FOOD REHEATING POSTER


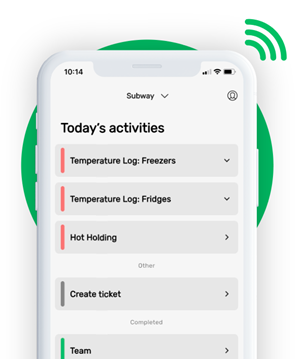
This is how our Digital Food Safety platform saves 20% of your time on daily tasks:
- Get upcoming task notifications
- Add data into the app
- Check the status of tasks in real-time

When food safety was still handled on paper, I typically spent a couple of hours per day getting the papers and going around checking or completing tasks… Now I can sit down and it's just all there in one place. It takes me 5-10 minutes.
Ruth B.
Store Manager
Reheating temperature
Some parts of every food business operating system are more vulnerable to the risk of contamination than others. A good example of this type of operation is when you reheat your food before serving or while holding it. These types of operations require close monitoring and temperature control to ensure food safety. Food handlers must first know the proper reheating temperature and consistently maintain it over time until the process is complete.
Although a very common task in households, reheating is more technical when it comes to food service establishment operations. Food handlers must prevent the risk of contamination and bacterial growth to protect consumers by following essential rules for the reheating process. Factors such as temperature, time, and size of the food container must all be considered to ensure that the operation will control the levels of pathogens.
What is the reheating temperature?
Foods must be equally reheated to an internal temperature of 74 °C for at least 15 seconds, and liquid foods, such as meat gravy and a bowl of soup, to a rolling boil to ensure food safety. This parameter has been suggested by the USDA Food Safety and Inspection Service. Food handlers must use a clean and properly calibrated food thermometer to ensure that the internal food temperature reaches the target range the entire time.
Reheating cooked or ready-to-eat foods is a critical food safety practice before serving or displaying potentially hazardous foods for hot holding or serving. It also helps reduce food waste. Reheating is also applicable to ready-to-eat food for service. This process ensures that potentially present food poisoning bacteria that may have grown during thawing or cold storage on batches of food are eliminated and will not cause significant foodborne illness.
Why is it important to monitor the reheating temperature?
The main objective of reheating cooked foods is to eliminate any potentially existing foodborne pathogens, such as harmful bacteria and viruses. To ensure that the growth of bacteria is achieved, the food must be reheated to the target core temperature.
The recommended internal temperature for reheating foods is based on the food temperature at which most pathogenic bacteria are weakest. Insufficient or uneven reheating of food may allow the survival of pathogens and potentially cause food spoilage or foodborne illness. Some people, such as pregnant women, can be very vulnerable to such issues.
Food handlers can monitor the reheating food temperature by regularly checking the internal temperature of the batches of food using a calibrated food thermometer and a cooking temperature log. Temperature monitoring can serve as proof of food safety compliance. These monitoring tasks must be part of every food safety plan and are often reviewed during restaurant inspections. Improper temperature monitoring can merit a significant violation from an environmental health officer.
Who needs to monitor the reheating temperature?
Reheating is a common food safety practice in the whole food service industry. Food handlers working in a restaurant and deli shops are required to understand how to reheat foods and monitor the reheating temperature.
Food handlers must also know the food safety rules when it comes to reheating perishable foods. Improper reheating may result in harmful foods and put the safety of consumers at risk.

