Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Food contact surfaces such as prep tables are potential critical sources of contamination when not properly sanitized.
The majority of restaurant kitchens' cooking process happens at the food preparation table. This is where the cutting, peeling, shredding, and assembling happen before and sometimes after cooking the food.
With all the interactions occurring at a food prep table, the likelihood of cross-contamination between the food supply and the food product contact surface and vice versa is significantly high. Food handlers must be trained on what is the proper way to sanitize a table that has been used for preparing food items.
Cleaning a kitchen table top or preparation table must be done according to the recommended sequence. The proper sequence of cleaning operations and sanitation ensures that the processes will be effective, and recontaminating of the food contact surface will not occur.
Follow these 5 simple steps steps to clean and sanitize food preparation tables:
Food preparation tables must be cleaned and sanitized regularly to prevent cross-contamination and foodborne illnesses.
Sanitation effectiveness relies heavily on the correct concentration, contact time, temperature, and pH of the sanitizing solutions used.
All foods in a restaurant pass through the prep table, making its cleanliness crucial to food safety.
Sanitizing food preparation tables is as critical as sanitizing other kitchen tools like knives and chopping boards.
Proper cleaning and sanitation techniques involve a sequence of wiping, washing, rinsing, sanitizing, and air drying.
Using the right materials like non-abrasive brushes for cleaning can enhance the effectiveness of sanitation without damaging surfaces.
Food-grade sanitizers approved by regulatory bodies like the EPA are essential for ensuring safety and compliance.
Hand sanitizers are not always suitable for food prep tables due to potential scent transfer and cost issues.
Food safety management software like FoodDocs can streamline sanitation operations and ensure compliance through automated reminders and checklists.
WHAT WE'LL COVER:
Food preparation tables must always be cleaned and sanitized. These tables are used to prepare almost any dish in a restaurant and therefore must be cleaned and sanitized.
A preparation table is one of the areas in a kitchen with the highest traffic value and has direct food contact. As such, the likelihood of cross-contamination occurring in this area is significantly high. This risk can be reduced with regular sanitation.
Sanitizing food preparation tables is an invaluable step to controlling food safety. Less frequent sanitation can lead to the unwanted growth of harmful bacteria and other pathogens.
Sanitation of food preparation tables is as important as with knives, chopping boards, kitchen sinks, and kitchen equipment. Continuous use of a food prep table may cause food buildup and attract contaminants such as foodborne illness-causing bacteria and pests.

To make the cleaning and sanitation more effective, food handlers will need to use some additional materials. You can use non-abrasive, clean produce brushes to help in removing food stains. Avoid steel wool brushes as this may scratch the table. Scratches can harbor stains or food debris, which may encourage bacteria growth.
Cleaning and sanitation must be part of every restaurant cleaning checklist.
Cleaning and sanitation of prep tables are performed to prevent the exposure risk of cross-contamination between the table and the food being prepared and vice versa. This food safety issue is the primary concern with an unclean surface. A preparation table is used for several food operations, such as preparing both raw foods and ready-to-eat food products.
Potentially present food contaminants may transfer from the raw material to the preparation table. Without cleaning and sanitation in between preparing different types of food, contaminants can freely transfer from one food ingredient to another.
In addition, liquid spills and food residues on the food contact surface may dry out and stick to the contact surface. Removing visibly large food debris may reduce the risk of contamination, but the dried fluids may still have the contaminants.

The general sanitizing solution used in restaurant food prep tables is diluted bleach water or chlorinated detergents. Alternative to a solution of chlorine bleach, restaurants also use quaternary ammonium salts or scalding hot water for sanitation as well. The important thing is that the utilized sanitizer has a potent antimicrobial activity.
The type of sanitizer used in a restaurant is often a personal choice of the food safety team. What matters in sanitation is its proper application. For the sanitizer activity to be effective, the following factors must be satisfied:
Other factors that may affect the effectiveness and activity of sanitizer include the temperature of used water, pH, and the table's type of material. The loss of activity at temperatures and pH values below the recommended range is common in some sanitizers. The bactericidal activity of chlorine sanitizers, for example, significantly changes depending on the pH and temperature of the water.
Each sanitizing solution will vary in concentration and contact time. For example, chlorine or bleach solution is generally used at 100 ppm concentration and applied for at least two to 5 minutes. On the other hand, squats or quaternary ammonium salts-based solutions are generally advised to be used at 200 ppm with at least 1 minute contact time.
For sanitation to become effective, the contact surface being sanitized must first be cleaned of any visible debris or food. Sanitizers can only remove pathogens that it comes in contact with. Large food debris or dried food liquids can obstruct the effect of sanitizer.
There are several types of detergents and sanitizers in the food industry. Some are alkaline detergents and acid detergents. The food industry imposes a strict protocol for approved sanitizers on metal surfaces to minimize safety risks and regulatory concerns. Only food-grade sanitizers that are approved by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) must be used in food businesses.

