Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Despite not being a federal law, the Food Code is an essential guide for food businesses in the US.
Overseeing a food safety system such as that of the United States is an enormous task for a single government agency alone. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration oversees at least 78% of the country's food supply.
With this much jurisdiction, the FDA employs the help of over 3,000 state and local food and health agencies to regulate food safety in related industries. To ensure an eye-to-eye level of understanding compliance with food law, the FDA publishes a new FDA Food Code every four years.
Food safety regulations often differ due to a very diverse food climate in the US. This can be seen in critical limits for additives, cooking processes, and other critical operations. Although there are minimal differences in particular regulations, one of the main food safety criteria is to protect customs from illnesses within food establishments.
In this article, we talk about the main set of guidelines issued by the FDA to different food safety agencies.
WHAT WE'LL COVER:
The FDA Food Code is a collection of guidelines published by the U.S. FDA to serve as the basis for food control jurisdictions of food agencies at any government level. This document provides technical and scientific information to guide the retail and food service industry.
It is important to remember that the Food Code is not a federal law and is provided for non-federal government agencies. It is under the jurisdiction of every state, local, or tribal food safety regulator whether to adapt to or adopt the guidelines in the Food Code.
The FDA Food Code tackles eight major areas of the retail and food service industry:
Each chapter lays out clear guidelines for food safety compliance and contamination prevention. Other health government agencies can use the information in the FDA Food Code to develop their own food regulatory policies.
The guidelines established in the FDA Food Code highlight operations that will help prevent foodborne illnesses and related injuries as a result of contamination of food for sale in the U.S. It also helps in the establishment of fair and standard approaches to food safety inspections and audits of food establishments by environmental health specialists.
The operations apply to food service facilities and food producers such as restaurants, mobile operations, retail food stores, catering operations, food processing plants, and institutions with food service areas such as schools and hospitals.
The Food Code also specifies customer groups that may be vulnerable to food safety issues, as well as the qualifications of a trained food safety employee. It helps secure that all served food to guests will not be harmful.
Together with the efforts of the Conference for Food Protection (CFP), the FDA has now established a 4-year interval for applying revisions from its then-usual 2-year interval.

The Food and Drug Administration writes the Food Code. In its establishment, major regulatory agencies, such as the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), regularly contribute significant inputs.
A significant part of establishing the Food Code is the industry meeting through the efforts of the CFP. At this meeting, significant representatives from the academia, food industry, and consumer groups meet to collaborate and collate information for the amendment and revision of the Food Code.
The Food and Drug Administration publishes the California Retail Food Code with support from the California Department of Public Health, Food and Drug Branch (CDPH). This law is based on the FDA Food Code and aims to protect public safety through safe food handling practices.
The California Retail Food Code is a food safety guideline and a part of the California Health and Safety Code. The document and food protection program contain requirements and standard operating procedures for facility structure, food equipment, and operations for the retail food safety facilities within the jurisdiction of California.
Unlike the FDA Food Code, the California Retail Food Code is state-specific legislation. Its enforcement is granted to the 62 local environmental health regulatory agencies of California.
The enforcement of the Retail Food Code is also facilitated by the Food and Drug Branch of the California Department of Public Health. This agency evaluates the operations included in the law and answers inquiries pertaining to the law.
The main purpose for the development of the FDA Food Code stays the same up until the present time, since its first establishment in 1993. The Food Code was developed as a reference for controlling food safety at all the different levels of government agencies.
The Food Code was initially set out to be revised every two years. This resolution ran from 1993 to 2001 until the FDA, with the support of the CFP, surmised to present complete revisions of the Food Code every four years instead in 2005.
In between the 4-year period, a Food Code Supplement was decided to be released for the public. The Supplement contains updates and clarifications on the provisions of the currently published Food Code. This includes the removal of redundant processes in maintaining food safety.
