Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Use this thorough yet simplified guide to start your GMP certification journey on the right foot.
If you’re wondering how to get GMP certified, begin with a thorough analysis of your quality systems and computer systems to ensure they comply with Good Manufacturing Practices standards, especially in terms of documentation, data integrity, and system security.
Next, conduct detailed inspections of your manufacturing facilities and equipment logs to verify that the physical environment and machinery meet the required operational standards.
Finally, review the qualifications and training of all personnel to confirm they are capable of performing their duties according to GMP regulations, culminating in a final assessment by the certifying body to decide on certification.
WHAT WE'LL COVER:
Being GMP certified means that your manufacturing facility has attained a Good Manufacturing Practices certification as a result of passing a third-party GMP audit that guarantees you meet all the compliance requirements. Failing to meet these requirements will result in a list of GMP violations that must correct before becoming certified.
A GMP certification lasts three years, on average. After that period, manufacturers must renew their GMP-certified status with another third-party audit from a certification body.


Thank you for downloading free template!
Want to get a customizable HACCP template?
Or set up your food safety system in 15 minutes?
You can schedule your third-party audit whenever you want. However, we recommend that the food manufacturers we speak with first ensure that they’re satisfying GMP compliance requirements.
Think of it like a “practice round”. There’s little point in writing a test you didn’t study for. To manufacture food products with high safety and quality standards, do what you can to meet these GMP requirements:
Ensuring the safety and integrity of products starts with the design and maintenance of facilities and equipment. They must be specifically constructed to eliminate risks of contamination, cross-contamination, and errors. This means carefully planning the layout of the facility to promote a logical flow of materials and personnel, which helps minimize mix-ups.
Operationally, equipment must be not only operated according to established procedures but also regularly maintained and calibrated (e.g., thermometers or meat slicers). This ensures that equipment functions properly and any discrepancies are quickly addressed so that teams can consistently produce high-quality products.
The backbone of any manufacturing operation is its team. Every individual involved in manufacturing must be thoroughly trained and qualified for their specific roles. This training includes a deep dive into GMP principles, job-specific duties, and staying updated with industry standards.
It's also crucial that each employee understands their specific responsibilities and the critical role they play in maintaining product quality and safety. This awareness is key to fostering a food safety culture of compliance and excellence.

A secure and robust system for documentation and records is essential for compliance with GMP standards. Manufacturers must maintain comprehensive documentation that describes all procedures and specifications involved in the manufacturing process in detail.
You must also ensure accurate and up-to-date records of each production batch. These records should detail the process, testing, and any deviations from standard procedures, and they must be readily accessible for auditing purposes. This level of detail supports transparency and traceability throughout the manufacturing process.
Quality control is a critical pillar in manufacturing. A rigorous quality control system must be in place, encompassing testing of all raw materials, in-process materials, and finished products.
These tests are designed to verify the identity, potency, purity, and quality of each item, adhering strictly to predefined standards and specifications. This level of meticulous testing ensures that every product consistently meets the required quality criteria before reaching the consumer.
Effective systems for complaint management and product recall are non-negotiable. Manufacturers must have procedures in place for efficiently receiving, reviewing, and addressing customer complaints to ensure that issues are resolved promptly and effectively.
Your business should also have a clearly defined process for product recalls. This includes thorough investigation, execution of the recall, and timely notification of regulatory authorities.

The first step in obtaining GMP certification involves a thorough analysis of your existing quality systems to ensure they align with GMP requirements. This includes evaluating your quality control procedures, documentation practices, and overall compliance with industry standards. It’s essential to identify any gaps or areas for improvement that could hinder certification.
Ensuring that your computer systems are reliable, secure, and capable of maintaining the integrity of data is crucial. The second step examines the software and hardware used in production and quality control to verify that they meet GMP standards, particularly in terms of data accuracy and traceability.
The third step involves a detailed inspection of your manufacturing facilities to ensure they meet the physical conditions required by GMP. This includes the layout and design of the facilities, air and water quality control, and the maintenance of a clean and hygienic manufacturing environment.
Reviewing equipment logs is critical to ensure that all machinery used in the manufacturing process is suitable for its intended purpose and is regularly maintained and calibrated. This fourth step checks for consistent performance and compliance with operational standards.
The fifth step assesses the training and qualifications of all personnel involved in manufacturing to ensure they are capable of performing their duties according to GMP standards. This includes evaluating training records and ensuring that ongoing training programs are in place.
The sixth and final step in the GMP certification process is the decision made by the certifying body based on the analysis and reviews conducted. This decision will determine whether your company is granted GMP certification or if further improvements are required.

