Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Physical hazards account for one of the most common reasons for food recalls in the food industry.
Inedible food materials, such as metal, bones, and seeds, are common contaminants of food during preparation. Most of the known physical hazards in foods are originally part of the raw material or the equipment used to process them.
Any physical hazard in food can be very dangerous for both the customer and your business. A common case can cause issues as light as a consumer complaint or as serious as a food safety incident or injury requiring intensive care.
Foreign materials or physical hazards were one of the most common food safety recall reasons in 2023. While the cases of recalls in 2022 due to foreign objects were reduced, the case still remains a top reason for food recalls.
The USDA report identifies foreign objects as the second reason for most numbers of recalls in 2022. Reports of recalls related to your business are considered bad publicity and will negatively affect consumer perception.
WHAT WE'LL COVER:
Physical hazards are naturally occurring or unintentionally introduced materials into the food system that can injure customers or cause foodborne illness. Physical hazards are otherwise called foreign materials. It is one of the major hazards during food preparation.
They can be synthetic materials and sharp substances that are from the environment of the food being produced, such as metal, plastic, glass fragments, or stones. Physical hazards can also be environmental contaminants or natural parts of a product that cannot be eaten, such as bones, feathers, and seeds.
The Food and Drug Administration identifies physical hazards as any hard or sharp foreign materials found in food. The presence of physical hazards in food can lead to injury from cuts or broken teeth, especially with hard objects. In some cases, they can also lead to choking. Some physical hazards are also known carriers of other types of hazards, such as bacteria and chemical substances like heavy metals.
Federal agencies established minimum guidelines that will trigger legal actions in case of foreign material detection in food. Detection of any physical hazard in food can cause a wide recall of products. Also, failure to control physical hazards can put public health at risk.
Physical hazard in food refers to a foreign object that can contaminate foods and cause food-related injuries to consumers. The hazard can be any object from the production environment or a naturally occurring object that is part of the raw material itself.
On the other hand, physical contamination is the presence of a physical hazard in food. When the hazard enters the production system, the event is called physical contamination.
Examples of physical hazards come in many different shapes and sizes. Depending on the nature of your food operations, the most common physical hazards may vary. For example, an operation using poultry meat is most likely to encounter feathers and chicken nail trimmings when compared with a fresh fruit and vegetable business.
To give you an idea, here is a list of physical hazard examples in food:
| Physical hazard | Common objects associated with the physical hazard |
| Metal fragments | Chipped equipment for processing, blades, tools, staple wires, jewelry, or loose clips |
| Glass | Broken light fixtures, windows, overhead structures, glass guards, and containers |
| Plastic or rubber | Packaging, equipment wrapper, plastic seal, gaskets, or pens |
| Stone/sand | Dirt from raw materials or improperly cleaned footwear |
| Wood | Wooden pallets, crates, parts of raw materials, pencil |
| Naturally occurring hazards | Bones from meat, pieces of shell from seafood, a feather from poultry, and seeds from fruits |
Any physical object from the food supply chain that can injure or choke the consumer can be considered a physical hazard. The unintentional presence of foreign materials in food may indicate poor food handling practices or the lack of critical controls in place. In some consumers, physical hazards may cause long-term health effects or chronic illness.
Monitoring raw materials upon delivery, maintenance of equipment, and proper cleaning and sanitation are key food safety standards to minimize the presence of physical hazards. You can ensure all of these operations are in check when you use a digital Food Safety Management System.
Using our digital solution, you can automatically get monitoring logs with detailed instructions that will help you ensure the correct execution of food safety tasks. Our system also features a smart notification system that reminds employees of tasks that need to be done on time.