Disinfectants approved by the EPA usually have the following active form of ingredients:
These active ingredients are presented on the label of solutions. They will determine the sanitizer's reaction to microorganisms. Review the effectiveness of the sanitizer you are using and the range of microorganisms it is effective against. An ideal chemical sanitizer would be able to kill a wide range of pathogens.
Similarly, the effectiveness of every sanitizer, while considering safety, can only be achieved with the correct minimum concentration. Correct use of concentration also ensures that the food in contact with sanitized tables will remain safe.
The sanitation process of tables will depend on the manufacturer's instructions on the sanitizer you are using. The most common contact time recommended by sanitizer manufacturers varies between 30 and 15 minutes.
Concentrated sanitizers require less contact time, whereas diluted ones must stay on the table longer. Contact time refers to how long a solution is required to stay on the sanitized surface to effectively inactivate target pathogens.
During sanitation, the preparation table must remain wet with the sanitizer, and drying must naturally occur after a prep table is cleaned and sanitized. Similar to utensils, drying must occur naturally without the aid of a kitchen towel to prevent recontamination of the surface.
Unlike the stainless steel tables used in the restaurant kitchen for food preparation, the front-of-the-house tables usually use wooden tables. Disinfection of wooden tables works slightly differently when compared with stainless tables. Wooden tables cannot be soaked with water or liquid solutions for long, or that can damage the table.
Follow these steps to disinfect a wooden table:
Unlike preparation tables, the turnover on wooden service tables is faster. Disinfection cannot take too long and must be wiped down quickly. Only paper towels or sanitized disposable cloth towels can be used to maintain the sanitized state of the tables. This ensures that the tables stay sanitized even after wiping.