It can take up to 12 months to become GMP-certified and as little as three months, on average. Of course, this depends on the complexity of your manufacturing company’s specific operations and how many of your existing processes need (or need not) to be changed.
GMP certification can cost anywhere from $10,000 and $50,000. The price range varies so widely because key factors that influence cost do, too.
For example, factors that can impact the cost of GMP certification include:

In addition to the factors listed above, here are some other areas that might incur further costs:
You can simplify your GMP certification journey by:
In today’s age, using technology is by far the most effective way to maintain food safety compliance — especially at scale. Check out our guide on how to buy food safety management software and keep reading to see how FoodDocs can help your business.

The easiest way to get GMP certified is to use food safety management software that helps manufacturers easily complete daily tasks, monitor operational compliance, and maintain regulatory requirements.
In addition to FoodDocs, some common GMP compliance software vendors for SMEs are:
Whatever software you choose, it should support your GMP-aligned needs.
Implementing an easy and intuitive food safety management software will help save businesses time, money and, more importantly, from non-compliance.
Try FoodDocs free for 14 days and see all the features below in action!
GMP standards mandate thorough and accurate documentation. FoodDocs stores every monitoring and traceability log you record, ensuring that all essential records are readily accessible for audits.
The food safety management software also safely stores documents such as your HACCP Plan, Standard Operating Procedures, Prerequisite Programs, training certificates or food handler cards, and any other critical documents your business requires for GMP compliance.