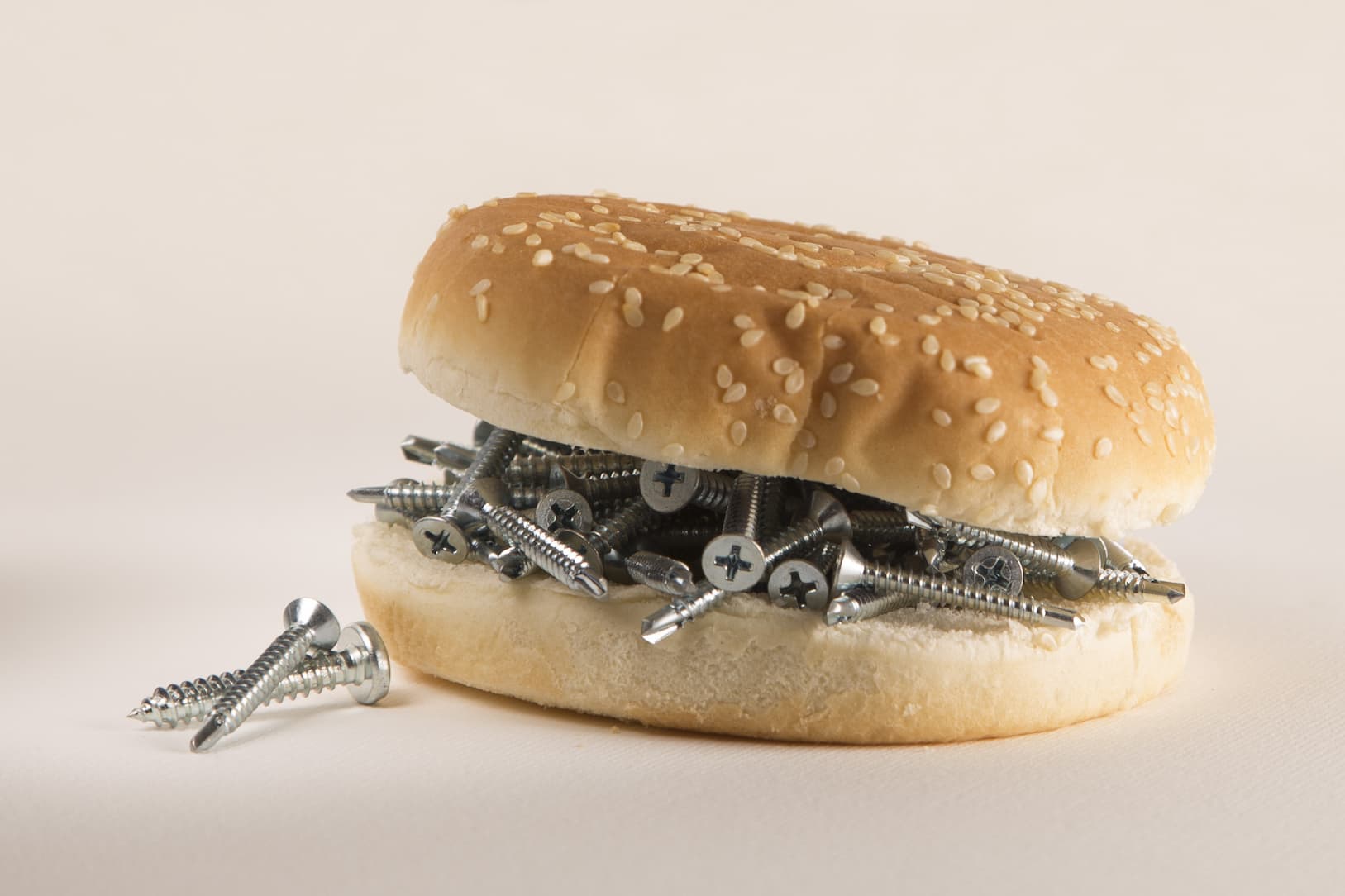

Some of the most common physical hazards in food include the following in no particular order:
The objects that are considered significant physical hazards may have different visual characteristics. This means that the risks that they have also differ significantly.
