Mastering Restaurant Sanitizing: Best Practices for Kitchens and Dining Areas
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
PLA is a safe and environmentally friendly alternative to common packaging materials.
Is PLA food safe? In short, PLA is a biodegradable and bioactive thermoplastic derived from renewable resources (e.g., corn starch or sugar cane). It's generally considered safe and used for packaging food.
However, we suggest using PLA products that specifically mention compliance with relevant food safety standards to ensure they are suitable for your particular food handling needs.
Polylactic acid (PLA) has recently emerged as a common material in the food industry. That’s because it offers a sustainable and innovative alternative to traditional plastics.
From packaging materials to disposable tableware, PLA's applications in the food sector are expanding. This is driven by a growing emphasis on environmental responsibility and the pursuit of more sustainable practices.
Does it contain any toxic particles or harmful substances? What about toxic chemicals? Read along as we explore these important questions in detail.
Polylactic acid or PLA is an adaptable material used to produce packaging for foods.
PLA filament is a specific type of PLA plastic used for 3D printing food packaging.
PLA is biodegradable, non-toxic, non-allergenic, and environmentally friendly. It doesn't commonly lead to health issues.
PLA is an organic material made out of food starches.
PLA can be used only for prepackaged food that is not hot.
PLA is sensitive to very high temperatures.
FoodDocs' smart Food Safety Management System features a temperature log for recording food temperature before packaging.
WHAT WE'LL COVER:
PLA is a biodegradable and bioactive thermoplastic made from corn starch or sugar cane. It is used as a sustainable alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics for packaging materials, disposable tableware, and other food-related products.
PLA’s material properties are enough to produce a plastic-like material that can act as packaging for foods at ambient temperature. At the same time, it is known for its eco-friendliness because it can break down into harmless byproducts in composting environments or does not release any toxic substances during degradation.
As a result, it’s gaining more popularity on an industrial scale because of the drive to reduce single-use plastic waste by using compostable materials for food products.
You might come across the term “PLA filament” and it’s important to distinguish it from PLA. PLA filament or plastic filament refers to a specific 3D printing material made from PLA using a 3D printer. This means that the filament is derived from PLA and combined with additional additives.
PLA is the general term for the polymer, while PLA filament is a specific form of PLA designed for use in 3D printing technologies.
While PLA filament is generally considered safe for food contact, the final safety of 3D-printed items depends on factors such as the quality of the filament, the print materials, execution of food-safe 3D printing, and any post-processing treatments (such as chemical smoothing) applied.
If the intention is to use 3D-printed items for direct food contact, it's advisable to use PLA filament labeled as food-safe and follow any recommended cleaning and maintenance guidelines.
That’s because not all 3D printing filaments pass safe food grading. Some may cause food safety concerns and develop dangerous chemicals or the growth of bacteria when they come in direct contact with food.
PLA is made mainly of cornstarch or sugar cane, a common food ingredient. The production process involves the following steps:
Food businesses using PLA must ensure the raw ingredients used to produce PLA are all food-grade materials that will not lead to foodborne illnesses.
PLA is generally considered safe for food contact. This property makes it popular for food packaging, disposable tableware, and custom 3D-printed items used in food-related contexts.
Despite this, ensuring the safety of PLA in food products requires attention to certifications, intended use, and considerations specific to the 3D printing process.
Here are four important considerations to keep in mind:
Importantly, PLA is not exempt from food contamination. Bacteria buildup may still occur if it’s not handled properly. This means handling PLA requires strict control of temperature and sanitation.
In a Reddit thread on PLA food safety, people agree that it is food-safe. Although in the context of 3D printing, some caution against using food-grade filament with wet unsealed food because the plastic is porous and its texture is often rough. This increases the likelihood of 3D-printed products collecting food and dirt, resulting in bacterial contamination.
You can use FoodDocs' smart Food Safety Management System to automatically generate monitoring tasks for recording temperature and sanitation practices. You want to record product temperatures before packaging to ensure they are not high enough to create a ground for bacteria.
