TWO-STAGE COOLING METHOD

Two-stage cooling method
It's true that cooking to the correct internal food temperature may be one of the most important food safety operations to protect public health. In addition to a proper cooking process, cooling the cooked food in restaurants as fast as possible can just save your food from the excessive growth of microorganisms and spoilage and your customers from any foodborne illness. One of the most effective cooling methods to make food safe is the two-stage cooling method.
Under the FDA Food Code, foods must be cooled to 21°C within two hours after cooking. Such a guide aims to protect consumers from the unwanted and rapid growth of pathogens to dangerous levels during the process. Food employees must be well guided regarding this principle and on how to properly ensure that it is being followed.
In this article, we teach you how to perform the two-stage cooling method and show you the quickest way to remind your team how and when to do it.
What is food cooling?
Food cooling refers to the critical control operation of bringing down the initial internal temperature of food, usually after cooking, to a safe temperature ready for further chilling inside a refrigerator. This proper storage food operation is performed in a commercial kitchen to prevent unnecessary bacterial growth on hot food.
As the prepared food cools down to proper temperatures, bacteria and other pathogens become more capable of growing on it. As such, the proper cooling process must be done as fast as possible to reduce the time of exposure to the foods.
What is the two-stage cooling method?
As the name suggests, the two-stage cooling method is the process of reducing the internal temperature of food using two steps. Using this method, freshly cooked foods with an internal temperature of 57°C has to cool down to 21°C within 2 hours as the first step. The first step is considered the critical time period. After cooling down, the second step requires the temperature of the food to go down to a minimum temperature of 5°C or less within the next 4 hours.
The whole two-stage cooling process is performed for a total of 6 hours. The first stage of the cooling process can be easily achieved by separating the food into containers in smaller portions and placing them in shallow containers. Alternatively, a piece of cooling equipment can be used, or placing the container of food with ice water would be effective. The second stage can be done inside the refrigerator for faster food cooling.
Freshly cooked foods are not advised to be refrigerated as their high-temperature range can significantly decrease temperature of the food in the refrigerator. This occurrence can have significant negative effects on the stored foods inside the refrigerator unit, especially on highly perishable foods.

Why is cooling food important?
Proper and fast cooling of food ensures that any cooked food will not stay at the temperature danger zone for too long. If foods being cooled stay more than two hours at 5°C to 60°C, then the risk of growth of bacteria and food poisoning increases. The temperature danger zone is the optimal growing condition for most pathogenic microorganisms. Improper cooling does not only make food unsafe but it can also lead to food waste and food poisoning.
As much as possible, foods are recommended to be cooled fast if they are intended to store for later or will not be served to customers hot. This food safety guideline also applies to potentially hazardous foods that will be placed in a cold holding equipment. Keeping food cold can help significantly prolong its shelf life.
Why do you need to monitor food cooling?
Food cooling is a time and temperature-sensitive operation. Its effectiveness is dependent on how accurately will the whole process be performed. To ensure this, food service operators must be trained to monitor food cooling and how to use an accurate food thermometer.
Time and temperature control for safety (TCS) food category must be cooled as fast as possible. The only way for food service operators to know if the process is still on track is to constantly monitor it. Regular monitoring also allows food workers to immediately apply corrective actions in case deviations occur.
Frequently asked questions
Here a few frequently asked questions to help you understand food cooling better:
How long does the two-step cooling method take?
The whole two-step cooling process takes a total of 6 hours to perform. Within the first two hours, the cooked food must be cooled from 57°C to 21°C, whereas the remaining 4 hours are dedicated to lowering the temperature to 5°C or less.
What is the maximum time allowed for Stage 2 Cooling?
As a recommended food safety standard by the Food and Drug Administration, the entire cooling process must be completed within 6 hours. An extended period beyond the time limit may increase the risk of spoilage.
What is the best cooling method?
The best way to perform the 2-stage cooling method is to divide the ready-to-eat food items into smaller portions and place the food container in an ice and cold water bath or a bigger storage container with ice packs.
What are the methods of cooling?
The 2-hour/4-hour rule on rapid cooling can be achieved by using any or a combination of methods depending on equipment availability:
- Separate food into smaller portions
- Ice-water bath
- Commercial blast chiller
- Two-stage unit refrigerator
- Tumble chillers
In the two-stage cooling method, what is the maximum for stage one?
The first stage of the two-stage cooling methodology must be achieved within 2 hours maximum time.
How can you help your team in cooling food properly?
