Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Food businesses must have appropriate allergen management plans for the big 8 allergens. The effects of food allergens on susceptible customers with food allergies can range from mild to life-threatening. Your team is responsible for informing customers about the potential food allergens in your products and ensuring allergen control.
In the US, at least 32 million people are estimated to have food allergies. Globally, around 1.1% to 10.8% of the population suffer from at least one food allergy. With this many people having food allergies, your approach to controlling allergens in your business must be a priority. Causing food allergy concerns can significantly affect your reputation and even warrant offenses from food safety agencies.
WHAT WE'LL COVER:
Food allergy refers to a medical condition where the immune system of an individual abnormally reacts to a stimulant food ingredient entering the body. When an individual has a food allergy, their immune system mistakes particular proteins in some foods as harmful substances and produces significant reactions as countermeasures.
Food allergy reaction is a serious public health concern and is considered a food safety hazard.
In some cases, food handlers mistake the term food allergies for food intolerance. Unlike food allergies, intolerance to foods manifest as chemical reactions of the body to ingesting a particular food. A great differentiating example of the terms is lactose intolerance and milk allergy.
While both require the removal of milk products or dairy in a food product, milk allergy involves hypersensitivity of the immune system, whereas lactose intolerance is the digestive system's inability to process lactose.

An individual may be allergic to one or more conventional food ingredients. When an allergen enters the body, an allergic person's immune system aggressively reacts by releasing chemical responses throughout the body, which causes inflammation in different body parts.
As mentioned, at least 1.1% to 10.8% of the global population have food allergies. The reaction of an individual's immune system to a food allergy may differ from others. For some, allergies could be mild, whereas, for others, the reactions can be life-threatening.
Some studies have shown that children with food allergies, such as egg allergy, often outgrow the reactions in time.
In the food industry, cross-contact with allergens is a serious food safety issue. In fact, allergenic presence has been named a top reason for food recalls in recent years.
The body reacts differently to food allergens. Typically, a food allergy reaction develops within a few minutes to an hour upon consuming the food allergen.
Food allergies manifest differently among individuals. Immune reactions in customers may depend on their general health. Some of the common symptoms of a food allergy may include the following immune responses:
Symptoms may show in combination, and even mild conditions of food allergy could last up to several hours. Severe cases of allergic reaction have severe health risks and require medical attention as it may sometimes lead to death.
In some cases, the first wave of allergic reactions may subside, and another set may manifest after a few hours. Allergic reactions require very strict monitoring.

In the US, the Food Allergen Labeling and Consumer Protection Act of 2004 (FALCPA) declared the eight most common allergenic foods. The list contains the most common foods that cause at least 90% of the allergic reactions recorded in the US. The top food allergens are:
Eggs, including egg products
Fish
Crustacean shellfish (e.g., crab, shrimp, and lobster)
Tree nuts (e.g., almond, cashew, and chestnut)
Peanuts
Soybeans
Wheat (gluten)
Milk
The recent establishment of the Food Allergy Safety, Treatment, Education, and Research Act (FASTER) has officially declared sesame as a part of what is now the big 9 allergens list in the US. The revisions indicated in this law will take effect on January 1, 2023.

Any food containing the listed products may trigger allergic reactions in people with food allergies. Cross-contact between food contact surfaces and allergenic foods can also become a source of contamination. The food production process of non-allergenic products in a facility that also prepares meals with allergens has a very significant chance of cross-contact.
As such, the FDA enforces food establishments to declare any food allergen that their products may contain. This regulation also includes labeling the product if manufacturers made it in a facility processing allergenic foods.
Proper food labeling with allergens in them is an essential step for food establishments. This is to protect consumers from any potential problems that may put their lives in danger. Use our free Food Allergen Poster to help customers and food handlers identify and familiarize themselves with common food allergens.
In the US, there are only 8 major food allergens. The provided information by the FDA is not an exhaustive list. At least 160 foods have already been identified to have the potential to cause allergic reactions in individuals. Food allergies are often specific to a particular protein in food. If a type of food has these allergenic proteins, it could also cause allergy.
In other countries, at least 14 foods are considered major food allergens. The UK, for example, mandates food businesses to properly declare whole ingredient lists with an emphasis on allergens for pre-packed or direct sales foods. This mandate is enforced through Natasha's Law in the UK.
In addition to the big eight allergens previously stated, Natasha's Law recognizes these 6 ingredients as part of the list:
Sesame
Lupin
Molluscs
Mustard
Celery
Sulfites (or Sulphur dioxide)
In the US, only the 8 major allergens, including sesame, must be identified on the food label. Despite this, having knowledge of all food allergens can significantly help your team create a management system for controlling allergens and any potential adverse reactions resulting from consuming your products.
Ideally, physical segregation of allergenic foods from non-allergenic raw materials must be regularly done. To prevent cross-contact, allergenic foods must be stored in a separate container. Airtight containers with proper labels are preferred.
When stored on shelves, place allergic foods on lower shelves to prevent cross-contact. Properly label containers and do not use them for storing non-allergenic foods without sanitation. Proper storage lowers allergen risk and the potential for cross-contact.
These conditions are only required if you are offering foods that claim to have no allergens. Customers must also be informed if your processing facility accommodates dishes and finished products that use allergenic ingredients as a precaution
Customers with weak immune systems and food allergies can be more sensitive than others. Their compromised immune system can trigger severe food allergies even with a small amount of the allergen.

