HACCP Plan for Restaurant Template: How to Create One (Free Sample PDF)
Get the exact steps to easily write a restaurant HACCP plan or download our free HACCP plan for restaurants template PDF and get compliant even...
Learn the ins and outs of the HACCP system, your responsibilities as a HACCP-compliant business, and more.
The food industry is riddled with risks and food safety concerns. One of the major things that a food business owner must consider when operating is how to minimize these risks and protect their consumers from certain foodborne illnesses.
To resolve this problem, major food safety agencies have developed the Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point system (HACCP system) that will address food safety risks before they cause problems.
Food businesses worldwide must implement a HACCP system or a risk-based preventive control system to address food safety concerns effectively.
The HACCP system is designed to prevent foodborne illnesses by focusing on critical food safety practices.
Monitoring, record-keeping, and food-handling practices are central components of the HACCP system, ensuring compliance and safety.
Implementing HACCP helps food establishments proactively manage food safety risks rather than reacting to issues as they occur.
The HACCP system begins with raw material delivery and covers all aspects of food processing, emphasizing hazard analysis at every stage.
Proper training and the formation of a HACCP team are crucial for the successful implementation and maintenance of the system.
Regular updates and verification are necessary to keep the HACCP system relevant and effective, accommodating new food safety regulations and practices.
A well-implemented HACCP system not only ensures food safety but also enhances operational efficiency, reduces waste, and builds consumer trust.
FoodDocs has an AI-powered HACCP Plan builder that can generate a comprehensive HACCP plan in just one hour, streamlining food safety management for businesses.
WHAT WE'LL COVER:
While often used interchangeably, the terms HACCP system and HACCP plan are different. HACCP system refers to the food safety management system used in the food industry to prevent the loss of control of food safety. On the other hand, the term HACCP plan refers to the written document that applies the principles and preliminary HACCP system steps.
What was initially a food safety management system made to produce safe products for astronauts became a globally recognized food management system. The HACCP system has also been used as the basis for more elaborate food safety plans in the food industry. This food system is recognized as an effective means of reducing cases of foodborne illnesses occurring globally each year.
To help food businesses learn how many principles the HACCP system involves and implement their HACCP system, we made this detailed article as your guide.

Thank you for downloading free template!
Want to get a customizable HACCP template?
Or set up your food safety system in 15 minutes?
Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point or HACCP system is a systematic and science-based approach to addressing food safety hazards before they cause problems such as foodborne illnesses. This system is an elaborate program with comprehensive hazard analysis and appropriate control measures to maintain food safety in a food business.
The HACCP system begins when the food is delivered as a raw material to a food establishment. It covers all areas of food processing, including raw material production, food receiving, storage, food preparation, proper cooking, and distribution. It aims to identify all potential hazards in a food business and then set up controls to ensure that these hazards are maintained to an acceptable level, if not eradicated.
The HACCP system and the applicable control measures vary depending on the nature of present food safety hazards and the operations of a food business.
Implementing the HACCP system starts by creating a team of individuals responsible for the different sections of your business. Your HACCP team must be well-versed with all of the associated food operations in your business to identify any potentially problematic areas.