In addition, the Supplement also contains a collection of information on current innovations in food science and any food safety issues during the period. The document also highlights any significant food safety hazards and proposed strategies to combat them.
The FDA Food Code was mainly created to help food establishments, such as any food service segment, for public health protection by preventing the production and distribution of contaminated food with potentially devastating health consequences. To accomplish this, the Food Code contains a set of uniform guidelines for more wholesome operating conditions in the food industry.
The FDA Food Code provides essential guidelines for food manufacturers in producing and labeling foods. It also provides significant information on how food safety can be preserved through strict cleaning, food sanitation, and equipment requirements.
The adoption of the FDA Food Code contents into food safety rules by the different states of the US paves the way for more uniform and efficient food safety standards and systems. Most recent versions now identify the roles of key food employees in maintaining food safety for food vending operations.

The first-ever version of the FDA Food Code was first published in 1993. During this time, the Food Code was revised every two years up until 2001. The format used in the first-ever FDA Food Code is retained until the present time.
To date, the most recent full version of the Food Code is the 2017 FDA Food Code. This version of the Food Code was initiated during the middle part of 2016, and the contents were approved in 2017. The entire version was published the next year after its completion.
The decision to revise the FDA Food Code every four years was realized when responsible agencies surmised that collecting significant data and revising the current information takes time.
Despite the significant revisions in the FDA Food Code, not all states of the US are able to adopt the most recent version right away. The most recent Food Code included several revisions to make terminologies more inclusive and understandable while widening the scope of some provisions.
Some of the most important revisions included in the 2017 FDA Food Code include:
To date, the FDA Food Code is revised, and a new version is published every four years. This resolution came from the efforts of the CFP and the FDA. Since rule guidelines and national standards took time to be adopted by the state and local agencies, the revision and application of changes to the FDA Food Code were extended.
Originally, new versions of the FDA Food Codes were released and published every two years. This trend continued from its first publication in 1993 until 2001. Immediately after the latter year, the next version of the Food Code was released in 2005.
According to the FDA and as of 2019, fifty (50) states have adopted at least some version of the Food Code. Among these states, California remains to be the only exception.
At least thirty-four (34) states have adopted at least one of the two recent versions, whereas eighteen (18) adopted the most recent FDA Food Code.
The Food Code regulates food establishments at the state level allowing state agencies to adopt the contents of the Food Code as their local regulations.

Similar to how the food industry continuously evolves, the FDA Food Code is consistently subject to changes and improvement. This is in addition to the fact that the FDA Food Code is a tough set of guidelines to follow.
The key to standing above the rest, ensuring the safety of your customers, and preventing financial losses from food safety issues is your team's ability to adapt fast. There is no better way to do that than to use a digital Food Safety Management System that is powered by artificial intelligence and can be easily customized whenever you want.
