Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Bacterial contamination causes the majority of foodborne illnesses in the food industry.
Like humans, bacteria need a source of nutrition, and they can use the same food that we consume. In a sense, bacteria and other pathogens are competitors of humans against the same food product.
The presence of bacteria in our food is considered a food hazard as it can cause foodborne illness. Food handlers must know the best way to limit the growth of bacteria in food to protect all consumers.
Key takeaways
The most effective and best way to limit the growth of bacteria in food is to properly cook it to the recommended internal temperature. Contamination of foods prepared in your kitchen can be reduced to safe levels by cooking. While other food handling practices such as proper storage conditions and food hygiene can help prevent contamination, the cooking process will be the last and very important step to limiting bacterial growth.
Applying adequate heat to food kills any present microorganism, such as bacteria in food production. The heat damages the structure of bacteria, making them unable to reproduce or cause any harm to your customers.
Different types of bacteria may have different requirements of heating levels` for inactivation. Some bacteria are more resistant to heat, whereas others can be killed with minimal heat treatment. This explains the varying recommended cooking temperature for foods.

But before getting into preventive methods for bacteria, you must ask:
Food, acidity, time, temperature, oxygen, and moisture (also known by the acronym FATTOM) are needed for most bacteria to multiply in food.
Without time or temperature control, exposed food surfaces would contribute to bacterial growth in food because they can introduce pathogenic contamination via traces of E. coli or Listeria monocytogenes.
Food handlers can effectively reduce bacteria to safe levels by applying proper food handling practices. These operations span from applying thermal processing to properly cleaning your food facility.
There are many ways by which a food handler can accomplish the objective of reducing bacteria to safe levels. Among these operations, the four most effective and essential practices include the following:
In addition to these basic food safety operations, the following must also be observed:
All the mentioned food handling practices are basic yet effective ways to reduce harmful bacteria and foodborne illness in food production to safe levels. These operations are essential for every food business in creating safe conditions for preparing foods for service.
Proper food handling practices help control and reduce the presence of pathogenic microorganisms that can spoil cooked or ready-to-eat foods and endanger public health.
Time and temperature are the two conditions for bacterial growth that you can control. You can effectively influence the spread of bacteria by safely managing these two factors.

Bacteria normally stop growing below 40°F (5°C) and above 60°F (140°C) on cooked or ready-to-eat foods. Within the temperature range 40°F to 140°F (5°C to 60°C), or the temperature danger zone, perishable foods are most likely to get spoiled from harmful bacterial growth.
Bacteria can optimally grow within the temperature danger zone and can spoil potentially hazardous foods. To prevent this from happening, foods must be stored in either cold holding or hot holding conditions, depending on the intended use of foods.
To ensure that very minimal to no bacteria will be left alive in fresh foods, cook foods to an internal temperature of 165° F (74° C) unless your local food safety agencies recommend a different internal temperature. Use an accurate food thermometer when monitoring the temperature of foods.
In terms of storage, keep refrigerated foods at 40°F (4°C) and frozen foods at 0°F (-18°C) to control the growth of bacteria in common foods. In addition, a temperature range of 135°F (57°C) and above must be used for hot holding foods.
When properly done, microwaving food can kill bacteria effectively. When we say properly done, we mean that the food heated in a microwave is evenly exposed to high temperatures.
When microwaving is inadequate or done improperly, the food may remain cold in the center. Surviving disease-causing bacteria in food production may further grow and cause food poisoning in consumers who will eat the product.
To ensure that microwaving kills bacteria, make sure to follow these steps:
The most evident proof of bacterial contamination is when the food produces off-odor. The problem with bacterial contamination is that sometimes, you cannot identify whether it is present or not until it produces obvious changes. Some types of bacteria do not produce obvious changes in food until they multiply significantly.
Here are 6 few common signs of bacterial growth or survival of pathogens in fresh food:
Contaminated food for service will often taste different, but we do not encourage to use of taste as a determinant of the presence of bacterial contamination. Some bacteria can produce toxins that, even in small amounts, can cause foodborne disease. Contamination can happen to both raw and ready-to-eat foods. Equal care must be practiced in handling any type of food.
Test your employee's aptitude on topics such as food spoilage using our food safety quiz tool. You can also use this free tool to constantly train food handlers as part of their training.
If you discover bacterial contamination on food in your establishment, do not use it as an ingredient nor serve it to customers. Bacterial contamination can occur at any point in the food processing chain. If the observed contaminated food is from the delivery of ingredients from a supplier, immediately inform the supplier and take the necessary actions to document the incident.