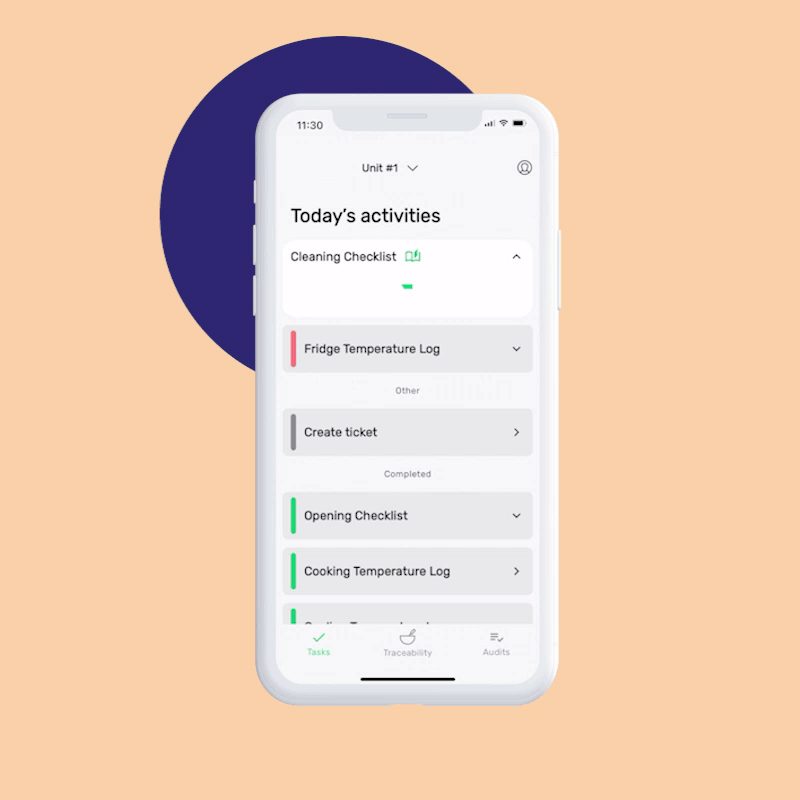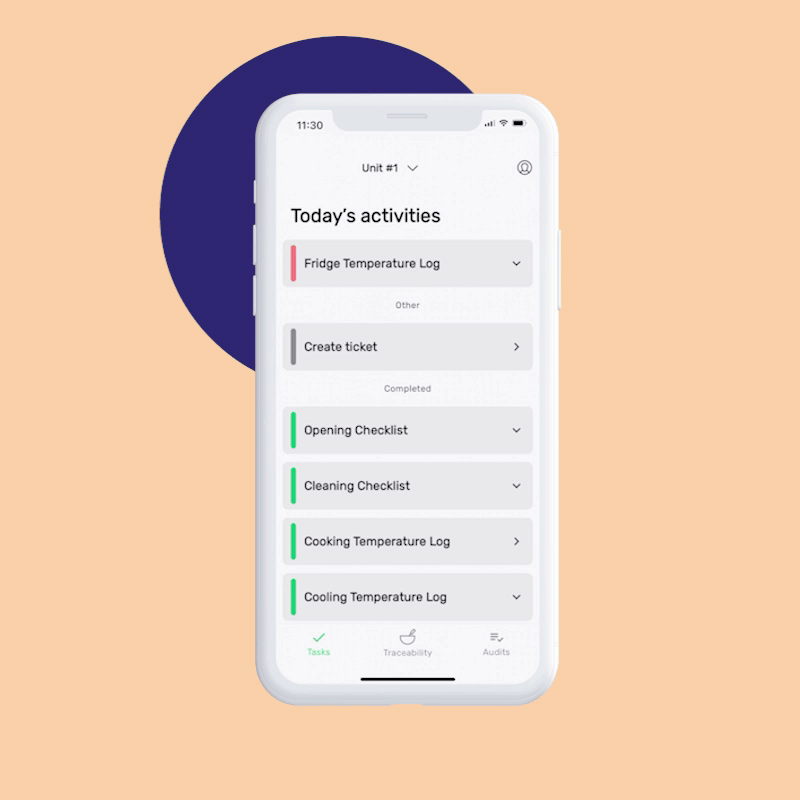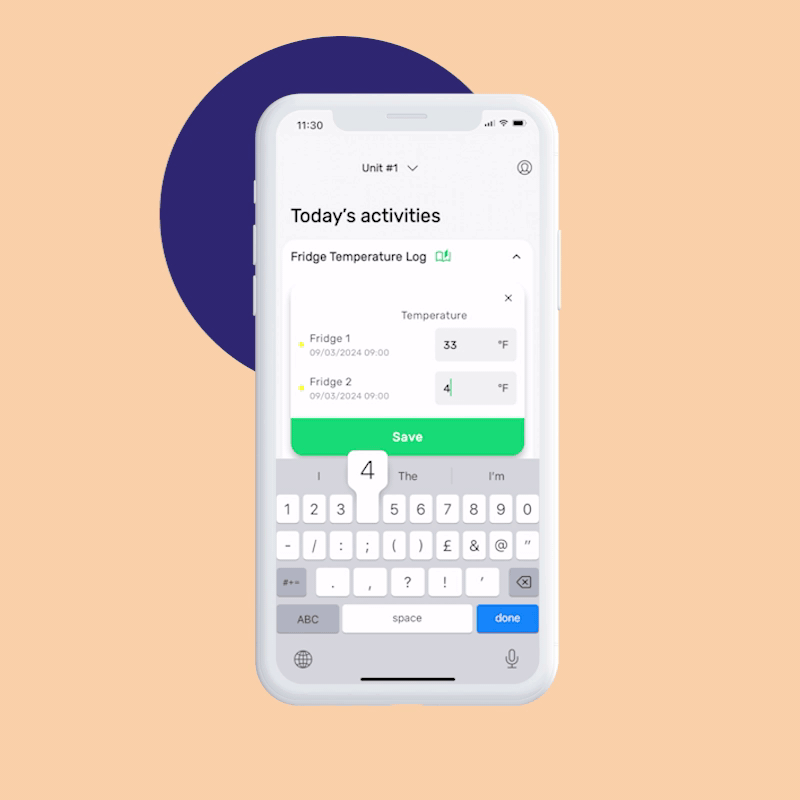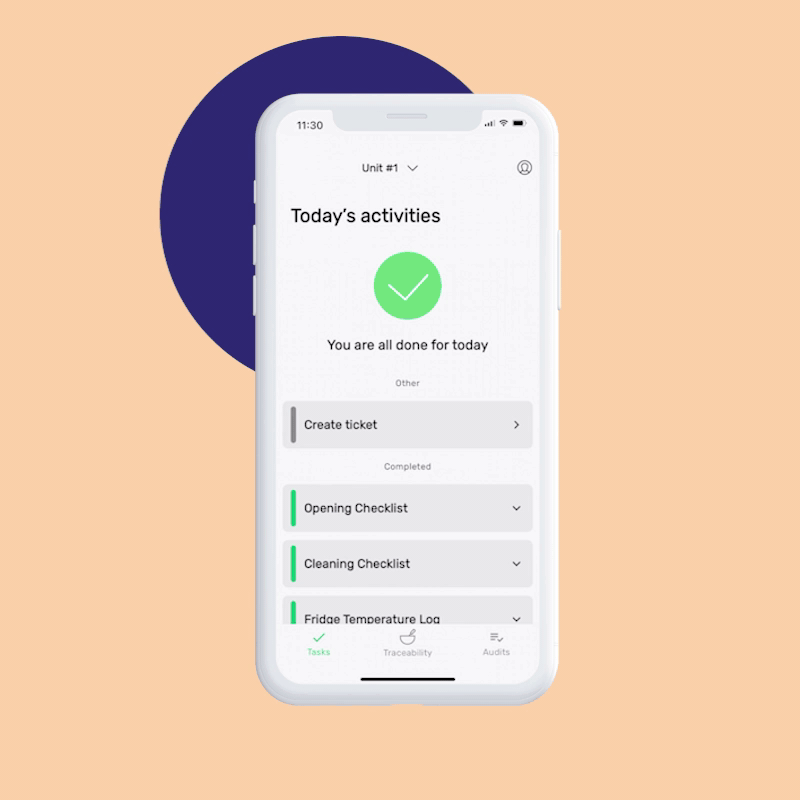
When setting up FoodDocs’ digital food safety system, you can assign role-based tasks to specific team members. Every day, they’ll get automatic notifications in the mobile app for their responsibilities.
Let’s take a temperature check or receiving log, for example. Digital monitoring checks include corrective actions so if an employee completes that task but something is out of range (i.e., temperature’s in the danger zone or a shipment was damaged), an immediate prompt will guide your team on how to respond, ensuring food safety and saving time on training.