PLA is generally considered non-toxic under normal use conditions. Here are a few key points about its safety:
Overall, PLA is a safer alternative in many uses, especially where direct contact with the human body or food products is concerned. However, it's always good to consider the entire lifecycle and conditions of use of any material to fully understand its safety implications.
PLA has a wide range of applications in the food industry. Here are five common uses you should know about:
Keep in mind that while PLA is considered more environmentally friendly than traditional plastics, its biodegradability depends on the presence of industrial composting facilities.
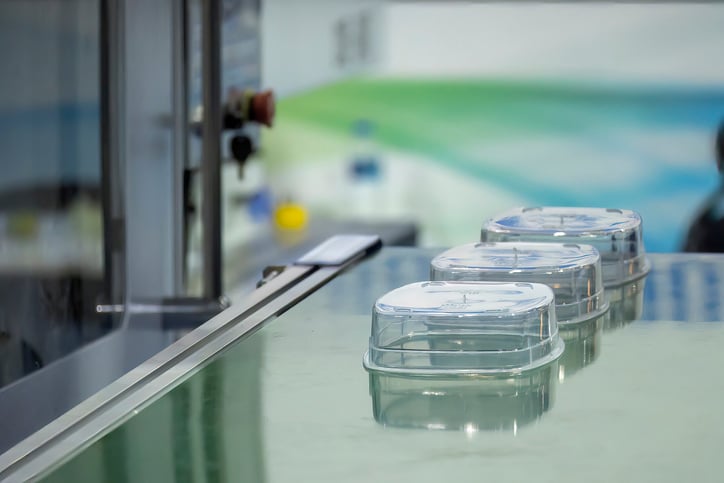

The effectiveness of PLA as food packaging can be achieved only if favorable conditions for the material are consistently maintained. This is why food handlers must ensure that PLA packaging materials are stored in the right conditions and used only for appropriate food products. FoodDocs' AI-powered Food Safety Management System can automatically generate relevant food safety monitoring tasks to help you ensure this. It offers:
Food inside PLA packaging must be at a temperature lower than 60°C (140°F). Steel hot food may cause shrinking or warping of the packaging material.
You can use FoodDocs' automatically generated monitoring tasks for logging the temperature of food before wrapping it in PLA packaging. This monitoring task will ensure that the integrity of the packaging material is retained even after shipping the packed product.
You can also further customize the temperature log by inputting the target internal temperature before packaging. Our system will then recognize this standard and suggest corrective actions in case of non-compliance.
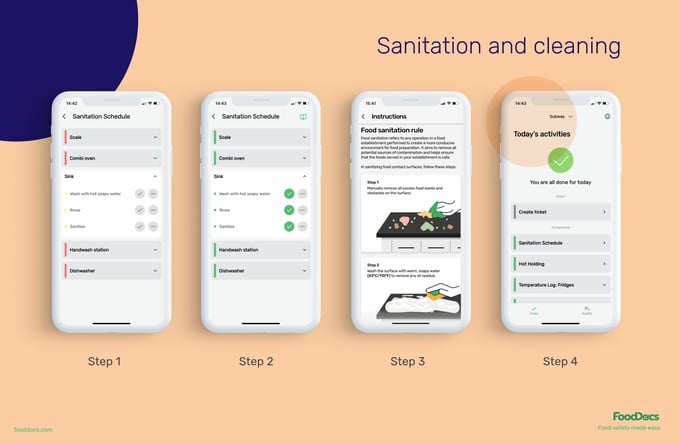
PLA must be kept in a clean space to prevent it from collecting biological hazards and causing food poisoning. This contamination is likely when you have an untidy kitchen and working area.
To prevent this, ensure that all food handlers and facilities in your business follow critical cleaning tasks using our automatically generated Cleaning and Sanitation checklist.
This checklist contains the essential tasks to protect PLA packaging and your products from any food safety hazards. You can also customize it by adding specific handling tasks for PLA packaging.