If an inspector or consumer finds any physical hazard in your products and files a complaint, your team will need to follow an investigation. The affected batch of foods may be held for inspection.
The FDA established guidelines for describing the physical hazards in foods and situations that can cause detention.
According to the guidelines, the food in question will be held for stricter inspection if the following are observed:
Stricter guidelines for issuing recalls are also available. Such reports show the significance of controlling physical hazards to maintain customer confidence and business status.
Foods in the kitchen can be contaminated by physical hazards without proper food safety management. The kitchen is a hotspot for contamination when there are no controls in place.
Food safety hazards from the raw materials can contaminate finished products and food handlers can unknowingly cause cross - contamination.
Some of the most common physical hazards or foreign objects in food that may occur in the kitchen include the following:

The foods prepared in the kitchen can be protected from physical hazards when there are proper controls in place. Preventive controls such as providing hair restraints and gloves can significantly reduce the risk of contamination of the food production process.
Food manufacturers and handlers must also undergo food safety training in any preparation process. This is a critical part of their routine to learn how to protect food and consumer health. In addition, establishing a pest management plan and maintenance program is critical for maintaining food safety in your operations.
Establish a complete food safety plan with critical programs such as waste, pest, and maintenance management programs with FoodDocs' digital Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point plan builder. Automatically get a comprehensive food safety plan that you can further customize to fit your operations better. Get detailed preventive controls and prerequisite programs that are essential for controlling physical and other types of food safety hazards.
Significantly large physical hazards can endanger the lives of consumers. In some cases, a customer may choke or get cut by a sharp object. On the other hand, less serious cases may lead to loss of appetite and consumer confidence, such as when they find a strand of hair in the food.
In general, physical hazards in food can cause the following effects:
Physical hazards can lead to a lot of problems for your food business. The cost of handling issues related to physical hazards can significantly outweigh your profits. In very serious cases, recalls due to physical hazards can lead to business closure.
In a study conducted by the Grocery Manufacturers Association, it was estimated that a food recall costs an average of $10 million. This cost significantly varies depending on the size of the distribution and other factors.
Food handlers must be particularly trained in analyzing physical hazards in food to understand their significance.
Always include the following factors when analyzing the effects of physical hazards:
Hazard analysis is a critical step for establishing preventive controls and monitoring procedures. The suitability of the preventive controls for the hazards will depend on the accuracy of the hazard analysis.
You can use our free Hazard Template as a guide for determining the appropriate controls for the physical hazards in your operations.
Foreign bodies can enter the food chain system at any point of the processing. Potential physical hazards can be inside the kitchen or introduced by outside factors. Without clear and comprehensive monitoring of important food safety policies, the foreign object may reach the customer and harm them.
In this section, we listed down some of the most common sources of physical food safety hazards in the food industry:
For example, strands of hair can carry hazardous toxins or other harmful microorganisms. They can also spread allergenic hazards when left uncontrolled.

Physical hazards may also come from other uncommon places such as clumps of dust from vents. It is important for a food business team to properly identify points where physical hazards may come from and set up monitoring controls when necessary. Food service professionals must also be trained on how to prevent the contamination of physical hazards in food.
Although the risk of physical hazards in food safety may be critical, its occurrence can be significantly reduced with very simple handling procedures. In fact, control methods for some extraneous materials are practical approaches like using a magnet or installing protective gears.
Follow this list of food safety guidelines and tips to help food workers control physical hazards:
Proper identification and analysis are keys to establishing working protective measures. When your team has analyzed which physical hazards are most likely to cause problems, you can save time in identifying the appropriate preventive controls.
Once the proper analysis and preventive controls are in place, your food facility can reduce the risk of physical hazard contamination. You can ensure safe food storage, clean food contact surfaces, and safe food items.
