Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Not only do food workers need a safe place to eat during breaks; they need a hygienic place to eat.
But where exactly can workers eat food without risking food safety violations?
The answer: designated break rooms and dining areas, completely separate from food prep zones.
These spaces protect both the food that's served as well as the physical and mental health of employees. In this article, we'll dive into the specific public health regulations and best industry practices for setting up compliant, comfortable break areas for your food service staff.
There are a handful of critical areas that businesses need to have a clear and consistent food safety guidelines on to keep both staff and customers safe.
Food service businesses should designate a clean, comfortable space for their workers to eat during their breaks. Ideally, these areas must be completely separate from any areas where food preparation, food storage, or food service occurs to prevent cross-contamination.

Health codes are very specific about where food service employees can and cannot eat during their shifts. Let’s take a look at the two main categories of approved dining spaces for food workers.
The most common option for staff meal breaks is a designated interior break room. According to the FDA Food Code, these rooms must be completely enclosed and separated from food prep areas by a door.
Some key requirements for on-site interior break rooms include:
Break rooms should be stocked with soap, paper towels, and a hand sanitizer dispenser. We also recommend you put up signage reminding employees to wash hands before returning to work, such as these ones:
Depending on the type of business, if time allows, it's a choice for food workers to leave the premises during breaks. But both smaller and larger food establishments, especially those with limited interior space, may opt to provide an outdoor area for employee dining. This is allowed under health department rules as long as the space meets important criteria:
Outdoor break spaces should also have a convenient handwashing station nearby for staff use before reentering the food prep area. If the sink is not in the immediate vicinity, hand sanitizer must be available.
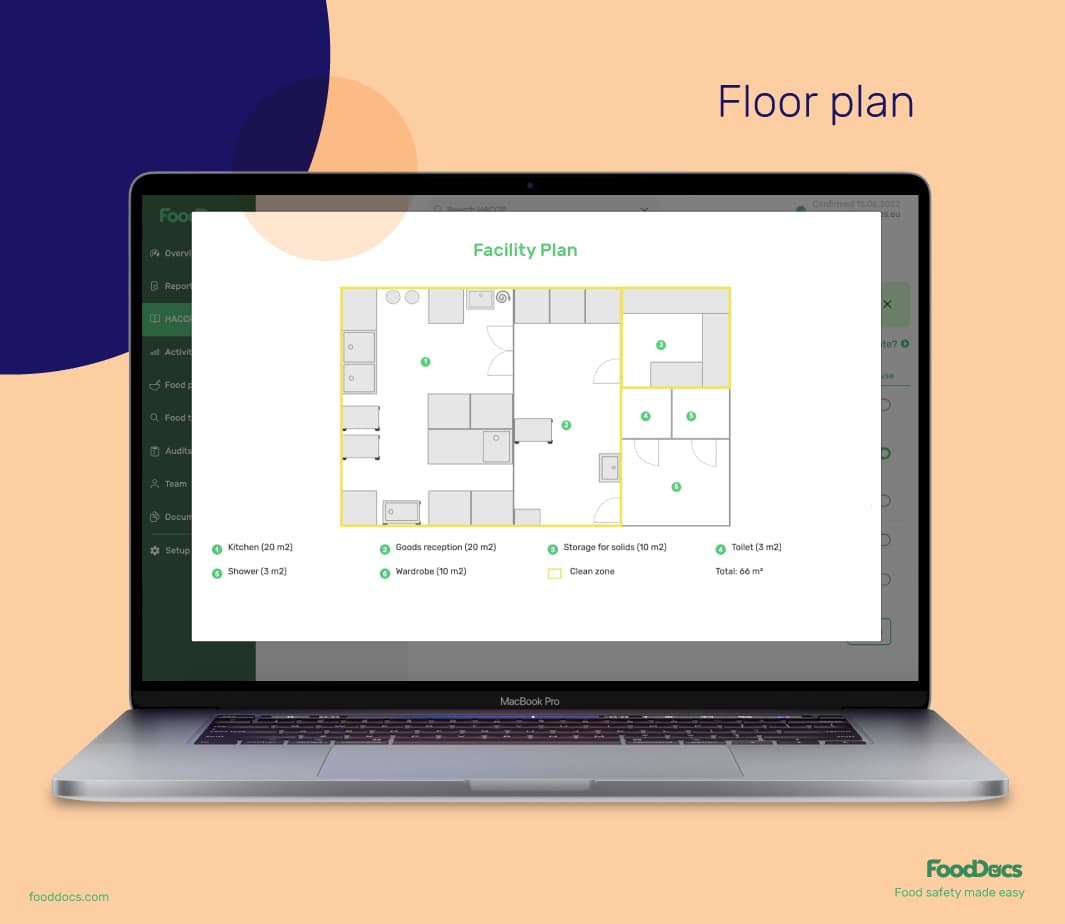
When you use the FoodDocs Layout builder, you can create and customize your facility's floor plan using a drag-and-drop solution that includes designated areas where food workers can eat on their breaks.
Beyond just the physical location, there are other important factors that go into creating a safe, sanitary environment for staff meal breaks. Food workers should always:
Quality, Food Safety, and F&B managers must provide staff with sufficient time to eat away from their workstations.
Let’s face it — when rushed, employees may feel pressure not only to quickly eat food during shifts, but eat quickly in unapproved areas. A workplace culture that respects a reasonable break time helps uphold food safety.
We touched in some of the benefits above, but here’s a more in-depth explanation of why these benefits matter for food businesses.
Designating a separate eating area for food service staff is crucial for maintaining food safety and hygiene standards. When employees eat in food preparation areas, there's a higher risk of contamination from personal items, food debris, and potential pathogens.
But businesses that provide a dedicated break room or dining area away from the kitchen will minimize these risks and keep food preparation environments clean and sanitary.
According to the FDA Food Code, food employees should eat and drink only in designated areas to prevent contamination of exposed food, clean equipment, and unwrapped single-service and single-use articles. This regulation highlights the importance of separating eating areas from food handling zones.