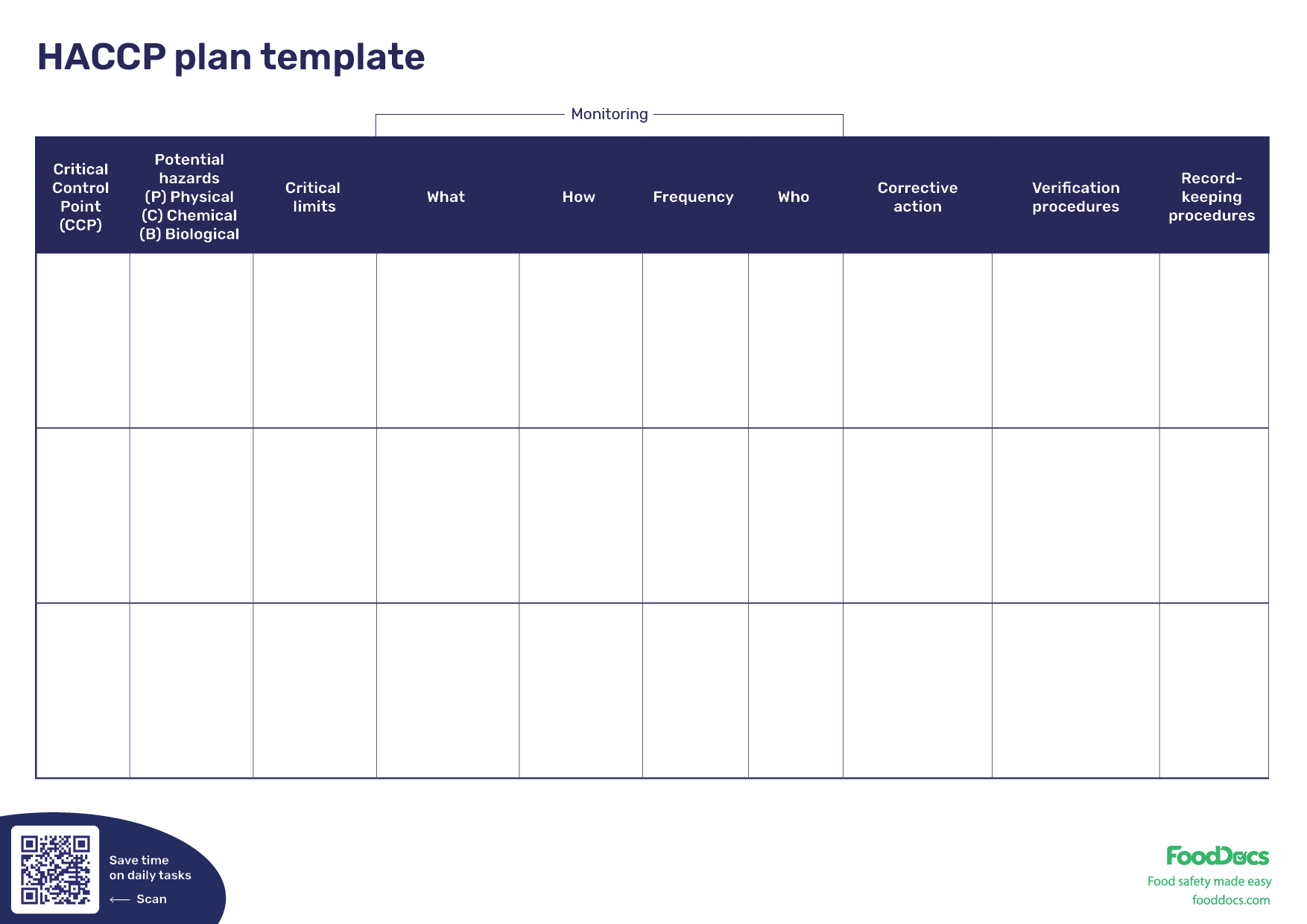
A quick explanation of how to implement a HACCP system involves identifying and thoroughly analyzing all food safety hazards in your food business operations. From these identified hazards, your team will set critical control points (CCP) and appropriate critical limits that will be used to prevent the identified hazards from causing problems.
Every critical control point in your food operation will be assigned CCP monitoring procedures and comprehensive verification activity to ensure that they are consistently controlled and that every finished product you release is safe for consumption. All conditions of the food safety system will be recorded as proof that your business follows food safety standards.
Every food business may have multiple HACCP systems as one program can be specific to a product or a process. Implementation of the HACCP system does not stop when your team has passed a food safety inspection. Your HACCP system must be regularly applied and monitored every day.

The main guiding principle of the HACCP system is for food businesses to prevent problems from occurring rather than addressing them as they happen. To do this, the concerned food safety agencies in the United States set up seven elaborate steps to create a HACCP system for food businesses.
Food safety is a constant battle between appropriate food handling and potential hazards. The HACCP food safety program ensures that every food safety hazard, whether biological, chemical, or physical hazard, is closely monitored at all times.
Potential hazards can come at any point in the food chain. The HACCP system uses critical control points, which are being applied to the essential production process of your food business. Since the HACCP system is not a zero-risk approach to food safety, its principles include corrective action plans in case of deviations and maintaining accurate records to protect your food business from public scrutiny and non-compliance sanctions.
The HACCP system for food processing was originally designed by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration and the Pillsbury Company to produce a wide variety of safe food products for individuals responsible for exploring outer space. The idea was to produce wholesome foods that were stable enough to last the expedition without causing the astronauts any foodborne illness.
The HACCP system was applied in the product formulation process up to its shelf-life and packaging materials testing. After the system's success in its intended use, the Food and Drug Administration adopted the HACCP system to address problems in producing low-acid canned foods.