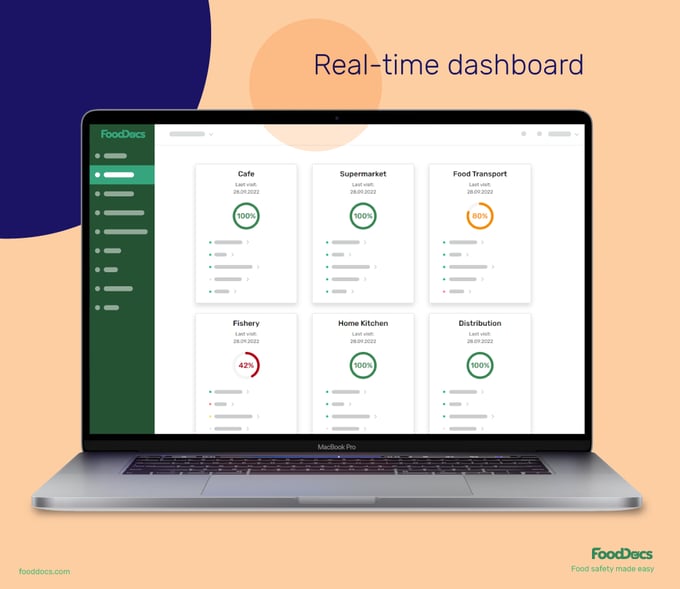
Ensure your team and operations comply with food safety standards with a quick overview using our real-time dashboard. With the help of this feature, you can easily identify key areas that require more attention. You can quickly detect non-compliant food safety tasks and come up with immediate solutions to minimize further problems.
Our research shows that this saves at least 20% of the time it takes you to supervise your team and allows you to focus on more meaningful areas of your business.
Remember, for PLA food packaging to work well, it's crucial to store it properly and maintain an appropriate food contact time. Food handlers can make this easier by relying on FoodDocs' AI-powered system, which automates monitoring tasks and helps maintain the quality of both the PLA packaging and the food inside.
Book a free demo now to understand how our software can help you.
Yes, PLA is a safe food substance that can be used in food containers. It is a commonly used material for food packaging due to its biodegradability and non-toxic composition. The chemical properties of the raw materials used make PLA a durable and eco-friendly alternative to plastics.
PLA is generally considered non-toxic and does not cause food safety concerns. However, ingesting large amounts may lead to digestive discomfort. Using PLA products as intended and not for human consumption is important.
Some forms of PLA plastic are FDA-approved for specific food contact applications. It's crucial to check the specific product's terms of food safety, certifications, and compliance with FDA regulations for the intended use.
Yes, PLA is an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional plastics and it stands out for its reduced dependence on fossil fuels.
PLA’s production involves the fermentation of natural materials to create lactic acid, which is then chemically processed and polymerized to form PLA. This reliance on renewable resources contributes to a lower emission of greenhouse gases.
However, the overall environmental impact of PLA is influenced by cultivation practices, waste management systems, and end-of-life disposal methods. Responsible use and disposal practices are essential to maximize its environmental benefits and mitigate potential drawbacks.
Yes, PLA is biodegradable. It is derived from corn starch or sugar beet pulp, making it a more sustainable alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics. It is designed to break down into simpler, natural compounds under certain conditions.
PLA’s biodegradation occurs in industrial composting facilities where high temperatures, high humidity, and the presence of microbial activity are all optimized. This leads to the growth of harmful bacteria, which starts biological decomposition and breaks PLA down into carbon dioxide, water, and organic matter.
PLA is considered non-allergenic and contains none of the common allergens we know about. Its most common ingredient, corn starch, is generally non-allergenic and has no adverse health effects on the human body. There are also no harmful chemicals associated with PLA.
Master restaurant sanitizing with clear steps for kitchens and dining areas. Learn methods, checklists, and procedures to keep your team safe and...
Learn challenges healthcare foodservice teams face today and key food safety practices to protect vulnerable patients. Get a free healthcare leader...
Learn what Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are and how to write effective SOPs that ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in your...