Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Discover the big 9 allergens and what food businesses need to know to manage them safely.
Food allergies are a ticking time bomb in the food industry. Every day, millions of customers walk into restaurants, cafes, and catering establishments, unaware of the potential dangers lurking on the menu.
As a food safety and quality manager or a frontline food handler, you are the last line of defense against a potentially life allergic reaction. The consequences of a mistake can be catastrophic, yet the solution is simple: knowledge.
Keep reading and you'll leave well-armed with the critical information you need to protect your customers and your business from the top 9 food allergens that can cause chaos in the kitchen.
Approximately 6% of adults and 8% of children in the United States have food allergies, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Top 9 food allergens are milk, eggs, peanuts, fish, crustacean shellfish, tree nuts, wheat, soybeans, and sesame, which account for 90% of all food allergic reactions.
Food allergies can cause severe reactions, including anaphylaxis, which can lead to life-threatening symptoms, such as difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat, and a drop in blood pressure.
The FDA takes a multi-faceted approach to protect consumers from food allergens, including establishing regulatory requirements, providing industry guidance, conducting inspections, monitoring reports, testing and sampling, and enforcing regulations.
Food labels are required to list the top 9 allergens in a specific way, but there are over 160 other foods that have been reported to cause allergic reactions.
The FDA can't change the list of top 9 major food allergens on its own, but it can require labeling for other food allergens if necessary.
Food manufacturers can request exemptions from food allergen labeling if they can prove that their ingredient doesn't cause an allergic response or doesn't contain allergenic protein.
Failure to comply with food allergen labeling requirements can result in severe consequences, including recalls, import refusal, seizure, and warning letters.
Knowing about food allergens is crucial for both companies and consumers, as it can help prevent severe reactions, protect reputations, and maintain customer trust.
Using food safety management software such as FoodDocs can help food establishments easily manage allergens and ensure compliance with regulations, reducing the risk of food allergic reactions and protecting customers' health.
Major food allergens identified by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) fall into two categories:

Milk is one of the most common food allergens among infants and young children. The FDA considers milk from domesticated cows, goats, sheep, or other ruminants as a major food allergen. This includes all forms of milk, such as whole milk, low-fat milk, skim milk, milk proteins like casein and whey, and milk by-products like lactose and milk fat.
Milk is often used as an ingredient in various food products, such as cheese, yogurt, ice cream, baked goods, and sauces. Individuals with a milk allergy may experience symptoms like hives, itching, swelling, stomach cramps, diarrhea, and anaphylaxis after consuming milk or milk-containing products.
People with a milk allergy need to be careful when reading food labels, as milk can be hidden in many products under different names. Some examples of milk-derived ingredients include lactalbumin, lactoglobulin, lactose, and milk protein concentrate. It's essential to note that lactose intolerance is different from a milk allergy.
Eggs are another common food allergen, especially among children. The eggs from domesticated chickens, ducks, geese, quail, other fowl as a major food allergen. This includes all forms of eggs, such as whole eggs, egg whites, egg yolks, egg by-products like egg protein and egg lecithin.
Eggs are often used as an ingredient in various food products, such as baked goods, pasta, sauces, and processed meats. Individuals with an egg allergy may experience symptoms like hives, itching, swelling, stomach cramps, diarrhea, and anaphylaxis after consuming eggs or egg-containing products.
People with an egg allergy need to be careful when reading food labels, as egg can be hidden in many products under different names. Some of egg-derived ingredients include ovotransferrin, ovomucoid, and egg white protein.
It's essential to note that some vaccines, like the flu vaccine, are grown in chicken eggs and may contain small amounts of egg protein. Individuals with an egg allergy should consult their healthcare provider before receiving these vaccines.
Peanuts are one of the most common and severe food allergens, affecting millions of people worldwide. Peanuts are legumes that belong to the same family as beans and lentils. The FDA considers as a major food allergen, including all forms of peanuts, such as whole peanuts, peanut butter, peanut oil, and by-products like peanut flour and peanut protein.
Peanuts are often used as an ingredient in various food products, such as baked goods, sauces, processed meats, and snack foods. Individuals with a peanut allergy may experience symptoms like hives, itching, swelling, stomach cramps, diarrhea, and anaphylaxis after consuming peanuts or peanut-containing products.
Peanut allergies are often associated with tree nut allergies, and individuals with a peanut allergy may also be allergic to tree nuts like almonds, walnuts, and cash. People with a peanut allergy need to be careful reading food labels, as peanuts can be hidden in many products under different names.