Organizations such as the National Advisory Committee on Microbiological Criteria for Foods (NACMCF) helped improve the then-existing principles of the HACCP system. By the early 1990s, the HACCP system became a mandatory program in Europe and some US businesses. This mandate in the US, particularly by the United States Department of Agriculture Food Safety and Inspection Service (USDA FSIS), created a 20% decrease in foodborne illness cases.
Plug-and-play free template
The HACCP system is made up of many different aspects of food safety. These aspects help the food chain keep safety in place and ensure that consumers do not have to worry about getting sick when dining in food establishments.
The principles of the HACCP system revolve around three major factors that are achieved through various subsequent steps. These factors include:
To control different types of potential hazards, the HACCP system uses specific food handling and employee practices. These employee practices may either be critical control points or prerequisite programs. The latter practices are general food safety controls such as food hygiene and employee health used to create a safe environment and sanitary conditions for food production. The former is specifically assigned to operations to control a defined hazard. Both operations aim to produce wholesome food and safe food products.
Food handling practices under the HACCP system can be simple operations such as visual observation of raw materials, a thermal process to the correct internal temperature, holding foods in refrigerated conditions with controlled moisture levels, and even proper cleaning and sanitation. They are observed to prevent the multiplication of pathogens in the establishment. To achieve a hazard-free working environment, the HACCP system involves programs for personal hygiene, waste management, and pest control.
To ensure the regular and correct application of food handling practices, the HACCP system requires sets of CCP monitoring procedures. For this factor, individual observation tasks and appropriate monitoring log forms are required.
These procedures for monitoring aim to check whether the established critical limits are being followed. CCP monitoring procedures can also help if the established operations are enough to control potential hazards or if they need to be improved or revised.
The compiled food safety documents are then used as proof that your food business upholds food safety compliance. In case of complaints, your team will refer to these documents for the aspect of verification. Record-keeping procedures also include employee training records, certification, internal audit results, and other important documents as proof of food safety compliance.
These three factors are the core concepts involved in a HACCP system. Regular maintenance of the food handling practices is key to achieving constant production of wholesome food. In the past, all of these operations had to be done manually, especially the procedures for the monitoring part.
Before implementing the HACCP system, food handlers must learn how many steps are there. A few steps need to be satisfied for the program to be effective. A HACCP system involves a detailed description of how you do things, what you produce, who is involved, and how you would control the safety of foods.
To fulfill these objectives, you need to do the following preliminary steps for making a HACCP system:
A HACCP system is built by members of your food business. They must be from different departments of your establishment so that all food production areas will be covered. Sometimes, your team may consist of a third-party consultant who will guide and verify your HACCP-making process.
A HACCP system is often specific for a particular food processing system. That means that one food safety plan may be inapplicable to another. As such, you need to adequately describe your product's target characteristics in detail. This task includes the external characteristics as well as internal traits of your product which can be achieved through chemical testing.
In addition to defining your product, you also need to describe how you intend to distribute your products. This task does not literally translate to logistics alone but the shelf-life stability, packaging, and conditions of distribution as well.
Describe how the product was originally intended to be used and its other potential uses for the customer. Additionally, your team must identify which segment of the population the product is designed for and which segment must practice caution around the product. This step is to protect immunocompromised people (e.g., the elderly, children below 5 years old, and pregnant women) from potential danger.
Building a simple block-type flow diagram of your operations allows your HACCP team to evaluate your operations and identify any points of entry for potential hazards. A flow chart must include all related operations to processing your product. Your flow chart may also include outside operations needed to complete your production process.
To ensure that all documents, including the block-type flow diagram, are correct, your team must perform an on-site visual inspection for initial validation activities. This operation will help you identify if all areas of the production process for a particular finished product have been covered in your preliminary documents.
In addition to the 5 preliminary tasks of building a HACCP system, your team must also review the sets of prerequisite programs present in your food business. This operation aims to identify whether there are basic programs that can minimize significant hazards to acceptable levels without further adding critical controls.
Once your team has covered all 5 preliminary tasks and prerequisite programs, you are ready to create your plan and establish a HACCP system.

The HACCP system is most widely known for having seven main principles. Originally in the 1960s, the HACCP system only had three principles that were improved in the early years of the 21st century. The seven principles of HACCP are elaborate step-by-step processes that aim to identify and address all potential hazards in a food business or food processing plant. The principles also ensure that there will be no loss of control over food safety throughout your everyday manufacturing process.
