Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Cold holding is a critical operation in any food establishment for keeping high-risk foods safe for consumption.
In a fast-paced restaurant environment or high-volume food production facility, several tasks are critical for food safety compliance. One of which is monitoring the cold-holding temperature of high-risk foods. This food safety approach is widely used in the food industry for preserving the safety and quality of highly perishable foods.
The maximum cold-holding temperature for food is 41°F (5°C) or below. At these cold-holding temperatures, the growth of harmful bacteria is slowed and the potential to cause foodborne illnesses is significantly low.
The maximum cold-holding temperature for foods refers to the highest temperature at which foods can stay safe for prolonged periods.
Maintaining the maximum cold holding temperature is a basic food safety practice and a critical task for any food business. Cold food temperature helps ensure that food supplies are optimized for use and prevent unnecessary food spoilage caused by harmful pathogens.
The maximum cold-holding temperature for high-risk foods is 41°F (5°C) or below.
Different food products may require lower and more specific cold-holding temperatures for safety. E.g. Fish and seafood require a lower maximum cold-holding temperature.
Cold-holding food ensures that the dishes are away from the temperature danger zone and are stored in containers away from contamination.
The cold-holding temperature must be consistently monitored to maintain effectiveness.
Cold holding is important for any food business as it helps protect public health, preserve the quality of foods, reduce food waste, help comply with food regulations, and prevent food safety issues.
Cold holding uses low temperatures to keep cold food cold, whereas hot holding is used to maintain high temperatures for hot foods.
According to the most recent FDA Food Code, the cold-holding temperature must be monitored at least every 4 hours.
You can use FoodDocs' smart Food Safety Management Software to monitor cold-holding temperatures and ensure food safety compliance intuitively. You can get digital monitoring logs and a smart notification feature to help you consistently monitor your operations.
WHAT WE'LL COVER:
It is important to note that the maximum cold-holding temperatures may vary depending on the nature and composition of food items. Food service establishments must adhere to strict food safety regulations to prevent the spread of foodborne illness. Constant and regular monitoring is required to ensure food safety.


Thank you for downloading free template!
Want to get a customizable HACCP template?
Or set up your food safety system in 15 minutes?
Cold-holding perishable food is a must for food businesses. Restaurants and other food establishments from the food industry handling high-risk foods identify cold holding as one of their critical control points.
The main idea of cold-holding food is keeping it away from the food temperature danger zone or ambient food temperature while storing it in an appropriate, airtight food container.

Regular maintenance of safe cold holding temperature is crucial for preventing the growth of pathogens, preserving food quality, meeting regulatory requirements, and protecting consumers.
Failure to maintain cold holding temperatures can result in several problems that can affect your food business brand. As such, all food handlers must be trained and oriented on maintaining cold-holding conditions.
to help monitor shelf-life
What's the difference between cold and hot holding temperatures?
Cold-holding refers to storing foods at low temperatures, around 41°F (5°C) and below, whereas hot holding preserves food stored at 135°F (57°C) or above by stopping bacterial growth.
Hot-holding and cold-holding food temperatures are two temperature ranges for maintaining food safety. Each correct temperature range is intended for particular purposes and types of food.
The hot holding temperature is used for holding hot foods in conditions where bacteria and other pathogens cannot grow. Hot holding temperatures are often used for displaying foods for service, such as soups, meats, and prepared dishes. Hot and freshly prepared foods are hot-held at 135°F (57°C) or above using steam tables or warming trays.
These operations are required to meet regulatory standards for protecting public health. Food handlers must maintain the correct food temperatures consistently and correctly through constant monitoring.
Cold food items should always be held at 41°F (5°C) and below to maintain food safety by preventing the growth of foodborne illness-causing bacteria. At this temperature, both bacterial and enzymatic activities are slowed down, and the peak quality of food is preserved.
The cold holding temperature is maintained using appropriate machines and equipment, such as a refrigerator, refrigerated display, and coolers. Although a freezer is technically used for cold holding (see our freezer organization chart and freezer temperature chart), its temperature is too low to use for displaying ready-to-eat foods. Along with these cold-holding machines, a calibrated digital food thermometer must always be available.