In the US, some of the most common food allergies are peanut allergy, milk allergy, and shellfish allergy. The listed major food allergies by the FALCPA are responsible for the vast majority of allergy cases in the US.
At least 1.2% of the entire population of the US is allergic to peanuts. More specifically, 2.5% of the children in the US have hypersensitivity to peanuts. Peanut allergy is even attributed as the leading cause of allergy-related fatalities among allergic children in the US.
In other publications, Americans from different age groups were identified to be most allergic to shellfish. It was also estimated that at least 40% of the younger population of the US is allergic to more than one food ingredient.

As a requirement under the FALCPA, food businesses are required to declare all food allergens in their food products. Food allergen declaration also applies to single-ingredient packaged foods such as evaporated milk and canned fish.
An allergen ingredient statement can help customers identify if an ingredient used in your product is derived from a major allergen or which ingredient contains the allergen. For example, products containing lecithin may not strike customers readily that the ingredient is made from soy or has soy components in it. Another example would be nut butter. Customers will be unable to identify which types of tree nuts are used in your product unless mentioned in the ingredient statement.
There are two ways how to identify allergens in your ingredient declaration according to the FALCPA:
In using advisory statements for the 8 major allergens, the exact wording used by the FALCPA must be used to avoid confusion (e.g., Milk, Soy, and others). For vague allergens such as fish, tree nuts, and crustaceans, you need to identify which ingredient is under which allergen category.
In some cases, food businesses also include a statement declaring that a product is processed in a facility that handles other allergens. Although not mandated by the FDA, this claim can help warn allergic individuals.
Advisory statements can also be included in menu boards as a restaurant menu disclaimer for food items.
Remember that an ingredient declaration is not a food business's scapegoat for liabilities in case of food allergy incidents concerning your product. The declaration must not be used as an excuse to allow cross-contact in your food service establishment.
The FDA conducts different activities to ensure that food businesses follow the established rules directly related to controlling allergens in the US.
Food businesses are entitled to the guidance documents released by the FDA, which shed light on the current understanding and take of the industry on allergen topics. In addition, the FDA performs inspections and audits to check if food businesses comply with rules such as the CGMP and PC rule. This rule includes the required preventive controls for allergens within the food industry.
In case of issues reported to the FDA are considered offensive, such as mislabeling, undeclared allergens, or the occurrence of cross-contact in a food establishment, the agency can order regulatory actions against a food business. Some cases can warrant product recalls, seizure of goods, or even declining import permits.