Contaminated food cannot be used for further processing as it can only endanger your customers. Using regular processing methods such as cooking on heavily contaminated food may not be effective enough to kill all bacteria.
Inspection of food materials used in your establishment must start from receiving ingredients from suppliers. Food processors and handlers must be trained on how to detect contamination in food supplies that can compromise food safety. Unapproved sources of ingredients may cause contamination of your other products.

The most effective way to reduce bacteria in raw poultry is through proper cooking. Poultry meat and poultry products must be cooked to a minimum internal temperature of 165°F (74°C) to ensure food safety. Always ensure that you are not using still-frozen poultry meat to ensure even cooking.
A common misconception in preparing raw poultry is that washing the meat reduces bacteria. Washing raw meat will only increase the chances of contaminating other areas and fresh produce in your kitchen.
Raw poultry is widely associated with the bacterium Salmonella sp. and has been linked to various cases of foodborne illness. In addition to an upset stomach, food poisoning from this bacterium can also cause symptoms of illness such as diarrhea, nausea, abdominal cramps, vomiting, and other signs of illness.
Bacteria are significant components of the food industry. Your food business' approach to food safety must always consider establishing strict controls against bacterial contamination. Failure to control the growth of bacteria in any type of food in your establishment can lead to potential outbreaks of food poisoning, profit losses, and loss of customer confidence.