You must check the temperature of cold food that is being held with temperature control every four hours, at least. According to the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) guidelines, that's best interval for measuring the temperature of cold-holding high-risk food products..
It is also important to note that the interval of measuring cold holding temperature may vary. You can monitor the temperature every two hours if the food is very high-risk. This option also ensures greater food safety.
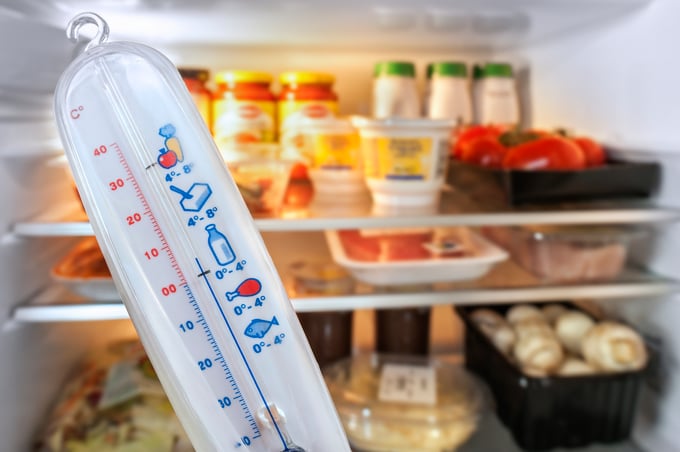

Cold holding requires precision in maintaining temperature and regular attention. These are key parts of restaurant food storage guidelines. The guidelines are used to ensure that the operation can protect the food from food spoilage and prevent foodborne illnesses from occurring.
By following these cold-holding temperature guidelines, the safety of customers and the prevention of the spread of foodborne illness can be ensured.

Temperature measurement is a very important part of cold-holding foods. It will help food handlers ensure that foods are being held at the correct and safe temperature that will prevent bacterial growth. In measuring the temperature of cold holding operations, the accuracy and preciseness of the measurement are critical food safety practices.
This set of tasks for monitoring temperature is very important and must be consistently followed. Failure to follow the steps can lead to inaccurate temperature readings, putting public health in danger.
In addition, the task must also be consistently performed in regular intervals to ensure proper cold holding. When food handlers follow this task, they can immediately apply corrective action procedures in case of unexpected non-compliance with food safety regulations.

Efficiently perform these tasks by using FoodDocs' smart Food Safety Management System. Our smart software uses artificial intelligence and a machine-learning program that can provide intuitive solutions for monitoring the temperature of your cold-holding units.
The recommended cold holding internal temperature for TCS food or time/temperature control for the safety food group is 41°F (5°C). TCS foods are considered significantly high-risk and harmful for consumption without proper temperature control. As such, they are very prone to contamination by different foodborne pathogens and can become spreaders of diseases and food poisoning.
TCS foods, such as dairy products, leafy greens, fish, eggs, cooked rice, ground meat, and poultry, require close monitoring and strict, proper food handling. Maintaining the recommended cold-holding temperature for TCS food is crucial to ensure food safety.
Exposing high-risk TCS food to the temp danger zone for more than 2 hours can significantly put public health at risk. If the temperature of food falls within this range, the chances of contracting foodborne illness increase.
The self-service line is a section of a food service establishment where customers can directly access refrigerated food. This is a common section for establishments like restaurants and retail food stores with salad bars, buffet setups, and cafeterias.
According to the US FDA Food Code, cold TCS food can only be added to the self-service line if prepared and previously stored at a temperature of 41°F (5°C) or below. After doing so, the TCS food must be consistently held at the same acceptable temperature range until consumed by the customer for safety.
The maximum receiving temperature for TCS foods in degrees Fahrenheit is 41 (i.e. 5 degrees Celsius). Maintaining this food-receiving temperature is critical in preventing the growth of harmful bacteria in potentially hazardous foods and occurrences of foodborne illness.
In case you come across this question on a food handlers test, cut tomatoes, cut salad greens, and sprouts must be kept at 41°F or lower for food safety or else you run the risk of unnecessary bacterial growth.