The seven principles of the HACCP system include the following:
1. Identify all hazards and conduct a hazard analysis. Your team must first identify all hazards present in your food operations. This step must include the proper analysis of each product which will include information such as their likelihood of occurrence and potential severity of consequences when uncontrolled. These factors will determine if the hazard merits a CCP or if loss of control can be prevented using prerequisite programs.
Complete and accurate identification is important. Missing even just one hazard may lead your production process to release hazardous foods into the market.
Hazard analysis requires the team to have substantial knowledge of the food industry and the wide variety of hazards. They must be able to determine the conditions that encourage the potential hazards to occur and the necessary control measures.
Hazards in the food industry may either be biological, chemical, or physical hazards. Depending on the nature of your production, all types of hazards may be present.
2. Establish critical control points (CCPs). Once hazards are properly identified and analyzed, your team must decide whether the hazard is significant enough to receive a CCP or not. The HACCP system uses critical control points, any operation within your processing system that can be used to significantly control food hazards to a safe level. These operations can be proper cooking, storage of foods, and holding at the correct critical temperature.
To determine if a manufacturing process is critical to maintaining safety or what operating would a hazard need for control, your HACCP team can use a decision tree or a risk assessment matrix, respectively.
An example of a common CCP is the cooking process for meat to the correct internal temperature. Different types of meats and other organic materials have different recommended internal cooking temperatures that inactivate common enteric pathogens such as Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Salmonella spp. To keep food safe, these critical temperatures must always be achieved.
3. Establish critical limits. Establishing CCPs and critical limits requires extensive knowledge. Critical limits are minimum, and maximum values are used to determine if a hazard has been controlled. These values are commonly collected as a result of extensive research and experiences.
Deviations of critical limits may signal that the produced food is not safe for consumption and can cause foodborne illnesses.
4. Create monitoring procedures. To determine if CCPs are being consistently performed and that the foods you produce are safe, your HACCP team must come up with comprehensive ways to monitor these operations. Procedures for monitoring involve visual observations of the operations and appropriate monitoring forms that will be able to capture the essential information of the CCP.
In addition to visual observations, other monitoring procedures may be performed through physical, chemical, or microbiological monitoring of representative samples. Perhaps one of the most common monitoring procedures is the use of a properly calibrated thermometer for measuring the critical temperature of food samples.
All observed information must be logged into a detailed monitoring form. These forms will serve as proof to regulatory agencies that your food business is following strict food safety standards, especially for a HACCP audit. A part of every company employee training must be to orient them on how to perform different procedures for monitoring.
5. Set up corrective actions. Since the HACCP system is nowhere near a zero-risk program, deviations may still happen. In such cases, your team must be prepared to handle non-conforming samples. In case critical limits have been exceeded, your team's first reaction cannot be the immediate disposal of products. Unless the food items cannot be saved, corrective actions must be performed to minimize losses while still keeping safety in mind.
A corrective action plan template includes detailed steps on how to bring back the hazard to acceptable levels. Batches of food applied with a corrective action must be closely monitored to ensure that if in case of problems, your team will be able to trace and address them.
6. Implement verification procedures. Verification and validation activities aim to check whether the HACCP system you established is effective or if it needs to be updated. Regular verification can be performed on-site and by reviewing the existing monitoring documents.
Initial validation of the HACCP system is performed after implementation. Once proven successful, validation activities will be set at regular intervals to monitor if the system is effective. This step also helps your team prepare for unannounced health inspections.
The verification of your HACCP system can be performed with the help of a food safety consultant. Alternatively, if you have a smart food safety management system, you can easily validate if your HACCP system is efficient and effective through a real-time dashboard.
7. Establish record-keeping methods. The HACCP system heavily revolves around document and record-keeping. Your best evidence that the food you produce is safe is to secure a detailed food safety plan and the regular results that you gather from everyday monitoring.
Record-keeping also includes the need for a well-documented HACCP plan, the list of team members, related food safety plans, and other certifications related to your food business.
The success of your HACCP system implementation depends on how well-put you make your plan. All hazards must be considered and complete control measures must be in place. Making a HACCP plan and implementing the system is not an overnight job. It will take your team months to build it, less if with the help of a consultant.

