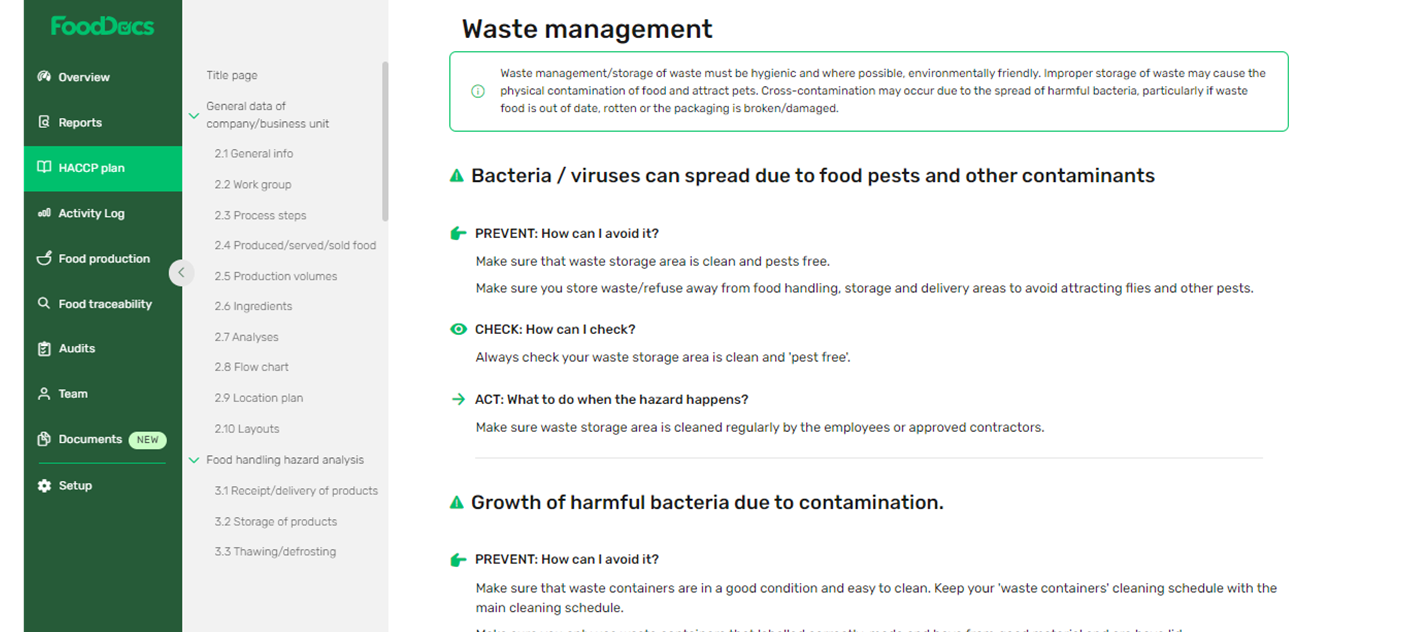
Proper waste management. Wastes attract pests and increase contamination risks or the chances of physical contaminants getting into the food preparation stages. As such, your team must create a comprehensive food waste management plan that clearly describes how your food service waste must be collected and disposed of.
Proper food safety hygiene. To prevent physical contamination that may come from food handlers, every employee must practice strict personal hygiene. These practices must include proper handwashing, proper wearing of uniform, regularly clipped nails, wearing of hair net, and not wearing any personal effects in food service.
Secure food supply from reputable sources. Ordering raw materials with low quality may mean more work for your food employees. When you receive vegetables, crops, and fruits that did not go through previous inspection and pretreatments from the supplier, the burden of inspection and preparations are transferred to your team. Secure a supplier that can provide high-quality ingredients to maintain food safety.
All of these operations that can help your food business prevent physical contamination must be part of your FSMS.
With our digital Food Safety Management System, you can get an automatically generated HACCP plan-based FSMS specifically on the nature of your food business. You can set up your food safety system in just 15 minutes.