As previously mentioned, the required cold-holding temperature for foods varies based on the food product. Some types of food may require a specifically lower holding temperature to prevent the growth of a particular pathogen.
For example, fish and seafood are required to be held particularly at 29°F to 32°F (-2°C to 0°C). This is because fish tends to oxidize and metabolize faster than other meats. At lower temperatures, these biological processes are slowed significantly.
To keep pasta salad safe, the dish must be held at a maximum cold-holding temperature of 41°F (5°C) or below.
Pasta salad is a popular dish often served in restaurants as an appetizer. Cooked pasta is considered a high-risk food because of its high moisture and carbohydrate content.
In addition, the pasta salad must be properly contained in a covered container and kept away from direct sunlight.
A salad bar must be consistently maintained at a cool temperature of 41°F (5°C) or below to maintain safety and freshness. Vegetables and fresh fruits are considered high-risk, hazardous foods and are very prone to contamination and spoilage.
Displaying food on ice or at low temperatures and exposing them to customers to pick from increases the risk of food contamination. The food must be cold-held at a consistently low temperature to protect salad ingredients from food spoilage and spreading foodborne illness,
The highest temperature allowed for cold holding tuna salad is 41°F (5°C). This temperature recommendation does not only apply to the tuna ingredient itself but also to the other ingredients in the salad.
Tuna salad comprises several high-risk foods, such as mayonnaise, vegetables, and potentially fruit. These ingredients can easily be contaminated and spoil fast, posing a significant threat to public health. To ensure the safety and freshness of tuna salad, it is recommended to store it in a refrigerator or on ice until ready to be served.
The maximum recommended cold-holding temperature for green salad is 41°F (5°C). However, food handlers must note that a green salad consists of multiple types of vegetables, which have varying susceptibility to contamination.
Generally, it is best to keep green salads refrigerated or on ice to maintain freshness and prevent bacterial growth. In addition, keeping the dressing separate from the salad until serving can help retain the freshness of the greens.
The maximum cold holding temperature allowed for shredded lettuce is 41°F (5°C). Lettuce, like other leafy greens, can quickly spoil if kept at higher temperatures. Lettuce is a known high-risk product. Therefore, it requires strict food handling.
When refrigerating shredded lettuce, make sure to keep it away from other raw ingredients to prevent cross-contamination.
Use our downloadable fridge layout poster to learn how to organize foods inside the fridge properly.
The maximum temperature allowed for cold-holding salsa is 41°F (5°C) and below.
Salsa is a great dip for many dishes. It is composed of different greens and vegetables, such as bell peppers, onions, and cilantro. Together, they make a dip that is very high in moisture and susceptible to contamination.
It is important to note that salsa should be prepared with no potential cross-contamination and food spoilage to prevent the spread of foodborne illness.
Similar to meat dishes, deli meat should be held at a maximum cold holding temperature of 41°F (5°C) and below. Above this temperature, the food item is exposed to the temperature danger zone and is at a higher risk of spoiling.
Deli meat should be immediately consumed within three to five days of refrigeration. This is the maximum time that the food item can remain fresh and safe for consumption, even when refrigerated.
Deli meats are raw food products. As such, they must be properly grouped with similar products to prevent contamination.
Download our free fridge organization chart to guide your food employees on how to store deli meats properly.
Displaying cheese requires it to be cold-held at 41°F (5°C). Cheese is a type of dairy product; therefore a high-risk food item. Food handlers must also remember that there are different types of cheese, and some can be more prone to spoilage.
For example, soft cheese like brie and camembert is more likely to spoil faster due to higher water content. As such, food handlers must increase the frequency of monitoring cold holding temperatures for this type of product.
The maximum cold-holding temperature for sliced egg salad sandwiches is 41°F (5°C). Egg salad is a very high-risk product. It contains eggs, mayonnaise, and some vegetables, making it very likely to be contaminated if unattended.
Ideally, egg sandwiches must be consumed within three to five days of refrigeration. When cold-holding prepared foods, the item must be placed in a food container to keep it away from other food products in the cooling unit or other cold food storage areas.