Verifying your HACCP system can be done through on-site visual inspection and reviewing your recorded documents. As explained, HACCP system verification is performed to determine if your system is effective enough to control the identified hazards in your establishment.
The aspect of verification also helps to determine if your company employees understand how the HACCP system works. To fulfill verification procedures, complete documentation of monitoring records and the HACCP plan is required.
One way a manager can verify that the HACCP system is working is to perform an internal audit.
A HACCP system is a continuously changing and improving system. As your food business grows and adapts to the trends in the food industry, so should your HACCP plan do so as well. As such, your HACCP system must be flexible enough to accommodate revisions and improvements after a thorough review.
The next question is, when should you review your HACCP system? A successful HACCP system requires regular updates for the following reasons:
At least once a year, your HACCP team must schedule a HACCP internal audit and review. This frequency is enough to keep your system up to date and adapt on time to the most important trends in the food industry. A review of the HACCP system also gives your team the opportunity to improve any poor functioning operations and introduce more efficient processes.

The implementation of a HACCP system helps food businesses in more ways than one. The benefits of having a food safety management system transcend both safety and quality control. It can also help a food business boost profit by earning customer approval and confidence.
When you implement a HACCP system, your food business can garner the following benefits:
Food safety will always be a key to the success of any food business. This aspect of running an establishment in the food industry must be maintained at all times and be interpreted through the safe food products that you serve the customers.
For budding food businesses, you need to get your HACCP system in place as soon as possible. The quickest way to do this is to use our built-in digital HACCP plan builder. All it takes for our system to create a comprehensive plan is for you to answer a few basic questions regarding your manufacturing process and other operations. In just a mere 1 hour, you can already become food safety compliant by implementing your HACCP plan.
Although the HACCP system is more concerned with the production of safe food products and the protection of public health, it can be considered part of a quality management system. Sources have pointed out that the nature of HACCP wherein it ensures objecting production of wholesome food makes it eligible to be called a quality management system.
The implementation of the HACCP system is recognized worldwide. Despite this, mandating the implementation of the system is under the discretion of the country. In the UK and several parts of the world, implementing a HACCP system is mandatory. This means that all food businesses operating in the UK are required to implement a HACCP plan.
In the US, the mandate is a bit more complicated. What's clear is that businesses involved in handling juice and seafood under the Food and Drug Administration are mandated to establish a HACCP system. In addition, the United States Department of Agriculture uses the same mandate for food businesses handling meat.
The US food system also includes finer regulations on this matter. Use this table to determine if your food business is required to implement a HACCP plan or create a risk-based plan according to the Food Safety Modernization Act of 2011.

Building a HACCP plan and implementing the system requires several resources including time and money at most. The whole process, including reviews and revisions, may take around 12 months and cost you thousands of dollars just to finish. While hiring a food safety consultant can significantly reduce the time of making the plan, the cost could possibly inflate depending on the rate of the consultant.
In addition to conceptualizing the HACCP system, your team would also need time to apply revisions from validation activities. Your team must create an adaptable HACCP system that can be revised without compromising quality and safety.
With the fast-paced evolution of the food industry, our team at FoodDocs has taken the abovementioned challenges and created a digital solution for food businesses.

Using our built-in HACCP plan builder, you can get a complete and comprehensive digital HACCP plan with the following components:
In addition to the major components of a HACCP system, our digital solution also covers the documents needed for prerequisite programs that include the following plans:

These plans are just some of the elaborate food safety documents that our digital solution can provide you with in just 1 hour.
Powered by artificial intelligence and a machine learning program, our digital solution uses your answers to some of our basic questions to create a comprehensive HACCP plan built specifically for your food business.
To accommodate any unique manufacturing process, our digital solution can easily be customized. You can digitize your own hazard analysis, indicate its risk assessment, and apply appropriate food safety operations.
If what we offer seems too good to be true to you, you might want to try it for yourself. You can get your HACCP plan in just 1 hour by using our free, 14-day trial. Avail of our full HACCP system product so you can download, print, or digitally share your HACCP plan with your food safety inspector and team.
Get the exact steps to easily write a restaurant HACCP plan or download our free HACCP plan for restaurants template PDF and get compliant even...
Get a clear and complete breakdown of the most common Critical Control Point examples in HACCP for biological, chemical, and physical hazards.
The HACCP allergen control program is one of the crucial prerequisite programs of an HACCP plan. These are the key components and goals of using one.