The best food handling practice to prevent physical hazards from injuring customers is to practice strict personal hygiene. This task involves not wearing jewelry, clipping nails, wearing hair restraints, and proper uniform. In addition, food handlers must also keep all loose objects, such as pens, away from the preparation area and always schedule equipment maintenance.
Once a physical hazard is detected, the most important reaction is to physically remove the foreign material without contaminating the food item. Once removed, the foreign material must then be properly disposed of. This method will significantly reduce the observed risk to food safety.
Other supporting corrective actions must also be done. Follow these steps when food handlers detect a physical hazard:
If in case the incident is caused by a food handler, a refresher training course is needed. Early detection and a quick response can significantly save your food business from a lot of trouble.
To identify and analyze a physical hazard, the food handler must perform an assessment. The following questions must be asked when analyzing a foreign object in food:
These questions will determine the nature and criticality of the foreign object.
Identifying and analyzing physical hazards can take a lot of time from your food safety operations. In addition, whenever you have a new or an alternative raw material and food product, you would need to perform the analysis again.
Accurate physical hazard identification and analysis will determine the effectiveness of your preventive measures. Failure to analyze the food safety risk of a foreign material may become an opportunity for the hazard to enter any stage of food production
When a business receives food, checking for physical hazards in food is also a critical monitoring task that requires completion.

At FoodDocs, you can automatically get a comprehensive list of the physical hazards related to your operations, along with the other types of food hazards. Our system generates a comprehensive, AI-powered digital HACCP plan for your business in just 1 hour.
FoodDocs' digital HACCP plan builder uses stored information from local food safety regulations and previously analyzed businesses to create highly detailed and customizable food safety plans.
.jpg?width=1065&height=924&name=HACCP_template%20(1).jpg)
When you use our system, you can get a customizable hazard analysis that contains the following components:
Our hazard analysis system uses a risk hazard assessment matrix to determine the criticality of food safety hazards. You can further tailor the analysis to your operation. For example, if a physical hazard is considered more critical for your business, you can simply click on the severity/likelihood scale to change the analysis.
In addition to the hazard analysis section, you will also get all of the other critical parts of a HACCP food safety plan, such as the following:

More than the main components of a HACCP plan, our software also generates the essential prerequisite program documents. You can get the most relevant programs for controlling physical hazards:
What sets our software apart is that you can get a digital HACCP plan in just an average of 1 hour! That significantly cuts the time you would have been spending using the traditional method for making a HACCP plan.
Our digital HACCP plan builder also incorporates revisions and suggestions for improvement from food safety inspectors. When you receive feedback, you can easily head to your HACCP plan dashboard, apply revisions, and further customize with just a few clicks!
Once you get compliant with the help of our software, you can continue your compliance journey by staying consistent with the preventive controls you established. FoodDocs' digital Food Safety Management System uses the same database and program to automatically generate the most essential digital monitoring logs, checklists, and smart features for maintaining compliance.
Make monitoring tasks easier with the following features:
Protect your consumers from all types of hazards using our digital solution. With our digital Food Safety Management System, you can ensure that food safety compliance is always controlled in the most efficient way.
Similar to our digital HACCP plan, you can further customize your digital monitoring system to accommodate unique operations. Get the flexibility that a monitoring system must have and the efficiency of smart solutions.
Experience our digital solutions using our free 14-day trial now.
Do you need more information about how to prevent physical hazards in your operations? Here are some of the most frequently asked questions about this topic:
Preventive control for a physical hazard is considered a critical control point if there is no other operation that will eliminate the risk of a foreign object from the cooked food. If the operation, such as metal detection, is the last task that can eliminate the physical hazard, then it is considered a critical control point. Cooking cannot remove physical hazards.
Physical hazards in food, whether unintentional or deliberate food contamination, can cause food-related injuries, including cuts, broken teeth, and choking.
The most common physical hazards connected with meat include fragments of bones and hair strands. These physical hazards are natural components of the meat and can enter the food processing system when improperly removed.
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...