Some examples of peanut-derived ingredients include peanut lecithin, peanut oil, and peanut protein hydrolysate.
Tree nuts are a common food allergen, affecting millions of people worldwide. The FDA is aware that there is no universally accepted botanical definition of the term "tree nut." However, tree nuts generally refer to edible seeds or nuts of trees, such as almonds, walnuts cashews, and pecans.
Tree nuts are often used as an ingredient in various food products, such as baked goods, sauces, processed meats, and snack foods. Individuals with a tree nut allergy may experience symptoms like hives, itching, swelling, stomach cramps,, and anaphylaxis after consuming tree nuts or tree nut-containing products.
People with a tree nut allergy need to be careful when reading food labels, as tree nuts can be hidden in many products under different names. Some of the tree nut-derived ingredients include almond milk, walnut oil, and cashew butter.
Fish is a common food allergen, affecting millions of worldwide. The FDA considers fish a major food allergen, including all forms of fish, such as whole fish, fish fillets, fish sticks, and fish by-products like fish oil and fish protein.
Fish is often used as an ingredient in various food products, such as sushi, seafood salads, and processed meats. Individuals with a fish allergy may experience symptoms like hives, itching, swelling, stomach cramps, diarrhea, and anaphylaxis after consuming fish or fish-containing products.
People with a fish allergy need to be careful when reading food labels, as fish can be hidden in many products under different names. Some examples of fish-derived ingredients include cod liver oil, fish gelatin, and anchovy paste.
Crustaceans, also known as shellfish, are a common food allergen, affecting millions of people worldwide. The FDA considers crustaceans as a major food allergen, including all forms of shellfish, such as shrimp, crab, lobster, and crayfish.
Shellfish is often used as an ingredient in various food products, such as seafood salads, sushi, and processed meats. Individuals with a shellfish allergy may experience symptoms like hives, itching, swelling, stomach cramps, diarrhea, and anaphylaxis after consuming shellfish or shellfish-containing products.
People with a shellfish allergy need to be careful when reading food labels, as shellfish can be hidden in many products under different names. Some examples of shellfish-derived ingredients include shrimp paste, crab meat, and lobster extract.
Wheat is a common food allergen, affecting millions of people worldwide. The FDA considers wheat as a major food allergen, including all forms of wheat, such as whole wheat, wheat flour, wheat germ, and wheat by-products like wheat starch and wheat gluten.
Wheat is often used as an ingredient in various food products, such as baked goods, pasta, cereals, and processed meats. Individuals with a wheat allergy may experience symptoms like hives, itching, swelling, stomach cramps, diarrhea, and anaphylaxis after consuming wheat or wheat-containing products.
People with a wheat allergy need to be careful when reading food labels, as wheat can be hidden in many products under different names. Some examples of wheat-derived ingredients include wheat protein, wheat starch, and wheat gluten.
Soy is a common food allergen affecting millions of people worldwide. The FDA considers soy as a major food allergen, including all forms of soy, such as whole soybeans, soy milk, soy flour, and soy by-products like soy protein and soy lecithin.
Soy is often used as an ingredient in various food products, such as tofu, edamame, and processed meats. Individuals with a soy allergy may experience symptoms like hives, itching, swelling, stomach cramps, diarrhea, and anaphylaxis after consuming soy or soy-containing products.
People with a soy allergy need to be careful when reading food labels, as soy can be hidden in many products under different names. Some examples of soy-derived ingredients include soy protein isolate, soy lecithin, and soy oil.
Sesame is a common food allergen, millions of people worldwide. Sesame is a seed that is often used as an ingredient in various food products, such as baked goods, sauces, and processed meats.
Individuals with a sesame allergy may experience symptoms like hives, itching, swelling, stomach cramps, diarrhea, and anaphylaxis consuming sesame or sesame-containing products.
People with a sesame allergy need to be careful when reading food labels, as sesame can be hidden in many products under different names. Some examples of sesame-derived ingredients include sesame oil, sesame seeds, and tahini.


Thank you for downloading free template!
Want to get a customizable HACCP template?
Or set up your food safety system in 15 minutes?
Approximately 6% of adults and 8% of children in the United States have food allergies, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The most recent data come from two reports published in 2021 for adult food allergies and children's food allergies.