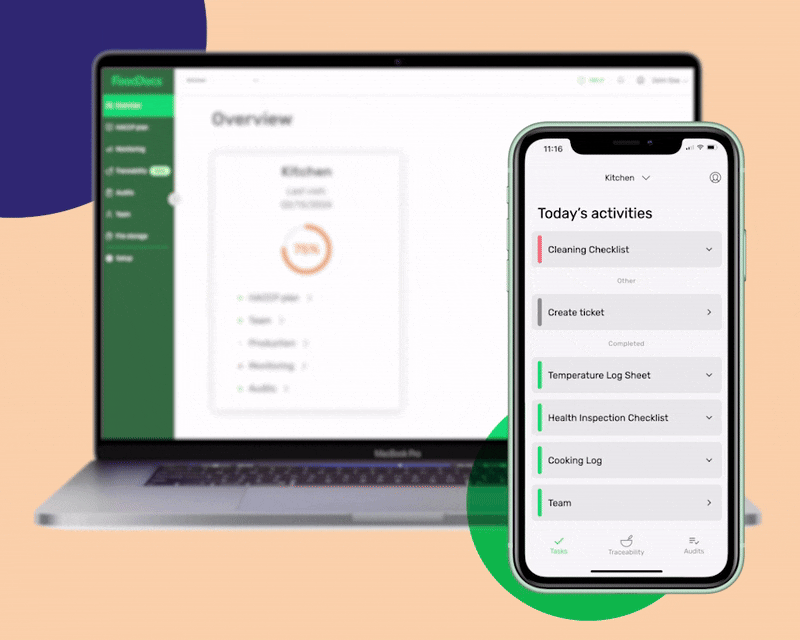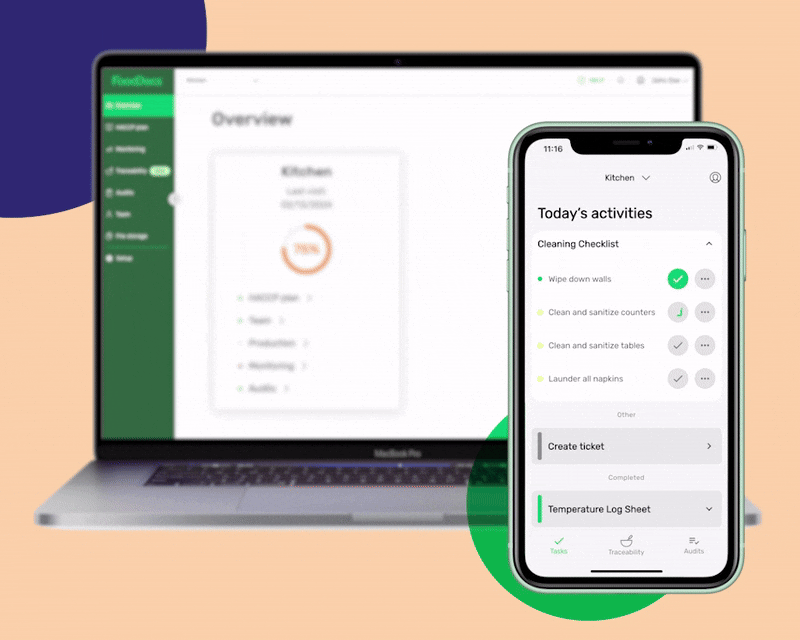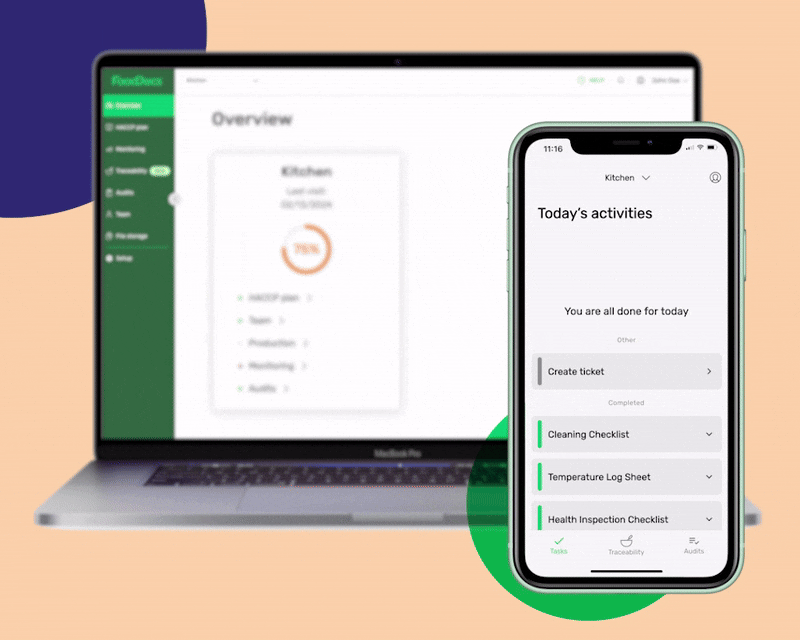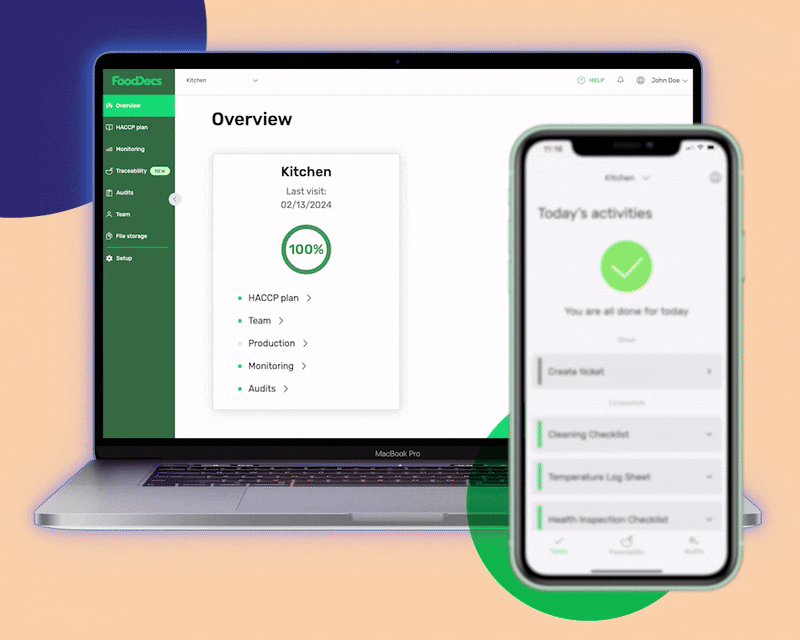
Using our digital solution, you can get the following benefits that will help you adopt the FDA Food Code in just 15 minutes:
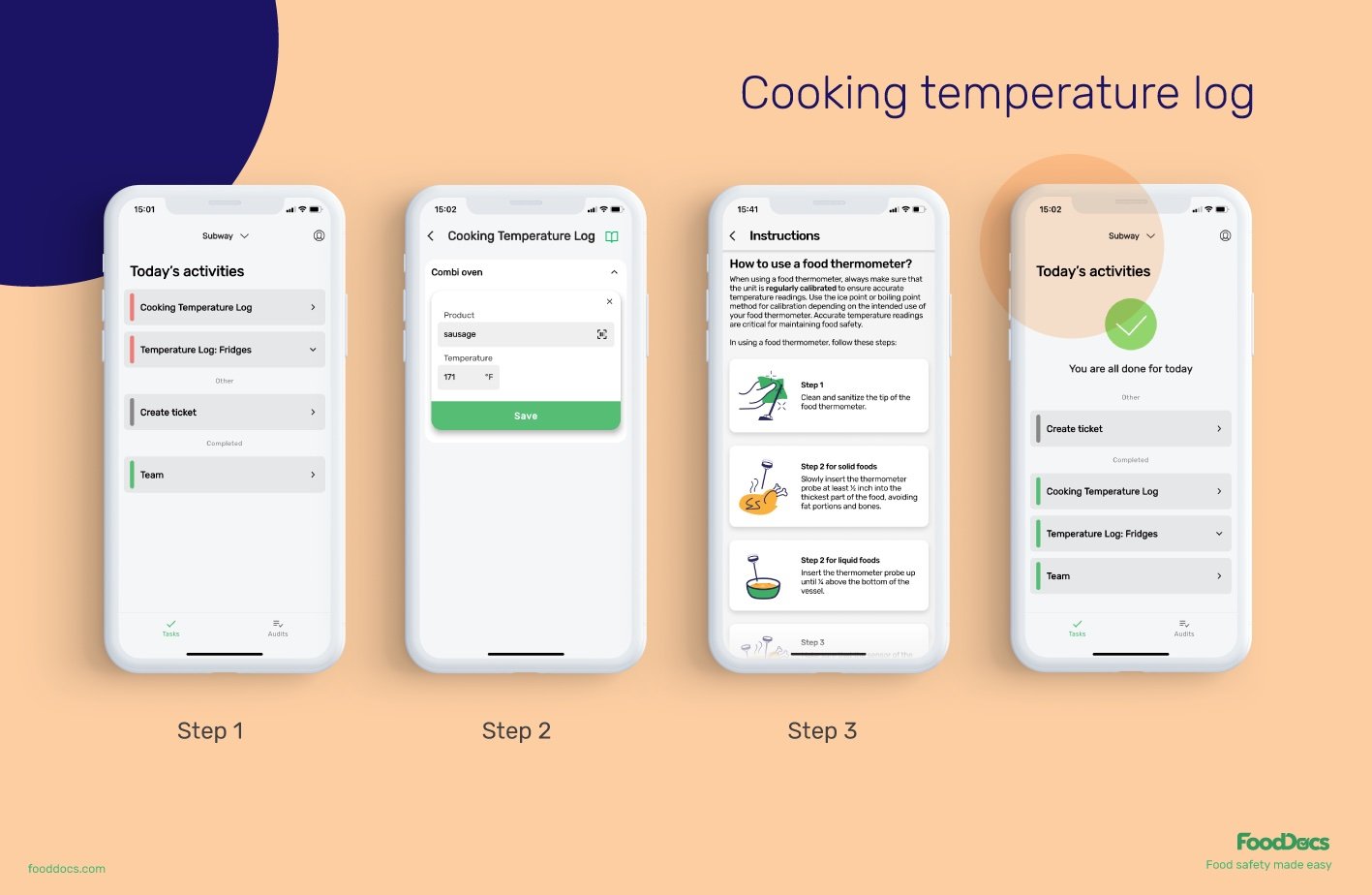
Cooking temperature log example in FoodDocs
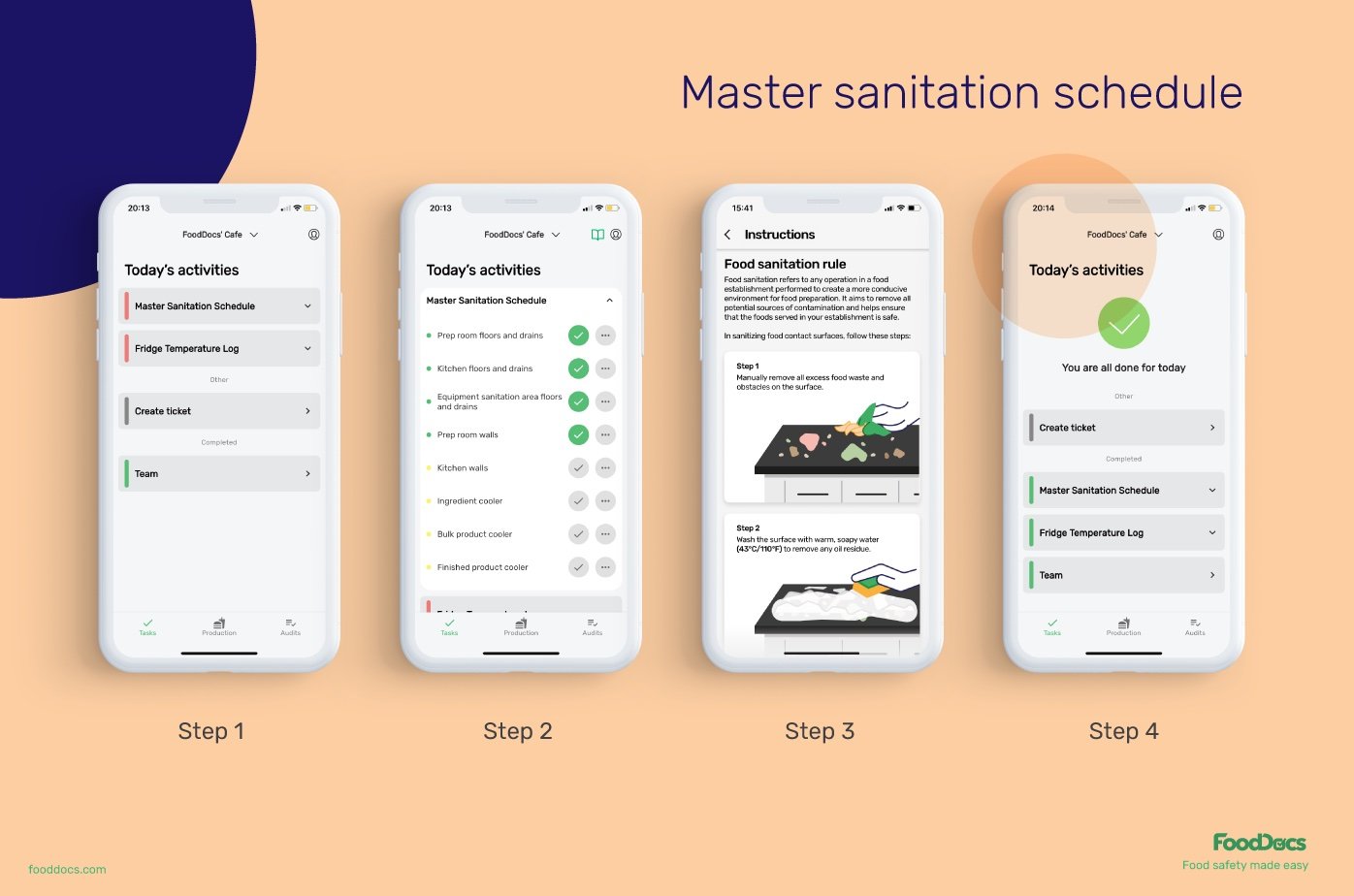
Master sanitation schedule example in FoodDocs
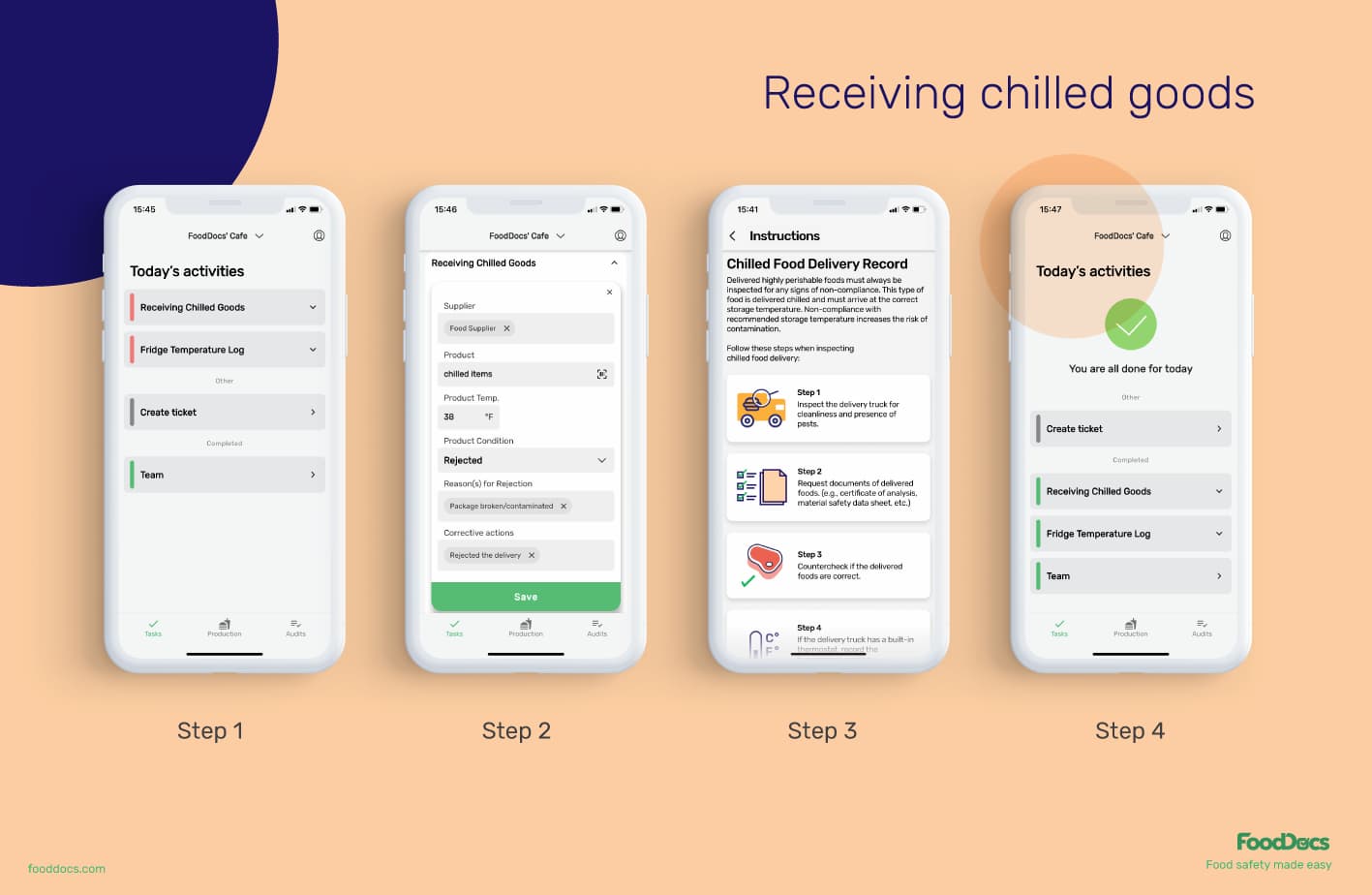
Receiving chilled goods log example in FoodDocs
