Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...

While the US has one of the safest food supplies in the world, one in six people still get sick from consuming contaminated food, with 128,000 ending up hospitalized and 3,000 passing away every year. This makes following food safety regulations crucial for the entire food supply chain. And that’s where the FSSC 20000 accreditation comes in.
In this article, we’ll talk about what FSSC stands for, its requirements, and how to get the FSSC 22000 certification. Let’s begin!
Learn more about the FSSC 22000 certification program and how can our innovative software help you efficiently achieve a significant label for your business.
WHAT WE'LL COVER:
FSSC 22000 is a Food Safety Management Systems (FSMS) certification scheme benchmarked by the Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI). It was developed by the Foundation for Food Safety Systems Certification (FSSC) to reduce internal and external food safety risks (such as contaminated food ingredients and pest infections).
The international standard offers a comprehensive certification program for auditing FSMSs. It also defines the requirements of a risk-based food safety management system.
Organizations operating within the food chain that get the FSSC 22000 certification show that they have implemented processes to reduce or eliminate the food safety hazards posed by foodborne illnesses, contamination, and other internal and external risks.
While FSSC 22000 is based on the ISO 22000 standard, it has now been revised from version 4.1 to version 5.1. The new version is based on the ISO 22000:2018 standard and complies with GFSI requirements which makes it a globally-recognized certification.
So, companies that acquire the FSSC 22000 certification after January 1, 2020, will get the version 5.1 certification. You can check with your certification body to understand what your audit situation looks like.
While the FSSC 22000 and the Safe Quality Food (SQF) code are both food safety certification schemes that play an important role in the control of food safety, they have several differences.
For instance, the SQF code expires within a year, while FSSC 22000 lasts for three. FSSC 22000 is also more flexible and not too descriptive, allowing organizations to create their own compliance system.
In contrast, the SQF code is stringent and requires food companies to comply with specific micro-system elements.
However, FSSC 22000 requires two on-site stage 1 and 2 audits, while the SQF code enables companies to perform stage 1 off-site and stage 2 on-site. This may make the SQF certification more accessible for international food companies.

Simply put, a wide variety of food chain members — including farmers, manufacturers, packagers, transporters, and retailers in the food and beverage industry — can obtain the FSSC 22000 certification to be able to sell stable products.
FSSC 22000 applies to a wide range of organizations that manufacture or process products within the following categories:
| Category | Description |
|
A |
Farming fish and seafood/raising animals for meat, egg, or honey production. |
| C |
|
| D |
Producing the following animal and pet food items:
|
| E | Providing catering services to consumers, such as restaurants, hotels, cafeterias, canteens, coffee shops, event catering, and food trucks. |
| F | Providing retail/wholesale goods for consumption. |
| G | Providing transport and storage services for perishable food/feed and ambient stable food/feed and packaging materials. |
| I | Producing food packaging materials. |
| K | Producing biochemicals like vitamins, minerals, enzymes, bio-cultures, processing aids, flavorings, and food/feed additives. |
It isn’t mandatory for any company in the food industry to get an FSSC 22000 certification. However, if you perform any of the activities described in the table, it’s best to get certified.
Why? Because the GFSI-benchmarked scheme can enable you to actively show that your products are safe to use. This can increase customer trust and broaden your market reach.
Non-GMO products are products made from ingredients that have not been genetically modified. This means that the organisms that produce the ingredients, such as crops or animals, have not had their genetic material altered through genetic engineering or biotechnology techniques.
In the food industry, most products labeled as non-GMO include fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, dairy products, meats, poultry, and packaged foods. They can either be raw ingredients or products made from ingredients that did not go through genetic modification.
FSSC 22000 has three components that offer comprehensive coverage:
ISO 22000 is a voluntary international food safety standard that provides companies with guidelines that help them ensure food safety. It applies to every food business, from manufacturers to packaging producers.
Becoming ISO 22000-certified enables companies to move on to the second stage of the FSSC 22000 certification program, which is PRP accreditation.
A prerequisite program (PRP) is a set of guidelines that helps companies control the likelihood of food safety hazards in the production environment and ensure food product safety.
For instance, personnel hygiene controls require companies to ensure workers wear gloves, hair caps, and aprons when working with any food items to reduce the risk of contamination.
Each PRP applies to food manufacturers in one industry. For instance, ISO/TS 22002-1 applies to all companies that transform raw ingredients into food products like cereal, snacks, dairy products like cheese, and canned goods.
Organizations might also need to record and review food safety management services like transport, maintenance, and utilities and ensure compliance with other regulations to effectively implement the FSSC 22000 standard.
However, these requirements will depend on your region, state, and business type. We’ll talk about them in the next sections.
FSSC 22000 requires food industry organizations to stick to the following technical specifications:
You can fulfill all the requirements listed above using FoodDocs food safety management system. FoodDocs helps you set a system that is compliant with FSSC 22000 rules fast and easy.