Although uncommonly used as a preparation table, some food businesses may use a wooden table. This material is also the common choice for service tables.
If you are a believer in natural products for sanitation and you do not want to use any commercial sanitizer chemical agent, you can use natural sanitizers for a wooden table. You can use vinegar, water, and essential oils or soap solutions.
You cannot use the hot water sanitization process for sanitizing a wood table as this may cause the wood to swell. To use this alternative and a natural sanitizer in food processing, follow these steps:
It is very important to test whether the solution, at the concentration you are using it, is effective and up to the standards of regulatory agencies. Ensure that the solution you use has enough germicidal activity against gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms.
You can use hand sanitizers on tables, especially if we are talking about service tables. Despite this, there may be a few problems that may result from using hand sanitizers on tables.
For one, hand sanitizers are more expensive than industrial, food-grade sanitizers. Using them can cost you a lot. Another problem is that some hand sanitizers may not be food-grade or approved by food agencies for use on food contact surfaces. There are a lot of hand sanitizers that are scented, which can transfer to the food served or prepared on the table.
The third step in cleaning and sanitizing a prep table rinsing the table with warm water to remove any residual detergent or soap.
The final step in cleaning and sanitizing a prep table allowing the surface to thoroughly air dry.
A food preparation table is often used in a restaurant kitchen, so there may be very few windows to insert a sanitation operation. Despite this, food preparation table sanitation is a must.
Cleaning and sanitation of food preparation tables must be performed in instances such as the following:
Regular sanitation is part of every food safety plan or food processing cleaning regime and is an essential operation that will keep food safety controlled. Failure to disinfect tables and other high-traffic areas can lead to unwanted food safety concerns such as attracting pests or causing food poisoning.
Want to help your food handlers remember to perform essential operations such as cleaning and food sanitation correctly and on time? FoodDocs' food safety management software can help make your food sanitation operations more efficient.
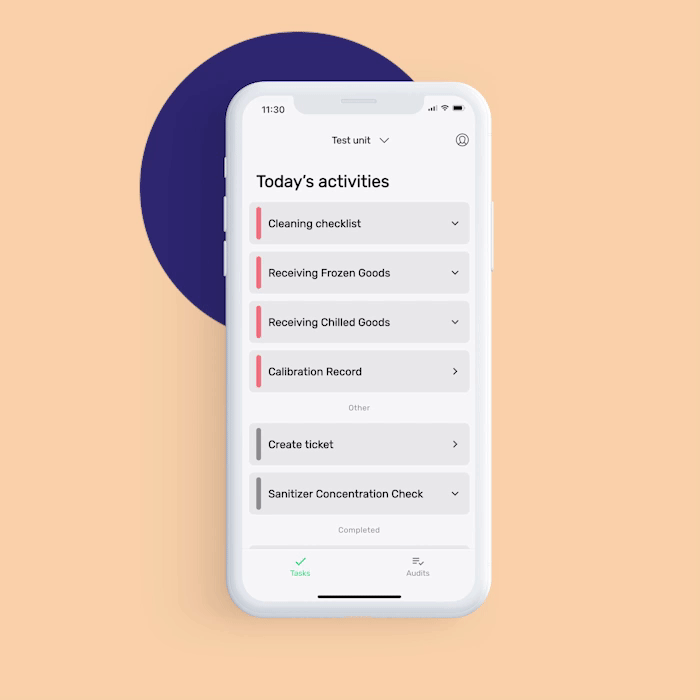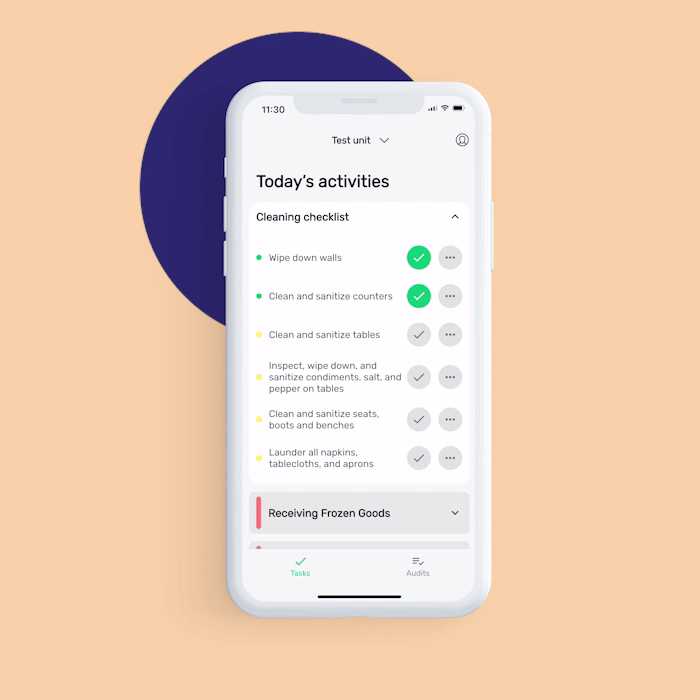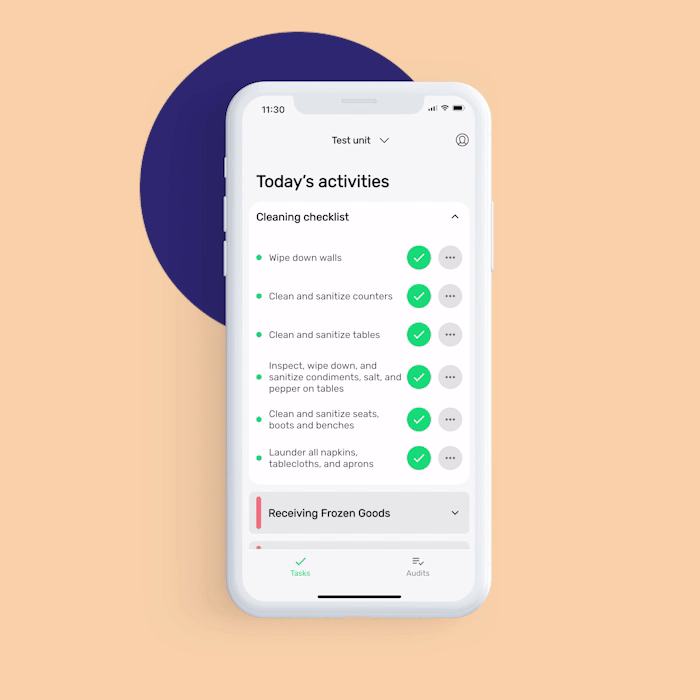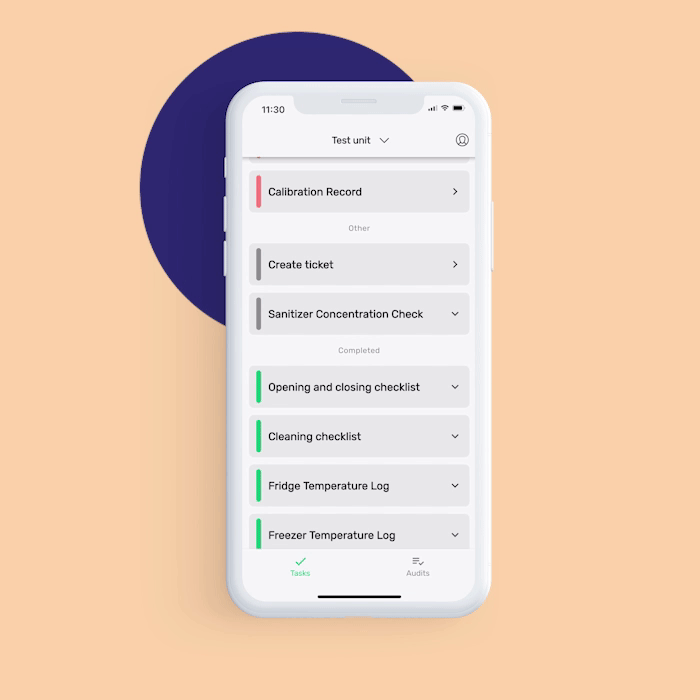

In addition to features that are helpful for employees, our digital solution also offers features to help food safety managers supervise your team:
Our digital solution can help you achieve more efficiency in achieving food safety compliance. You would need to worry less if your employees are doing the operations correctly as we provide detailed instructions to them.
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...