Allergen management refers to a comprehensively documented system built to identify, control, and prevent food safety issues regarding food allergens in a food business.
The allergen management system entails detailed documentation of the following topics:
Allergen management aims to equip food handlers with the necessary knowledge on how to properly handle allergenic foods, their risks, and the potential problems they may cause. This system also aims to create a way how to communicate the risks of potentially present allergens to your consumers.
As part of food safety regulations, food businesses are responsible for protecting sensitive individuals from allergens in their foods. Allergen management is an essential part of food safety systems such as a HACCP plan. It involves collecting information, control procedures, corrective actions, and monitoring techniques for managing allergens.
While an allergen management plan can be confusing and is traditionally done manually, we have developed a digital solution that is easy to set up and use. Using our built-in, customizable HACCP plan template, you can get an Allergen Management Plan along with a comprehensive HACCP plan by just answering a few questions about your food operations.
Read more on how to get your allergen management plan and a HACCP plan in just 1 hour at the end of this article.
Allergen control is a systematic plan used by food businesses to identify and establish control procedures against potential issues from allergen contamination. Allergen control is otherwise known as allergen management.
This plan consists of steps and procedures on how to store, handle, process, and distribute foods without the risk of allergenic reactions, the same we talked about in the previous chapter. It involves procedures on how to teach food employees and educate customers regarding the risks of allergens and hypersensitivity towards them.
Several components of an allergen management program start with knowing your food products. Food safety teams must be fully aware of what ingredients are used to build the product, the machines and areas involved, and who are the authorized food handlers to handle allergenic foods.
Causing an allergic reaction within your food premise or as a result of consuming your products may put the life of a customer in danger. In serious cases, allergy cases can cause a life-threatening reaction. It is part of your commitment as a food business to protect consumers from any potentially hazardous food source.
Food handlers must have a substantial understanding of what food allergens are and how their management applies to food safety.
Below are some steps needed when starting a food allergen management process:
A part of the management plan is being ready in case contingencies occur. Sometimes, food safety issues may happen, and customers can become affected. In some cases, corrective actions such as assisting customers with allergy symptoms and seeking medical attention from professionals may be tasked to your food employees. It would even be helpful if at least one employee is trained to administer first aid to suppress adverse symptoms.
Additionally, and as part of the corrective action plan, your team must also have an appropriate traceability plan to track potentially cross-contaminated products to prevent further damage. In case food safety agencies detect any significant non-compliance from your food business, you will need to have a clear plan on how to track potentially affected areas in your market.
Food safety training must include instructions and protocols on how to handle allergenic foods on your menu. Food handlers are expected to be knowledgeable about the risk of allergens on public health. Food allergy training should also be regularly updated and refreshed to help food handlers cope with the changes in their operations and food regulations regarding food allergies.