Some key food allergy statistics from the adult and children reports include:
The most common food allergies are milk, eggs, fish (including popular varieties like bass, flounder, and cod), crustacean shellfish (such as crab, lobster, and shrimp), tree nuts (including almonds, walnuts, and pecans), peanuts, wheat, soybeans, and sesame.
The 2004 Food Allergen Labeling and Consumer Protection Act (FALCPA) highlighted the "big 8 allergens", which accounted for 90% of all food allergic reactions. In 2021, the Food Allergy Safety, Treatment, Education and Research (FASTER) Act added sesame to the list, which is why the name has been updated to the "big 9 allergens".
This designation is critical in helping individuals with food allergies identify potential allergens and take necessary precautions to safeguard their health.
The common symptoms of an allergic reaction to food include:
It's essential to recognize these symptoms and seek immediate medical attention if you or someone you know is experiencing an allergic reaction. A kitchen and food handler team trained in food safety and allergen management will enable them to more promptly recognize and start (or facilitate) treatment that can save lives, and being aware of the allergy warning signs is crucial in preventing anaphylaxis-related fatalities.
A. Chili powder
B. Vegetable oil
C. Cooked zucchini
D. Spaghetti noodles
Spaghetti noodles contain a major allergen recognized by the FDA: wheat.
Here's the reasoning for the options provided:
Now you'll know the answer if you ever see this question on a food handlers practice test or a food safety quiz.
The FDA takes a multi-faceted approach to protect consumers from the big 9 food allergens, including:
These measures aim to minimize the risk of food allergic reactions and protect consumers from the big 9 allergens.
Yes, there are over 160 foods that have been reported to cause allergic reactions, in addition to the top 9 major food allergens. However, food labels are only required a to list the top 9 allergens in a specific way. If you're allergic to a food that's not on the list, you may still react to it, but the label may not warn you.
The FDA can't change the list of top 9 major food allergens on its own, but it can require labeling for other food allergens if necessary. For example, if a spice or flavoring contains a food allergen that's not on the list, the FDA can require it to be disclosed on the label.
Yes, manufacturers can ask the FDA for an exemption from labeling requirements if they can prove that their ingredient doesn't cause an allergic response or doesn't contain allergenic protein. They'll need to provide scientific evidence to support their request. If the FDA grants the exemption, the ingredient won't be considered a major food allergen and won't be subject to labeling requirements.
If a food label can't comply with allergen labelling requirements, the FDA can take regulatory action. This can include recalls, import refusal, seizure, and warning letters. Firms that make non-compliant food products may also be put on import alert. In most cases, firms will voluntarily recall their products from the market to avoid these consequences.
The reason why it's important to know about food allergens has two perspectives worth highlighting:
As a food establishment, knowing about food allergens is crucial to protecting your business and reputation. Failure to identify and manage food allergens can result in severe consequences, including:
Having a solid understanding of food allergens can help you to:
By taking food allergens seriously, you can minimize risks, protect your customers, and maintain a positive reputation in the industry.
As a consumer, knowing about food allergens is a matter of life and death. If you have a food allergy, accidentally consuming an allergenic ingredient can trigger a severe reaction, including anaphylaxis. This can lead to:
Being able to access to accurate information about food allergens can empower you to:
By being aware of food allergens, you can take control of your food choices, protect your health, and live a more confident and carefree life.
Allergen management is an essential part of every food establishment's food safety plan. FoodDocs' digital food safety management system helps your team monitor and trace ingredients in your cooking or production process with an intuitive, easy-to-use mobile app.
If needed, you can also get an AI-powered, done-for-you HACCP plan that includes the necessary measures, corrective actions, and monitoring procedures needed to control any potential presence of allergens.