In addition to features that can help optimize your operations, our system can also help managers ensure that all operations are working according to the Food Code.
Our system works based on the most updated food safety regulations. So, you can ensure that using our digital FSMS will help you satisfy Food Code guidelines at all times. What is even greater is that our system is built to be customizable, making it easier to adapt to any changes established by food safety agencies.
All of these comprehensive benefits and features can be yours in just an average of 15 minutes when you use our digital Food Safety Management System. The whole process only requires you to answer a few basic questions that will describe your operations to our system. Using artificial intelligence and a machine-learning program, our system will automatically generate a comprehensive digital FSMS.
Start your food safety journey on a digital platform now using our services at FoodDocs. You can get a free 14-day trial for your first sign-up!
Need more information on the topic of Food Code? Here are a few frequently asked questions to help you understand this topic better.
The Food and Drug Administration mainly creates the Food Code. Valuable contributions and insights are given by the United States Department of Agriculture and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to help build the Food Code Guidelines.
The Food Code is produced by the government of the U.S.A. through the Food and Drug Administration.
The FDA Food Code is a set of model guidelines for all food establishments in the U.S. and provides uniform standards for common food safety resources and operations. It contains information, suggestions, and a standardized approach to inspection, food preparation, equipment design standards, employee hygiene, working conditions, and other essential areas that contribute to public safety. The Food Code was produced to safeguard the health and interest of the public from adulterated and unsafe food characteristics.
The Food and Drug Administration of the United States publishes the Food Code.
Charts with the Food Code 3-401 must be displayed in a visible and clear spot accessible to customers. This chart will help customers understand the required level of food safety standards that a food establishment operates under and ensure safe foods.
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...