Here are a few features of our digital FSMS that can help you manage food safety when it comes to controlling physical contamination:
Equipment cleaning and maintenance log: With this digital monitoring form, you can immediately note any faulty equipment that needs maintenance to prevent the occurrence of physical contamination.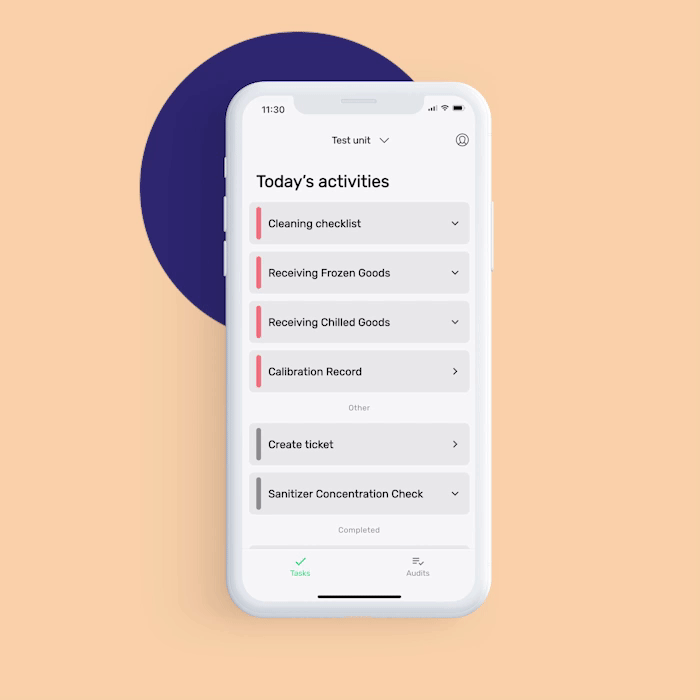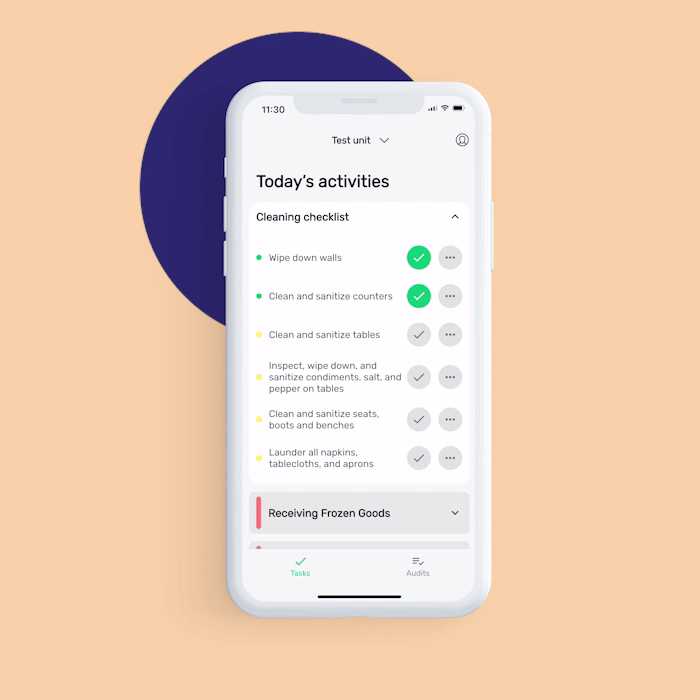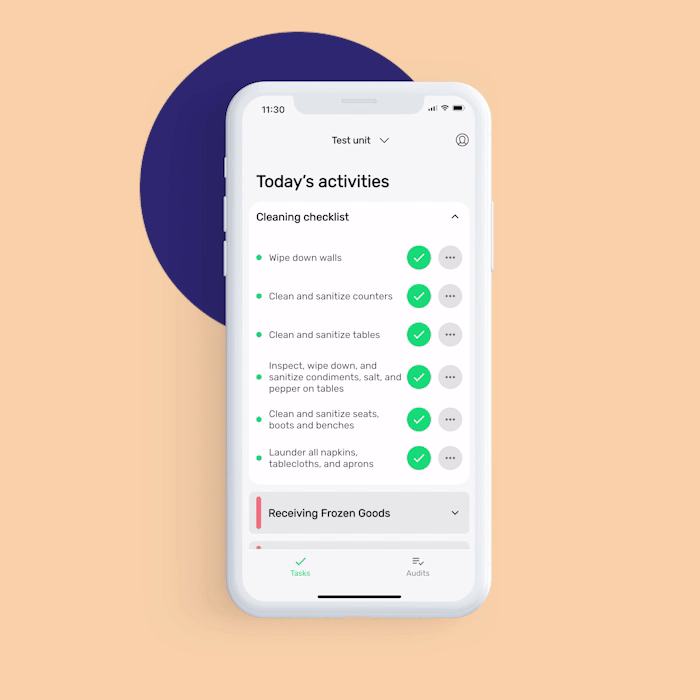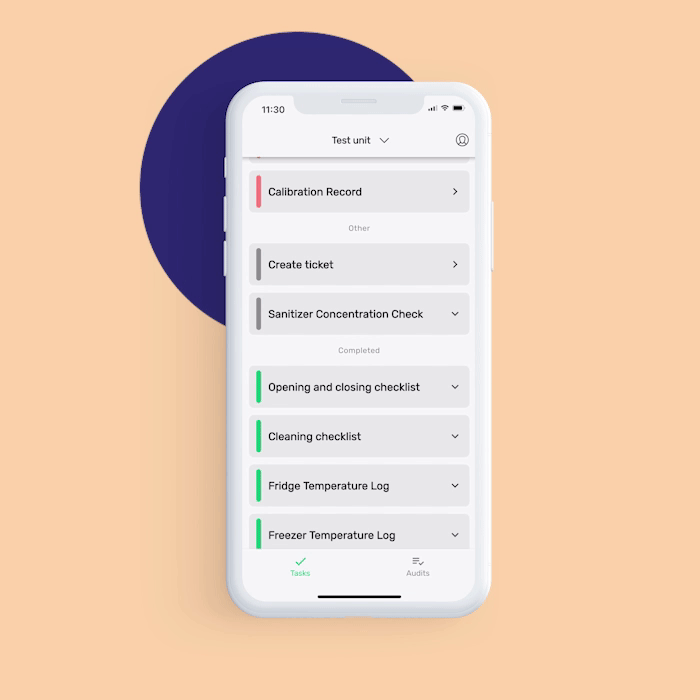

Smart notification system: Our system can intuitively send alerts to the concerned department for their immediate attention and corrective actions. This feature facilitates seamless coordination with the food safety team and the maintenance department.

In combination with our digital FSMS, we also feature a built-in HACCP plan builder for your food business. It uses the same machine learning program as our digital FSMS and can generate a complete HACCP plan for you in just an average of 1 hour. All you have to do is describe your food business by answering a series of questions from our system.
Not only does our built-in HACCP plan builder software generate a complete HACCP food safety program for you, but it also includes a feature that can accommodate prepared plans from third-party businesses.
You can easily upload pre-existing pest management and our system can help you digitize this audit plan.
Our HACCP plan also includes an automatically generated comprehensive waste management plan for your food business.
In addition to the complete components of the HACCP plan such as properly identified food safety hazards, critical control points, corrective actions, and critical limits, our system also includes a list of the most important concerns such as food contamination related to your food business. We also included verification steps, how to prevent them, and proper monitoring procedures for every hazard for a more detailed management plan.
Our team's main objective is to make food safety compliance and its maintenance an easy and efficient job. We have developed a system that takes out the repetitive and complicated tasks of crafting the most difficult compliance documents. In just mere minutes to an hour, we can help you become compliant with the most significant food safety regulations.
Experience how our system features can help you first-hand by starting our free, 14-day trial.
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...