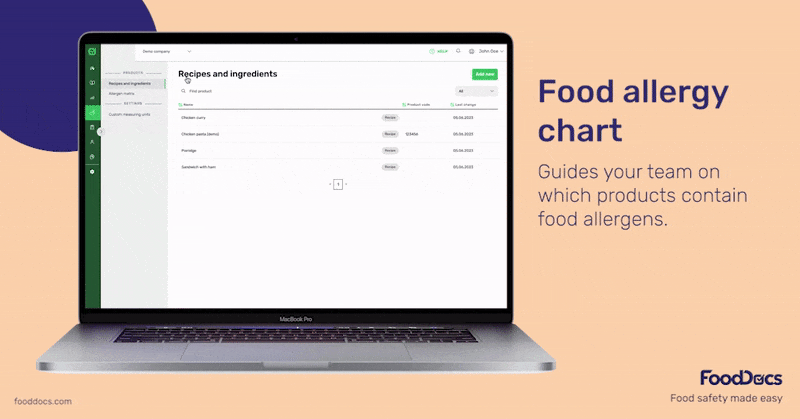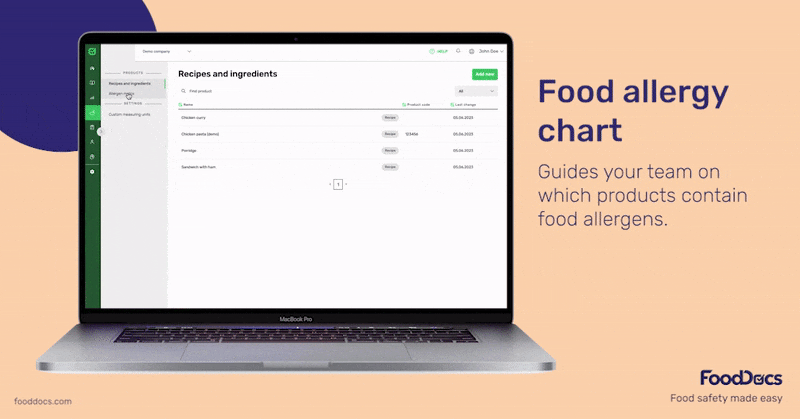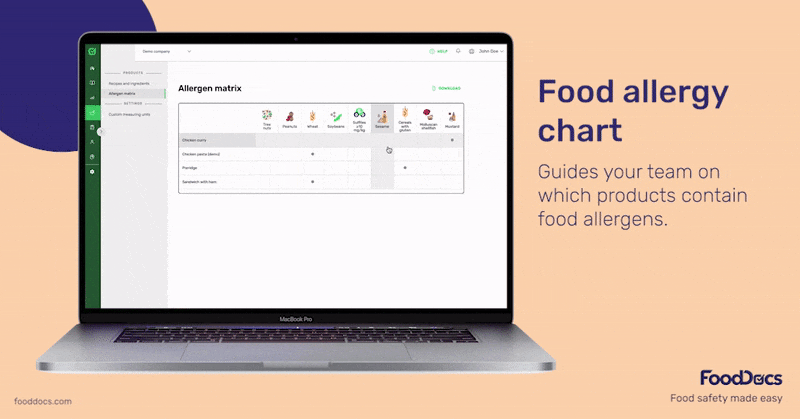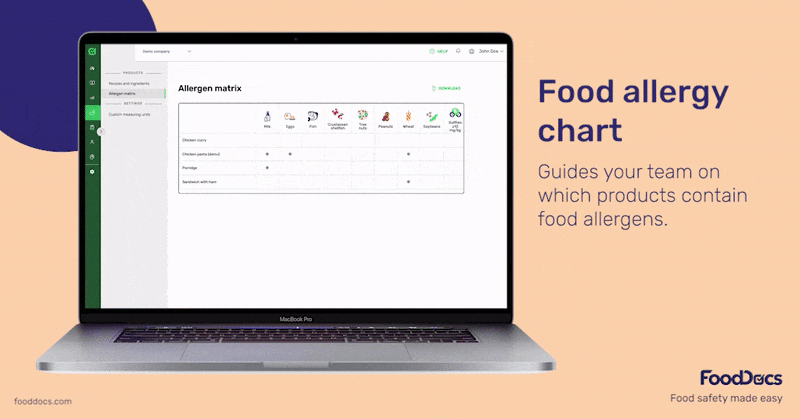
You can get started free for 14 days or book a personalized demo to see how FoodDocs can support your business specifically.
The FD&C Act (Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act) is a law that requires food labels to list each ingredient by its common name, except for certain ingredients like spices, flavorings, and colors.
No, molluscan shellfish (e.g., oysters, clams, mussels or scallops) are not considered a major food allergen under the FD&C Act. However, crustacean shellfish (such as crab, lobster, or shrimp) are considered major allergens.
The FDA considers the following categories of fish to be allergenic:
The FDA Food Code is a model code that provides guidelines for retail food establishments, such as restaurants, grocery stores, and hospitals, to follow to ensure food safety and prevent foodborne illness. The Food Code includes provisions related to food allergens, including:
The Food Code is updated regularly, and the 2022 version includes updated information on food allergens.
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...