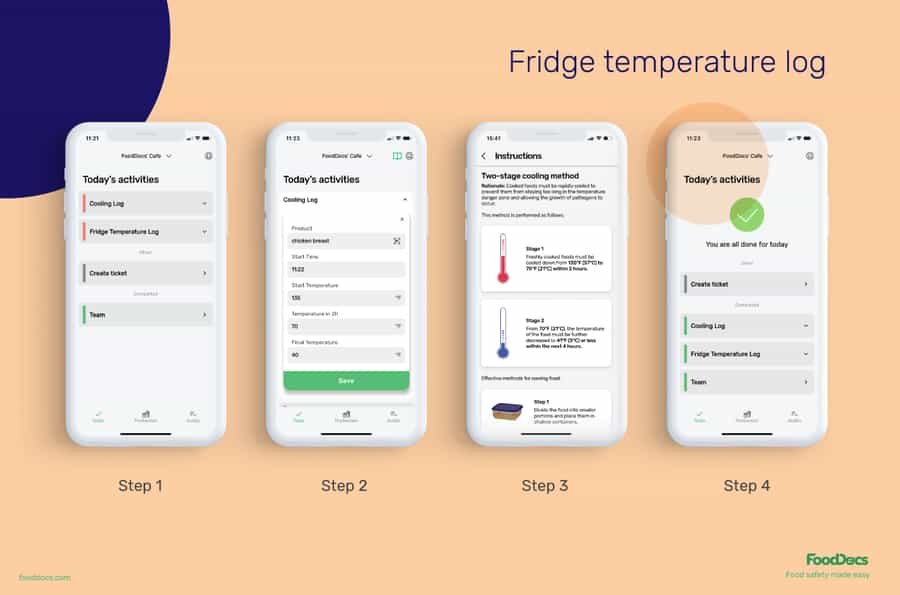
The two-stage cooling process is a very technical operation in commercial food service. It is a critical food safety practice that requires time and temperature control to become very effective. Food handlers must be well-oriented on how to perform it as well as the consequences of non-compliance from health departments. To help your team understand the process, use our free two-stage cooling method poster tool as a guide for training your employees. Additionally, this poster can be used to remind all food handlers to do the method correctly.
To be effective, your poster must be visible at all times. Download and print this food safety poster from our HACCP plan template hub for free. This poster solves one of your many food safety concerns, but how about the others? There are hundreds of other food safety operations that you need to remind and teach your employees of.
To help you optimize your operations and make food safety compliance more efficient, our team of food safety specialists at FoodDocs has come up with a digital solution for your business. Monitoring all of your food preparation tasks, including cooling foods, can be easier and more effective using our system.
With our digital solution, you can get the following benefits:
-
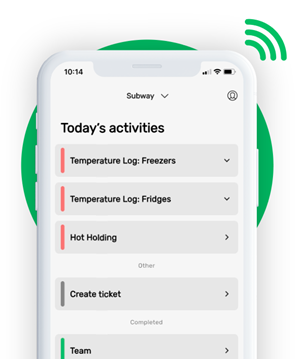
You can facilitate the onboarding and training process even better with our app's detailed instructions on each food safety operation, including cooling methods. The detailed instructions show how to properly cool foods as a reminder and how to monitor the method.
-
Our automatically generated monitoring forms can help you make more accurate information logs as they are equipped with an auto-fill feature. Not only that but this feature has been proven to save your team's time from manually inputting the information themselves. All that they need to do now is to verify the logged information, which is based on previously inserted data.
-
Help your team remember food safety tasks and deadlines using our system's smart notification feature. Use this feature to remind food handlers of when to monitor the temperature of your foods being cooled.
Monitoring cooling foods in the FoodDocs app
Our digital solution was also made to make the lives of food safety managers easier. With our digital Food Safety Management System we'd be able to help you increase your food safety compliance efficiency:
- Our system only needs an average of 15 minutes to set up. Powered by artificial intelligence, our system uses your answers to our basic questions to automatically generate the most important food safety documents for your team, including cooling log.
- Save at least 20% of your time supervising your team with our real-time dashboard. With this feature, you can oversee your operations and identify areas that need improvement at a glance.
- Collect and secure all of your digital documents in cloud storage dedicated to your business.
Going digital has never been this easy. In just about 15 minutes, you can already get a comprehensive digital food safety management system. This digital solution also contributes great significance to becoming more sustainable as you leave behind your paper-based monitoring system.
Fulfill your compliance to sensitive operations such as the two-step cooling process most efficiently through our help. If you want to try our services before committing, you can do so by availing of our free, 14-day trial.
With our digital solution onboard your food business, compliance with tough food safety regulations can be much easier. All it takes is for you to spend 15 minutes and start your food safety compliance journey with us!