As a result of the above scheme requirements, food and beverage industry companies may have to develop the following documentation when looking to get certified:
While the FSSC 22000 might seem challenging at first glance, there are several reasons why you should strive to pursue this certification. Let’s look at five of the most important ones below:
The ISO 22000 FSMS in the FSSC certification enables you to standardize your approach to food safety hazards, ensuring you don’t need to risk systemic complications.
The FSSC 22000 standard also provides a roadmap to food safety for companies that are just starting out. This can lead to improved risk management from day one and reduced food safety issues.
When you commit to the FSSC 22000 standard, you show customers that you provide high-quality and safe food or food products.
When people are aware of your commitment to food safety standards and food safety culture, it boosts customer confidence. This, in turn, can increase retention, referrals, and return on investment (ROI).
Since the FSSC 22000 is GFSI-recognized, it enables you to sell your products or produce in the international market. This gives you a wider market reach, access to more consumers and companies, and potentially higher revenue.
Once certified, you can easily provide customers with your products once a sale happens. There won’t be a need for further inspections or checks. This can increase operational efficiency by reducing time wastage.
As we mentioned before, food hazards cause over 100,000 people to end up in hospitals every year. However, these can be reduced when you commit to a consistent food safety scheme like FSSC 22000.
Getting the FSSC 22000 certification checklist
Now that we’ve looked at the various requirements of the FSSC 22000 certification, let’s understand how you can get it. Below are 8 steps of the process of gaining an FSSC 22000 certification:
Before getting into the food safety system certification process, you need to ensure your product complies with the FDA’s food quality and safety regulations.
For example, if you’re planning to sell perishable plant products, you’d need to consider food safety risks and think about the final taste, nutrient content, and color.
Once you’re aware of what goes into your products, you’ll need to comply with all relevant laws and rules, such as the Produce Safety and Food Traceability rules.
Once you’ve ensured your product complies with food regulations, ensure your food manufacturing environment and process comply with the FDA Preventive Control for Human Foods Rule as well.
You might also have to comply with other food laws and regulations depending on your business and industry. So, find out about those laws, read through them, and implement their requirements.
After you’ve ensured compliance with all local, state, and federal laws, you should understand what FSSC 22000 requires you to adhere to.
For instance, to start the process, you need to comply with ISO 22000: 2018. This standard provides access to management systems that enable you to reduce the risk of food contamination.
Once you’ve understood which technical standard you have to adhere to, you also need to comply with 15 FSSC 22000 additional requirements. You can read more about these requirements in detail here.
Now that you understand what the compliance process looks like, create an official food safety program team to design, document, and implement FSSC 22000 processes.
It should include a food safety team leader, an implementation specialist, and a regulation consultant.
After you have a team on board, the food safety team leader should work with the management to perform a GAP audit to find out the gaps in the company FSMS or HACCP system. They can modify the requirements for the certification process to create a criterion for the audit.
Once the results come in, the implementation team should identify changes that need to be made and outline how they will be done. This will form the basis of the implementation plan.
Once your safety team has created a plan for FSSC 22000 implementation, they should provide training to all food handlers, managers, quality assurance and control associates, and teams responsible for the project.
This FSSC 22000 training will enable everyone involved in the food safety implementation plan to begin the implementation.
Plus, at this stage, they should also train employees to become internal auditors who will check the final system and find implementation gaps. This will be relevant once the project is complete.
After the FSSC 22000 implementation plan has been completed, an internal food safety audit must check the implementation against the plan to find out any gaps, if there are any.
If there aren’t, your food safety team should consider what you could make better. But if your team finds gaps, they should be resolved, with an internal audit conducted within a few weeks by skilled auditors to understand whether the measures worked.
Once the system is running smoothly, continue the process for at least two to three months and then move on to the certification audit.
Before getting the certification audit, you need to select a certification company from those listed on the FSSC 22000 website. Once you pick one of the available auditing services, book an audit date and get all your documents in order.
If you do everything right and fulfill the audit requirements, you’ll get your FSSC 22000 logo. However, you’ll need to strive for continuous improvement and keep your system updated to get recertified three years later.
Complying with FSSC 22000 requires months of preparation, extensive food safety documentation, and countless hours dedicated to restructuring the business environment.
FoodDocs’ Smart Food Safety Management System comes with an built-inHACCP plan builder that can help you obtain and maintain the FSSC 22000 certification.
Our software streamlines all steps of the FSSC 22000 certification while improving food safety systems for food industry companies. In addition to others, these are the most important advantages you get by using FoodDocs:
An essential element of the FSSC 22000 certification program is ensuring your food business can effectively track product movement along the entire food chain.