FoodDocs’ smart mobile app offers a time-saving, pre-filling solution. It fills in monitoring checks automatically according to previously inserted data. All you need to do is confirm the logs or change them.
This saves your team’s time on repetitive activities and enables you to focus on the most important things in your kitchen. Other features such as auto-calculating shelf-life dates further enable employees to work faster and smarter toward GMP compliance.

If you’re striving to be GMP certified, your daily food safety management tasks should reflect that goal. FoodDocs allows you to use pre-set or customized step-by-step instructions for every single task in your system. You can even add photo or video examples of what completing the task successfully looks like (e.g., a cleaned stock room or good versus bad shipment).
What this does is effectively help train employees on-the-go. By all means, have regularly scheduled team-wide training. But in an industry that requires and rewards continuous improvement, FoodDocs’ step-by-step instructions is an easy way to increase knowledge and improve accountability when it comes to GMP compliance.

Managers can access FoodDocs’ real-time overview dashboard. This is a great way to get a high-level view of your present-day GMP compliance. If it’s not trending well, you can easily create an internal GMP audit and conduct a mock walkthrough with your team.
Completing this audit — successfully or not — will give your team a clearer picture of which aspects of the GMP audit they need to improve before the real thing. Is it in personal hygiene? Processes and controls?
Plus, an ongoing record of the internal audits you’ve run is a great way to prove to third-party auditors or inspectors that you’re always trying to improve your GMP compliance.

Ultimately, FoodDocs helps everyone from managers and supervisors to food handlers save more time so they can focus on the product and the customer.
Traceability logs are simple too, taking only three taps: select the product by searching for it manually or using a built-in mobile scanner to make the process faster thanks to EAN/QR codes. Then enter the supplier name, invoice number, and an image of your invoice as proof and quality control fields if necessary.
FoodDocs’ Traceability system helps to track your ingredients and food items through all stages of production. You can even complete traceability logs and attach monitoring tasks to the same product batch right away. Simply log important quality checks like the cooking temperature of the prepared batch during the preparation process.
This ensures necessary traceability and visibility in case of a recall or customer complaint and will help you ensure high-quality food safety.
Whether recalls or customer complaints, a digital traceability log also makes it possible to find a product’s historical data for your local authority or auditor in seconds. You can easily search by product, batches, ingredient, or expiry date (which are automatically calculated) to prove compliance.
Companies in the manufacturing sectors of food, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and dietary supplements need to ensure their products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards.
GMP certification is issued by third-party organizations that specialize in auditing manufacturing processes against set GMP standards.
A GMP-certified facility is one that has been audited and certified to meet the specific standards required under Good Manufacturing Practices, ensuring products are made safely and in compliance with regulations.
Yes, GMP certification is highly regarded as it demonstrates a commitment to quality and safety in manufacturing processes, enhancing product credibility and consumer trust.
GMP certifications can be verified by checking with the issuing certification body, or by viewing the certification details typically displayed on the manufacturer’s website or directly on product packaging.
Yes, there are various GMP certification courses available that provide training on the GMP guidelines, procedures, and compliance strategies for individuals and companies in relevant industries.
The five key GMP requirements typically include:
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...