The recommended cold-holding temperature allowed for a slice of watermelon is 41°F (5°C) and below. Food service operators must use this safe temperature range for when displaying watermelon slices in salad bars.
Watermelons must be immediately refrigerated after slicing to minimize the likelihood of contamination.
The maximum required cold holding temperature for cut cantaloupe is 41°F (5°C). This temperature requirement is used to minimize the growth of harmful bacteria in foods such as cut fruits and vegetables, which could potentially lead to food-borne illnesses.
The maximum cold-holding temperature for yogurt is around 41°F (5°C), according to the FDA Food Code. This temperature is ideal to prevent the growth of dangerous bacteria and other pathogens.
Yogurt is a ready-to-eat food and must be placed on the topmost shelf of a refrigerator. This placement will help prevent the risk of cross-contamination from other raw ingredients.
Learn how to organize your fridge using our downloadable cold food storage rules.
One of the most critical aspects of temperature control is consistent monitoring.
Monitoring temperature must be done at regular intervals continuously so that food handlers will be able to determine if there are any potential problems.
Without temperature monitoring, foodborne illness-causing pathogens can freely contaminate the food and become a source of a foodborne illness outbreak. If your food safety team can establish a consistent monitoring system for cold-holding temperatures, you can ensure food safety across your food supplies and dishes.
Use FoodDocs' intuitive solutions to help food handlers monitor holding temperature efficiently and effectively. Our digital software takes only 15 minutes to set up.

Upon signing up, our smart software can automatically generate a customizable digital Temperature Log. This log can be used to monitor the cold holding temperature of your food products during storage. Log the information digitally to save time and efficiency. Help your team monitor and record temperatures easily.
All generated monitoring logs can be further customized to fit your unique operations. Allow the team to attach photos or videos as proof of monitoring.
In addition to customizability, this Temperature Log is equipped with a prefilling solution. This smart feature automatically logs temperature readings based on previously logged data. Increase the accuracy of temperature recording with this solution.