Our smart food safety management system covers both monitoring tasks and traceability. You can use our Smart Traceability System to easily log and access information about your product and ingredient batches. You'll have quick access to historical data on production batches, making it a breeze to handle situations like food recalls.
And when you need to find specific product-related information in a hurry, our Advanced Search options enable swift document retrieval.
Customizable monitoring tasks from the FoodDocs software
One of the primary goals of FSSC 22000 is to create a robust food safety control system for your food business. You can get the necessary tools, such as a task monitoring system, to document compliance through our software.
Our system is capable of automatically generating monitoring tasks tailored to your infrastructure. Some frequently used monitoring tasks from our software include the following:
These tasks can be fully customized to align with your business needs. You can enhance each monitoring task in accordance with FSSC 22000 guidelines. You can also add additional fields, sub-tasks, reminders, and parameters that require monitoring to ensure that your FSMS captures the crucial information required by the FSSC 22000 certification.
In addition, you can improve the comprehensiveness of monitoring tasks by implementing recommendations from FSSC 22000 certification auditors. That’s because FoodDocs lets you promptly edit monitoring tasks and integrate their suggestions, showing your commitment to food safety.
Customizable monitoring tasks from the FoodDocs software
Another crucial goal for getting FSSC 22000 certification is for your team to show they’re aware of all food safety and hygiene rules. FoodDocs lets you show your company's commitment to food safety by giving your food safety team clear training guidelines.
Each checklist and monitoring task created by our system comes with concise, step-by-step instructions for task execution and monitoring. These instructions are seamlessly integrated into each monitoring task to serve as a valuable reference for food handlers.
Managers can utilize these instructions for training new staff in food safety practices, while saving their own time on training. Plus, our system makes it easy for administrators to personalize these guidelines, allowing them to upload videos or images as needed.
You can also upload or create checklists on your mobile devices for in-house assessments using our software.
This allows you to spot areas that need extra attention and fix potential issues in your food processes before the FSSC 22000 audit. Our smart tools help you review and ensure everything is on track.
You can also use insights from the gap analysis to improve your auditing checklists, evaluate your team's problem-solving effectiveness, and prepare for annual surveillance audits.
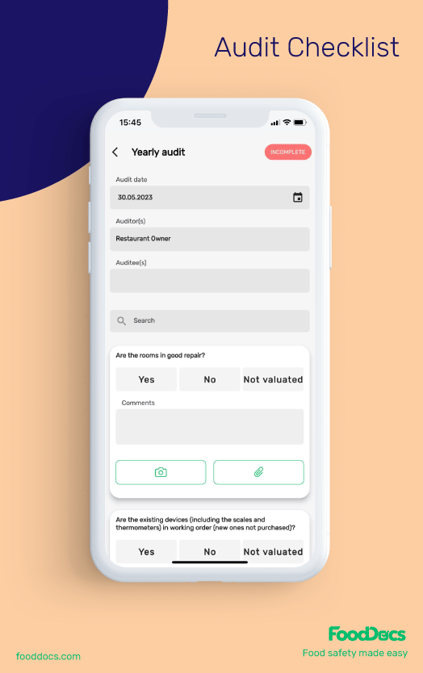
Smart auditing tools from FoodDocs software
You can take a big step forward in your journey to get FSSC 22000 certified with our handy HACCP plan template builder. Our software simplifies the process by creating a comprehensive digital HACCP plan template automatically, and you can tweak it to suit your needs.
You can meet crucial FSSC 22000 requirements in about an hour using our built-in HACCP builder. Plus, it's flexible. You can easily add suggestions from accrediting bodies because our digital HACCP plan is fully customizable.
If all of that sounds interesting, give our FSSC 22000-ready system a test run with our free 14-day trial. Experience firsthand how our software can simplify your path to compliance.
You can also schedule a one-on-one demo with our food safety and software experts. They'll guide you through our smart software, demonstrating how it can efficiently help your business get FSSC 22000 certified.
To help you understand more about FSSC 22000 certification, here are a few of the most common questions asked regarding this topic:
Yes, the FSSC 22000 is GFSI recognized. While the older FSSC 22000:2013 version 4.1 certification wasn’t recognized by GFSI, the new version 5.1 is benchmarked. Being recognized by GFSI gives organizations worldwide recognition and enables them to be accepted by retailers and food manufacturers all around the globe, including the United States.
Unlike FSSC 22000, the ISO 22000 standard isn’t recognized by the GFSI. The FSSC 22000 certification also comes with other sector-specific regulatory requirements. For instance, to implement ISO 22000, you only need to comply with its 2018 standard requirements.
In contrast, FSSC 22000 requires you to comply with ISO 22000: 2018, ISO/TS 22002-1-6, and additional requirements like service management, management of allergens (C, E, F, G, I, and K), and environmental chain monitoring (C, I, and K).
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...