In addition to the components of an allergen management plan, a food business must have a comprehensive food safety management system that will ensure compliance with food safety laws when it comes to controlling pathogens.
At FoodDocs, we can help you cover all areas mentioned in this list and create a comprehensive Allergen Management Plan in the fastest way possible.
In combination with a complete HACCP plan, your team must have a monitoring system that will ensure the exclusion of allergens in food products when you claim to be completely allergen-free and ensure the safety of your consumers. Luckily at FoodDocs, we offer a combined digital HACCP plan and Food Safety Management System software.
With our digital solutions, you can ensure that all areas that are expected to have no allergens will remain as such. In addition, our digital solution can help food handlers improve efficiency in performing other food safety tasks.
Allergen management is an essential part of every food establishment's food safety plan.
To help your team manage allergens, you must set up your food safety plan as soon as possible. This plan will include the necessary control measures, corrective actions, and monitoring procedures needed to control any potential presence of allergens. We offer what may be the fastest way to get a comprehensive HACCP plan template with an Allergen Management Plan fit for your operations.
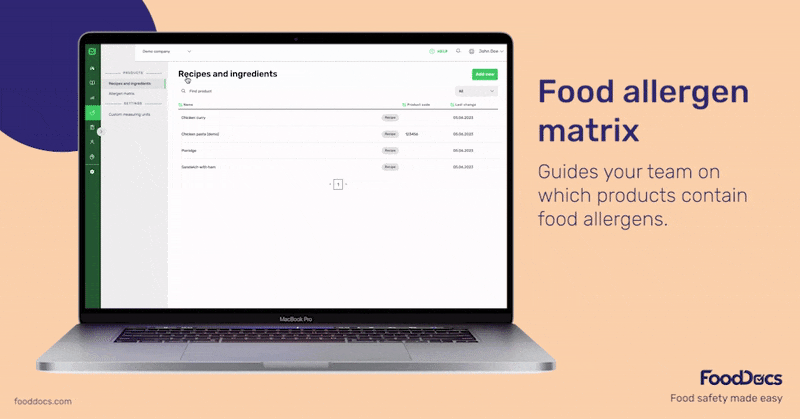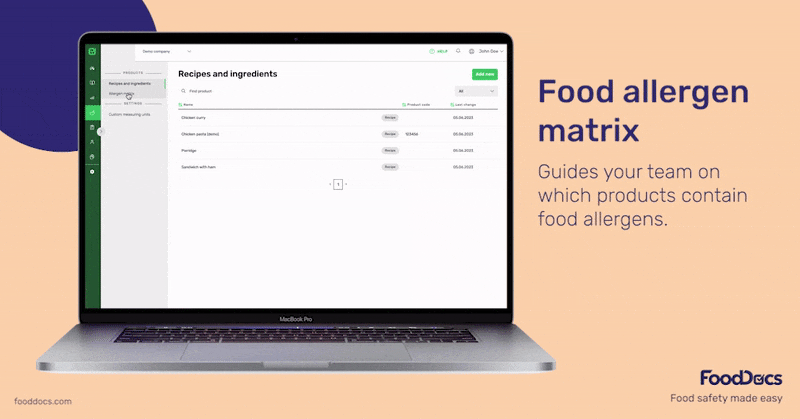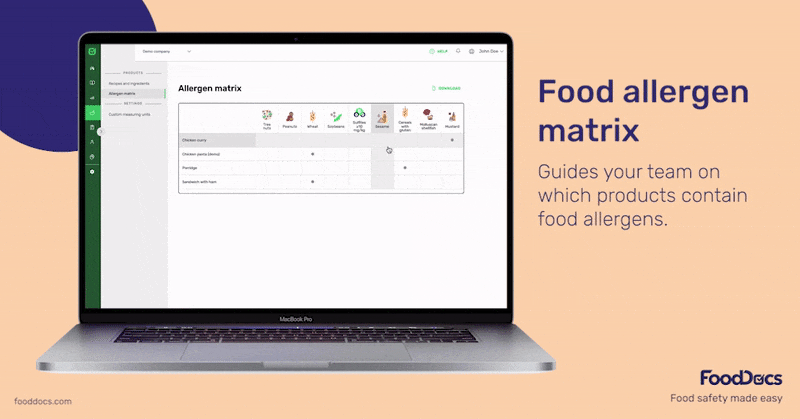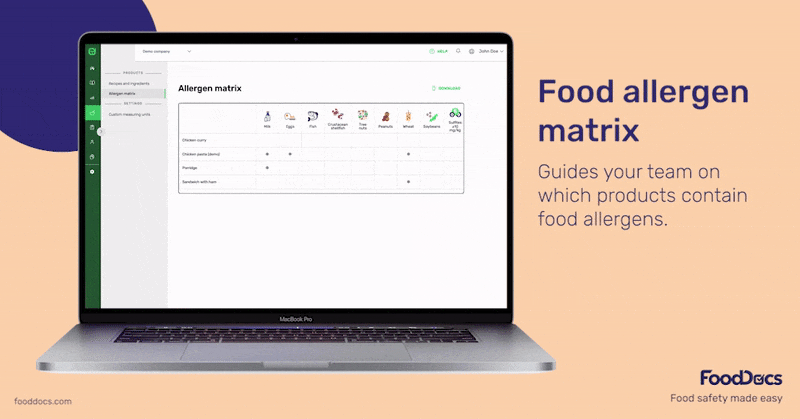
Using our HACCP builder, you can get a comprehensive HACCP plan template with all of the basic and advanced parts of a HACCP plan. In line with allergen management, our software generates an Allergen and Consumer Information section with the following components:

You can build all HACCP plan documents and allergen management systems with FoodDocs in 1 hour. All you need to do is answer a few questions describing your operations to our system. The whole process is 500x faster than manually doing all the documents.
In addition to a comprehensive digital HACCP plan template and an allergen information section, we also offer a digital Food Safety Management System with smart solutions for maintaining food safety in your establishment.
Our digital FSMS is powered by a machine learning program, enabling it to automatically generate food safety documents needed by your food business.
The features that our digital solution can provide you to help manage allergens include the following:

When you try our digital FSMS product, you can get access to an Allergen Management SOP template and store them in the Document depository of our application. In addition to the mentioned features, our digital FSMS solution can also help managers improve efficiency in managing food safety.
You can get a real-time dashboard that gives you an overview of your entire food safety operations. This feature can help you save at least 20% of your time from supervising food safety tasks. With a real-time dashboard, you can immediately identify areas of concern and address them before they go out of hand.
Using our digital solutions can significantly save time as you get the food safety plans you need in just minutes. You can focus more on implementing food safety regulations and ensuring that your establishment has the necessary tools to control common allergens.
Protect your customers from food safety issues and start your food safety journey with us. Try our services now by using our 14-day free trial.
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...