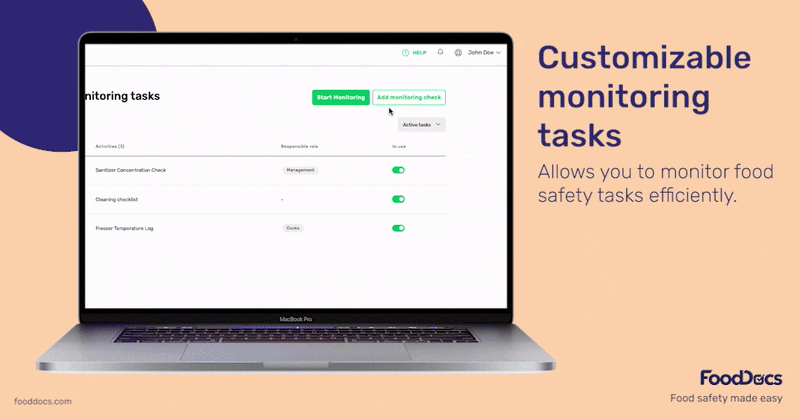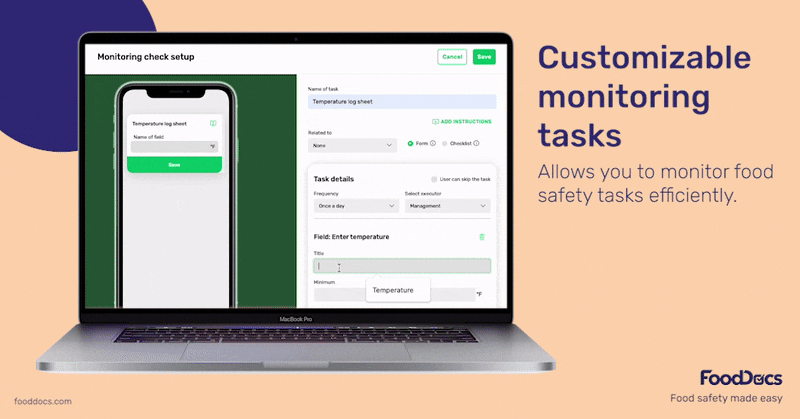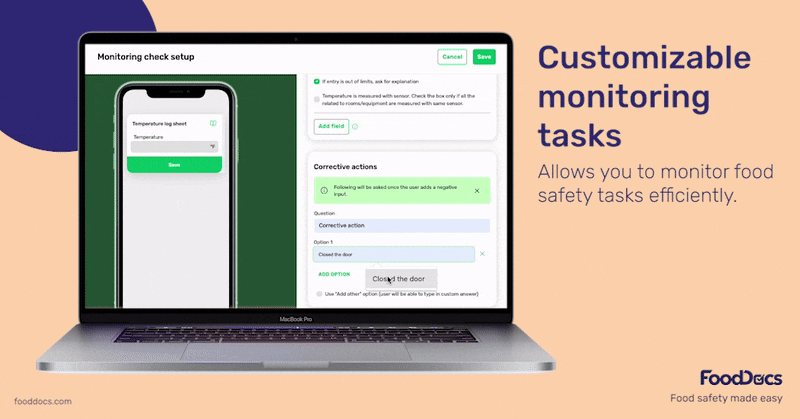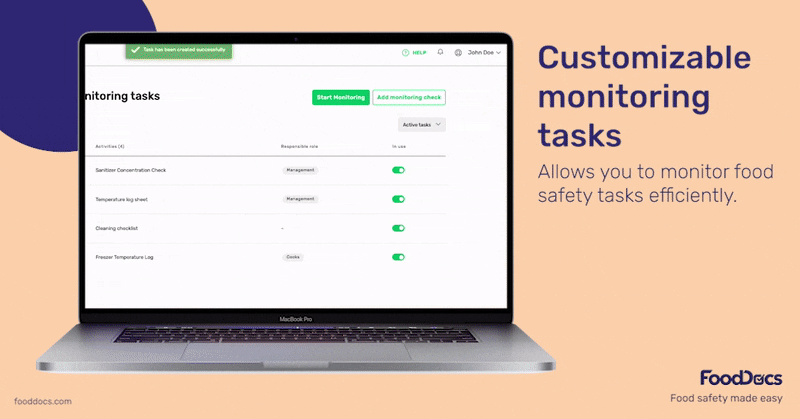
Get a real-time dashboard that will give you a quick overview of the status of your entire operations across your food business branches. Ensure that all monitoring tasks, including the ones related to cold-holding foods, are accomplished correctly and on time using this dashboard.
Use this feature to verify the completion of food safety tasks and ensure everything is up to code. The dashboard also shows areas that need more attention. Managers can quickly identify areas that require corrective action and prevent further problems.
Save up to 20% of your time and immediately identify areas that need more improvement.
Pair our customizable digital monitoring logs with our intuitive notification system from our smart app. Using this feature, food employees will get alerts whenever a task needs to be done. Set the frequency of monitoring the cold holding temperature and help your team never forget monitoring.
With our smart task notifications, you can ensure that cold holding temperature and other essential aspects of food safety are properly and timely monitored. Keep track of food safety tasks and ensure public health safety with this feature.
Powered by artificial intelligence and a machine-learning program, we can generate a comprehensive digital Food Safety Management System for you based on your food safety operations.
For cold holding to become an effective food safety operation, consistent monitoring must first be implemented. Using our smart digital monitoring solutions, you can ensure that monitoring tasks are seamless and that all the necessary information is captured as proof of food safety compliance.
Start your digital food safety compliance journey using our intuitive Food Safety Management System. Get free access for 14 days using our free trial or check out our full suite of product features.
Cold food can be held without temperature control for up to 6 hours as long as it is held at 41°F (5°C) or lower before removing it from refrigeration. As a rule of thumb, never reheat food with hot-holding equipment unless it was designed for that purpose.
Holding food at colder temperatures than recommended is an example of time-temperature abuse, posing a potential risk to food safety. This involves the incorrect storage or handling of food at temperatures that encourage the proliferation of harmful bacteria.
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...