Providing a comfortable and well-equipped break room demonstrates that the company values its employees' well-being. When staff have a dedicated space to relax, socialize, and recharge during their shifts, it can significantly improve morale and job satisfaction.
Studies have shown that happy employees are more productive and engaged in their work. A survey by the National Business Group on Health found that 91% of employees believe their employer's support for health and well-being will affect their future loyalty.
This goes to show that doing things like prioritizing staff welfare through proper eating areas can help food businesses foster a positive work environment that encourages employee retention and reduces turnover costs.
Take a second to think of where you like to enjoy a meal, no matter how big or small. It probably isn’t in a cluttered and unsanitary room.
So when creating a food workers’ break room, maximize its benefits by considering these elements:
A well-designed break room can serve as a gathering place for team bonding and social interactions, further enhancing workplace culture and employee relationships.
Providing a designated eating area for staff helps restaurants comply with Department of Labor laws and regulations. Many states require employers to offer rest and meal breaks, and having a proper space for employees to take these breaks ensures that restaurants meet these legal obligations.
For example, in California, employers must provide a 30-minute break for shifts lasting more than 5 hours and a 10-minute rest break for every 4 consecutive hours worked. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in penalties and legal issues for the business.
It may seem like a small gesture, but the average food worker feels underappreciated. So allocating a specific area for staff to eat and take breaks can help demonstrate the food business’s commitment to following labor laws and prioritizing employee rights. And the benefits of this are two-fold:
While having a designated eating space is essential, restaurants must also ensure that the area is properly maintained and cleaned regularly. This includes:

In order to ensure that team members never miss a food safety task, managers who use our FSMS software set up digital checklists that can workers can easily complete with the FoodDocs mobile app.
Encouraging staff to take breaks in a designated eating area can help improve work-life balance. It's far too easy for employees to skip meals or eat while working when there isn't a proper space provided, which can lead to burnout and reduced job satisfaction.
Providing a comfortable break room allows staff to disconnect from their duties for a short period and recharge mentally and physically. This promotes better self-care habits and helps employees maintain a healthier work-life balance.
Moreover, when staff feel cared for by their employer, they are more likely to be loyal and engaged in their work. This sense of belonging can translate into improved performance and customer service.
Having a designated eating area also encourages food service staff to practice mindful eating habits. As we mentioned earlier, food production and retail employees who are forced to eat on the go or in the kitchen are more likely to consume their meals quickly and without much thought.
Anyone who’s worked in the food industry knows this — especially in restaurants — working with urgency is different than worked while rushed.
A simple solution is to put reasonable efforts into creating a separate space for meal breaks that will allow food manufacturing plants and retail establishments businesses to slow down, savor their food, and engage in proper digestion. This not only promotes better physical health but also supports mental well-being by allowing employees to take a moment for themselves amidst the chaos of a busy shift.
To support mindful eating habits, restaurant managers can:
The more that businesses foster a food safety culture that values mindful eating and the mental health of employees, the more they’ll create an environment that their staff view as positive and supportive.
Can food workers eat at their workstations? The short answer is no.
To maintain food safety standards and good hygiene practices, food workers are not allowed to consume any food or beverages at workstations where food is prepared or served to customers. All dining must take place in approved break areas away from food handling zones.
Proper handwashing is one of the most important steps food workers must follow before and after eating. Employees are required to wash their hands thoroughly with soap and warm water for at least 20 seconds. This helps remove any germs or bacteria that could contaminate food.
While hand sanitizers can be useful for quick cleaning, they are not a substitute for proper handwashing when it comes to food safety. Employees must always wash hands with soap and water before handling any food, even if they have used hand sanitizer.
It's always an option for food workers to bring their own meals and snacks, but these food items must be stored properly to prevent contamination. All perishable foods should be kept in the designated break room refrigerator at a temperature below 40°F (4°C) to avoid the danger zone.
Employees must label their food containers clearly with their name and the date. Any unlabeled items may be discarded by management. Non-perishable snacks can be kept in lockers or designated storage areas, but never at workstations.
Maintaining a sanitary break room is a shared responsibility among all food workers. After finishing their meals, employees must wipe down tables and disinfect any surfaces they touched. All trash, including food wrappers and disposable cups, should be disposed of promptly in covered garbage cans.
Management should schedule regular deep cleaning of break rooms and ensure an ample supply of cleaning products and disposable paper towels. Doing so will simplify pest management and prevent cross-contamination.
Open drink containers like uncovered cups, mugs, and glasses pose a significant contamination risk in food preparation environments. Imagine a busy kitchen with workers moving around quickly, chopping ingredients, stirring pots, and plating dishes. It's all too easy for an uncovered drink to get knocked over, spilling liquid onto food contact surfaces, ingredients, or even the food itself.
Bacteria from a worker's mouth can also transfer to the drink container rim. If that container is then placed on a food prep surface, that bacteria could contaminate the area and eventually make its way into customer meals. Hair, dust, and other airborne particles can also land in uncovered drinks. All of these scenarios put food safety at risk.
To minimize contamination risks, any beverages food workers consume while in food preparation areas must be in closed containers with lids and straws. The lid prevents spills if the drink gets bumped. The straw allows the worker to drink without placing their mouth on the cup rim, reducing bacteria transfer.
Beverage containers must also be stored below any food contact surfaces. They cannot be placed on cutting boards, prep tables, stove tops, or anywhere food is handled. Most kitchens designate a low shelf or spot under the work area for employees to keep their drinks. This prevents containers from getting knocked over onto food surfaces.
Proper handwashing is always critical for food workers, but it's especially important when they've been handling their personal beverage containers. After taking a sip of a drink, the worker should wash their hands before resuming any food handling tasks.
The same applies if they refill their beverage or get a new one. Food workers must wash their hands before returning to work.
While lids and straws minimize risks, frequent handwashing ensures any bacteria from the cup or the worker's hands doesn't transfer to the food.
Avoiding open cups, properly storing drink containers, and washing hands after handling them goes a long way in preventing the contamination of food, surfaces, and equipment — all while staying hydrated.
To ensure your staff has a pleasant, relaxing place to eat during shifts, provide enough seating and table space to accommodate all employees on break at once. Consider the size of your team and peak break times when determining the number of chairs and tables needed.
Opt for durable, easy-to-clean furniture made from non-porous materials like metal or laminate. Avoid upholstered seating which can harbor bacteria. Arrange tables and chairs with enough space between them for comfortable movement and to prevent overcrowding.
Proper handwashing is crucial for preventing the spread of foodborne illness. Install dedicated handwashing sinks in employee dining areas, separate from restroom facilities. Equip sinks with hot and cold running water, soap dispensers, and disposable paper towels.
Post clear signage near sinks demonstrating proper handwashing technique. Include reminders to wash hands before eating, after using the restroom, and after touching high-contact surfaces. Consider adding visual aids like step-by-step graphics to reinforce the message.

Make it easy for staff to keep dining spaces clean by providing ample cleaning supplies. Stock the area with disinfectant wipes, spray cleaners, paper towels, brooms, and dustpans. Establish and communicate clear expectations for employees to tidy up after themselves.
Create a cleaning schedule assigning specific staff members to wipe down tables and chairs after each use. Empty garbage cans regularly to avoid overflow and odors. Consider implementing a bin system for employees to sort waste and recyclables.
In addition to daily tidying by employees, schedule regular deep cleaning of staff dining areas. Hire a professional cleaning service or assign trained staff to thoroughly sanitize all surfaces, including floors, walls, and furniture. Don't forget often-overlooked areas like light switches, door handles, and microwave keypads.
Conduct routine inspections of employee break rooms to ensure cleanliness standards are being met. Use a checklist to assess things like overall tidiness, handwashing sink supplies, functioning equipment, and pest control. Address any issues promptly to maintain a hygienic environment.
Educate all food service staff on expectations and protocols for using employee dining spaces. Incorporate break room hygiene into new hire orientation and ongoing training. Cover topics like:
Post written reminders of key policies in highly visible areas. Reinforce training regularly through team meetings, posters, and digital communications. Foster a culture where all employees feel responsible for maintaining clean, hygienic dining spaces.

Whether you're in food service, food production or food manufacturing, teams use FoodDocs FSMS software to manage their employees' food safety training materials and certificates.
Food service workers face unique challenges when it comes to eating during shifts. Designated break rooms or outdoor dining areas, separate from food prep zones, are a must. Handwashing before and after meals is non-negotiable. Covered drinks only in work areas. Proper food storage and regular cleaning keep everyone safe and healthy.
Providing clean, comfortable spaces for staff to eat shows you value their wellbeing. It boosts morale and productivity too. Plus, it's the law.
So, how does your workplace measure up? Do you have enough seating and sinks? Are the rules clear and enforced? If not, now's the time to step up your break room game. Your staff (and the health inspector) will thank you.
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...