Controlling bacterial contamination in fresh food must always be on the priority list of your food business. Also, government food inspectors from different health departments prioritize such areas during a food safety audit.
To efficiently do this, our team at FoodDocs offers a smart, digital solution. With our help, you can ensure that food processors and handlers will never forget how and when to perform operations that help limit the growth of bacteria.
With our digital solution, you can get the following features and benefits:
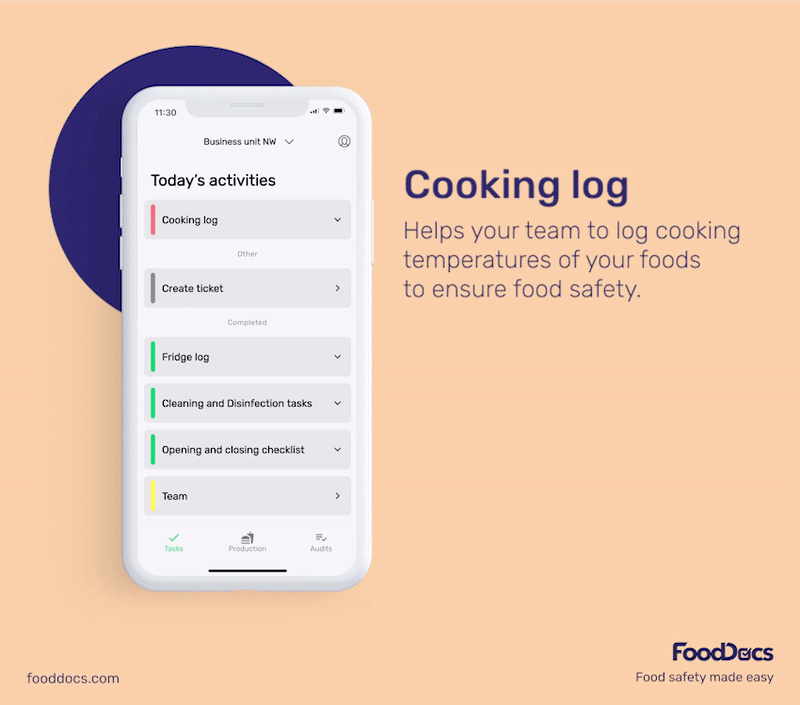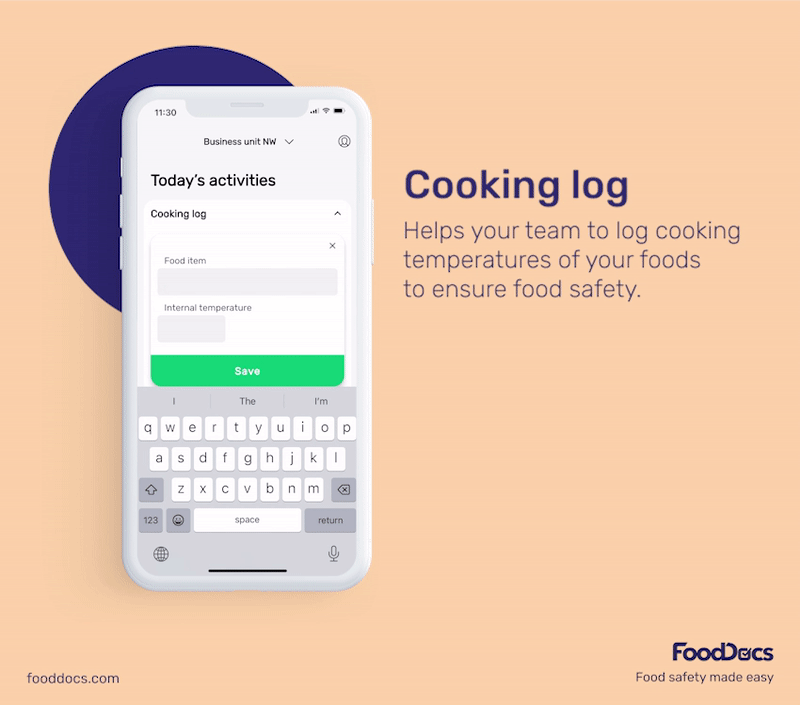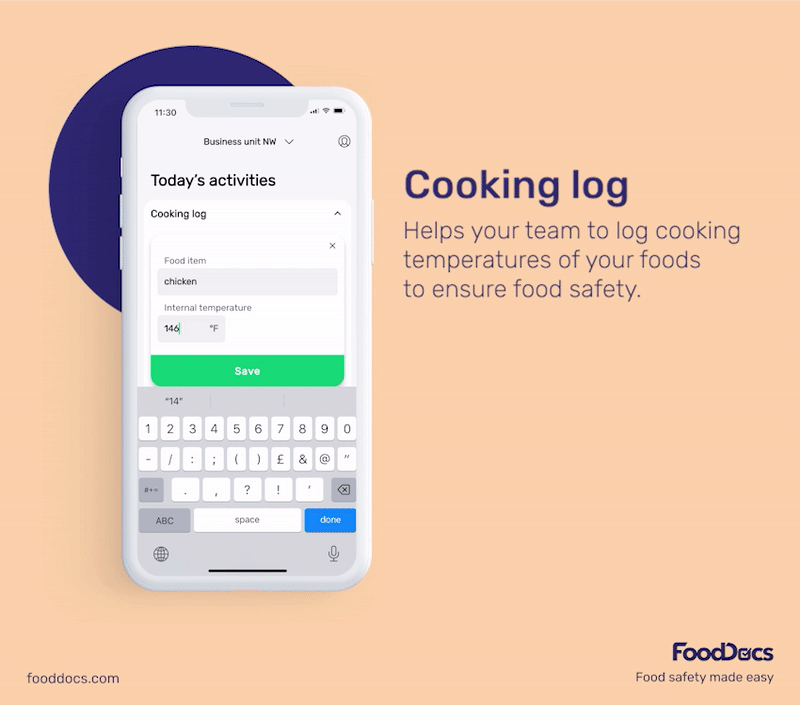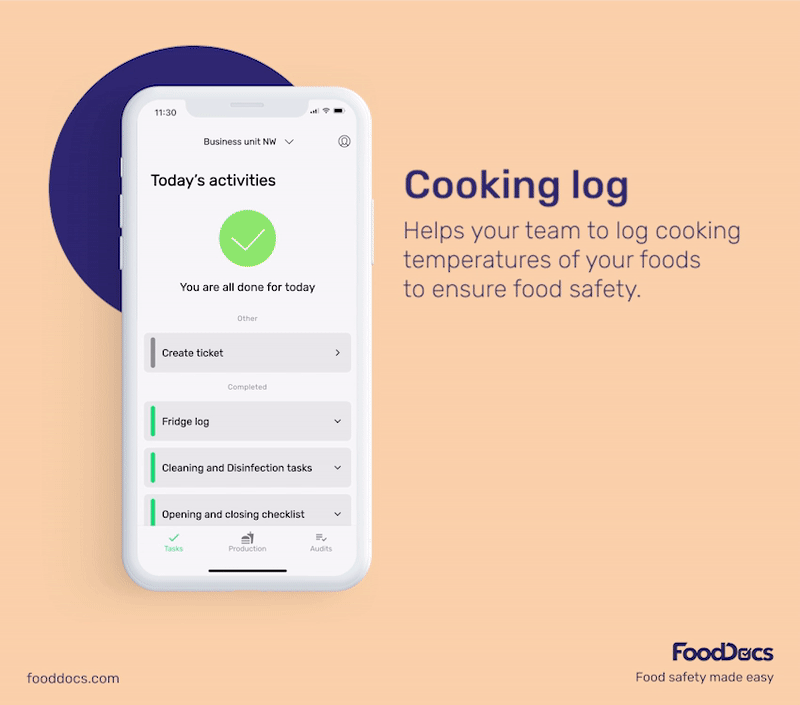
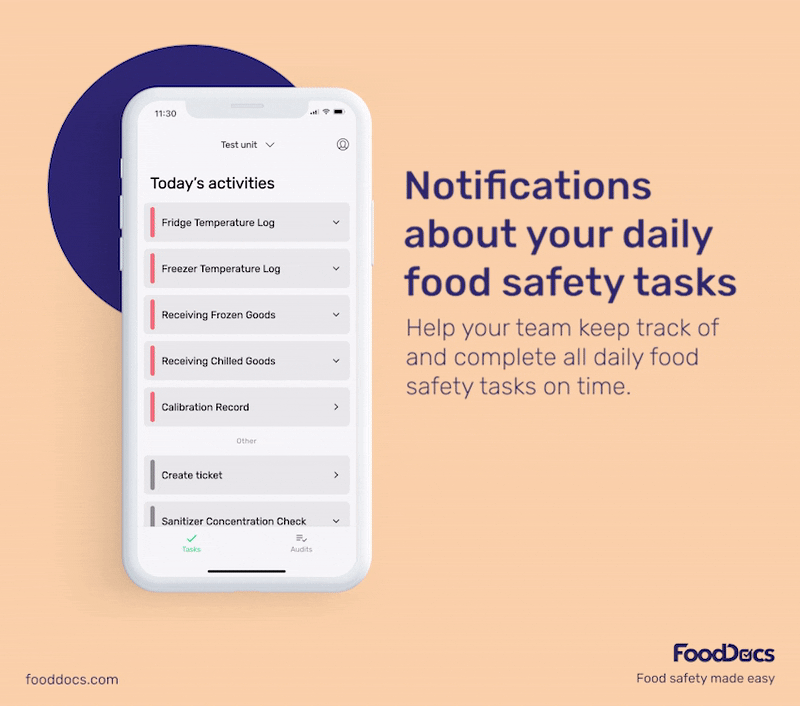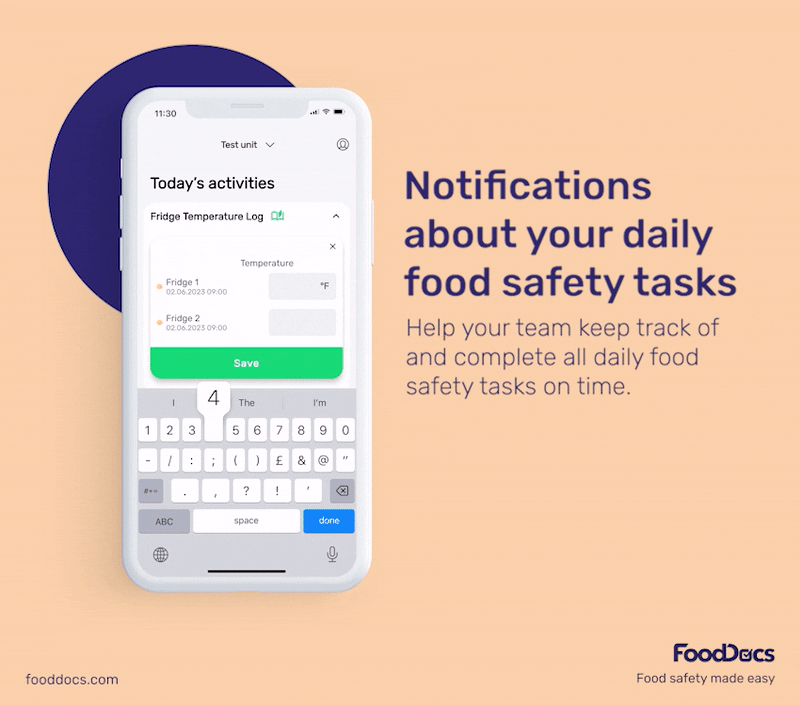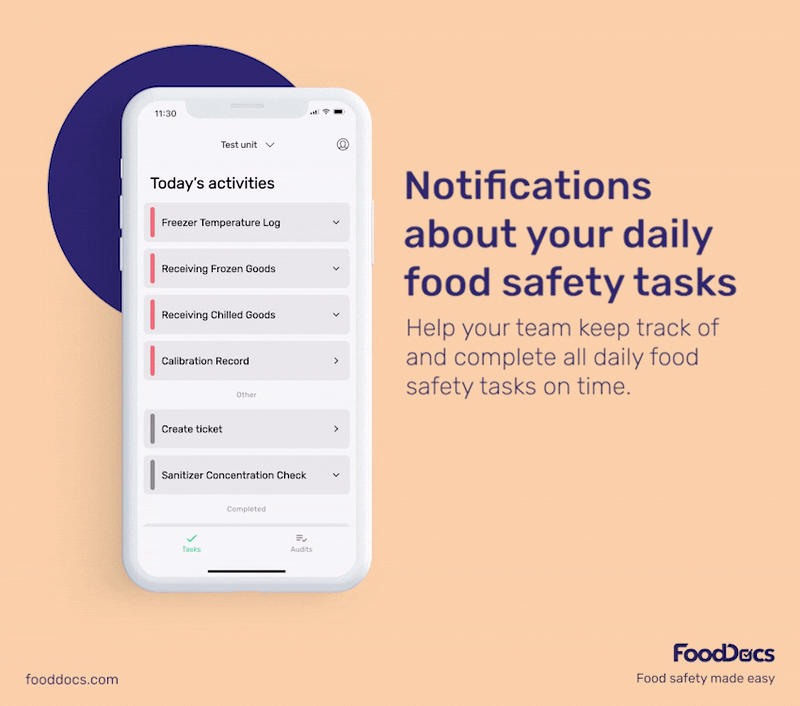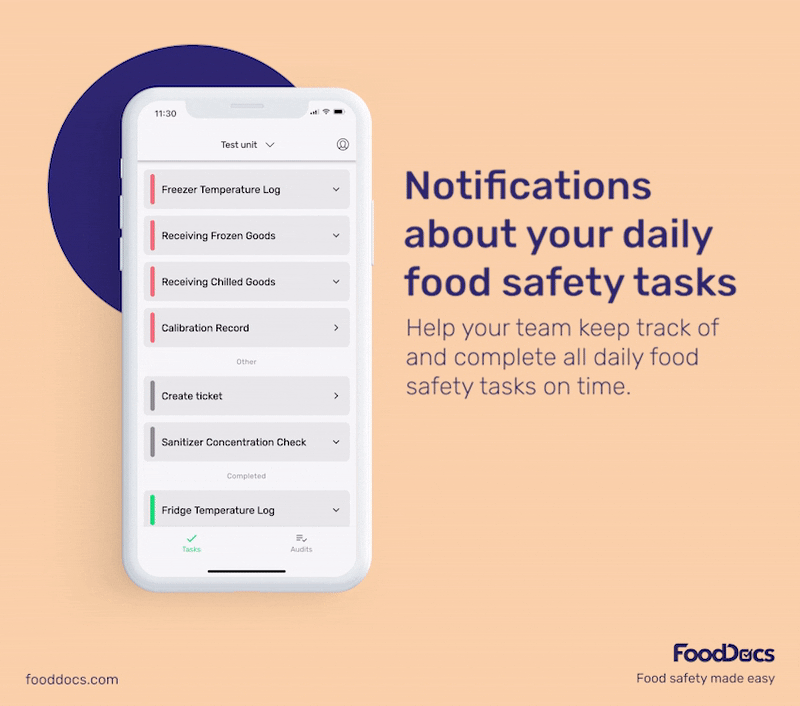
With our digital solution, you can easily ensure that bacterial contamination in your food establishment is always kept to a minimum or safe level. All areas that require safe temperature control can be efficiently monitored with our digital Food Safety Management System.
In addition to solutions that help food handlers fulfill food safety tasks, our system can also help managers improve efficiency in overseeing their operations.
Bacterial contamination can be quickly addressed and controlled when you have a comprehensive food safety plan. At FoodDocs, you can get that and more. You can ensure that every food safety standard is complied with at all times.
Make sure that every dish you put out for service is safe and free of bacterial contamination. Want to experience switching to a digital platform right now? Great! Use our free 14-day trial to see how our product can help you achieve compliance more efficiently.
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...