What is the best way to reheat food?
The best way to reheat common food, such as frozen leftovers, depends on the types of food or meals you reheat. You can reheat foods using the following equipment:
- stovetop and pan
- oven
- microwave
The equipment you will be using must be able to perform uniform cooking and reach a safe temperature as fast as possible with the proper heat source. The longer the time it takes for cold foods to reach the correct temperature, the more opportunity there is for food contamination.
You can use any convenient method for your available food equipment. Some types of equipment will need extra tools, such as a pan or casserole for a stovetop and a microwave-safe, shallow container for a microwave. A stovetop burner is a great piece of equipment to use for large amounts of liquid food. Some types of equipment can accommodate larger quantities of foods.
To reheat foods, food service establishment operators must never use hot holding equipment, such as chafing dishes, Baine Maries (double boiler), slow cookers, and steam tables. The sole purpose of these types of equipment is to keep hot food hot and not to heat foods. The hot holding temperature is not enough to ensure food safety for reheating foods and will not be enough to prevent outbreaks of food poisoning.
Rules for reheating foods
Although fairly common, reheating foods is a technical food safety practice for food businesses. It is not enough that the food becomes warm after reheating. In fact, this is a very dangerous step. Food handlers must be familiar with the required steps and rules for reheating foods.
Below are some of the most important things to remember and basic food safety tips when reheating foods:
- Reheat foods immediately after removing them from the refrigerator. Refrigerated foods, whether recently thawed frozen food or not, must be immediately reheated once you take them out of the proper cooling unit. High-risk foods, such as cooked meat, chicken, and green vegetables, must not be exposed to the food safety temperature danger zone, which is the optimal condition for the growth of bacteria. These foods require time and temperature control for safety and must be handled with critical care.
- Reheat foods to the correct internal temperature. As mentioned, it is not enough to just warm ready-to-eat foods. Reaching the correct internal cooking temperature of foods during reheating ensures that there are no existing pathogenic hazards in the food. The food must reach the minimum temperature of 74 °C for at least 15 seconds.
- Use a food thermometer to measure the current temperature. The only accurate way to be sure that the reheating process is properly done the entire time is to use a food thermometer to guide food handlers. Ensure that the kitchen thermometer you will use is properly calibrated. Use our Thermometer Calibration Chart as a guide.
- Reheat foods once. Although there is no strict rule of how many times you can reheat frozen food, food handlers are suggested to do so only once. Reheated food products exposed to external factors during preparation or hot holding are very prone to transferring pathogens to food. To prevent loss of food quality and food safety issues, such as the unwanted multiplication of bacteria, food handlers must limit reheating of foods.
- Serve the reheated foods immediately. Delaying the service of reheated food, especially high-risk food items like leafy greens, cooked poultry, and egg products, increases the chance of outbreaks of food poisoning.
- Use the proper equipment for reheating foods. Reheating is commonly accomplished using a microwave, an oven, or a saucepan. The proper equipment is important to reach the cold spots of foods in the fastest method possible. Never use hot-holding equipment to reheat items of food.
- Do not overload reheating equipment. Overloading your reheating equipment can make the process more inefficient and produce contaminated foods. Reheat individual dishes or batches of food at a time and monitor the reheating temperature closely. Advance preparation must be done by portioning foods that will fit the reheating equipment.
What can go wrong when reheating food?
The reheating process presents several opportunities for food contamination. The risk of food poisoning increases with improper reheating methods. In addition to reheating, extra steps such as preparing and serving food must also be properly conducted to ensure food safety.
What could go wrong when food service operators do not know how to reheat foods? Here are a few mistakes your team might make when performing any method for reheating.
- The internal food temperature is not reached. This goal is mandatory for any reheating method of food. Reaching the target safe temperature ensures the safety of the food that will be served.
- The reheated food was held for a very long time. As reheated foods have already been exposed to the surrounding environment, the risk of contamination is already present. Holding reheated perishable foods for extended periods can be dangerous for customers.
- Foods were not properly stored at refrigerated food temperatures before reheating. You can only expect safe food from reheating if the materials are properly prepared and stored. Make sure to store foods for later reheating in airtight containers, preferably microwave safe, before refrigerating. This rule includes ensuring a clean food contact surface for preparing and storing food for service.
- The food was improperly thawed before reheating. Thawing foods in advance is commonly a preparation before reheating, such as for frozen leftover food. It is not an additional reheat step that can be skipped. If the refrigerator thawing process is not properly done, reheating may become ineffective. Food spoilage may occur right after improper refrigerator thawing, or longer reheating time may be required due to the increased microbial load.
Food service operators must always be knowledgeable on how to perform reheating, whether it is using a microwave oven or a toaster oven with food thermometers or a stovetop burner. Timing and proper monitoring are essential to always make sure that the reheating process will result in safe foods.
Use our diverse selection of Cooking Temperature Charts to help your food handlers ensure proper reheating and cooking of foods.
How can you help your team to complete reheating correctly?
Precision and focus are key ingredients when monitoring any reheating process. Contamination of foods prepared may occur without properly observing the steps for reheating foods. Food handlers require constant guidance and reminders on performing reheating. To solve this problem, you can use our Reheating Temperature Poster. Place this chart near a visible and accessible spot to serve as a reference for your employees.
In addition to our useful Reheating Temperature Chart, we offer a more advanced digital solution to help your team correctly complete reheating all the time. Take our FoodDocs application into use and get the following benefits:
- Get intuitive alerts reminding food handlers when it is the proper time to complete reheating monitoring tasks using our smart notification system. Using this system, you can always ensure that no one forgets to complete temperature logs.
- Use our auto-fill solution that automatically prefills monitoring logs to save you time from doing repetitive food safety tasks. This solution can significantly improve the accuracy of your monitoring data and would only require food handlers to verify the information.
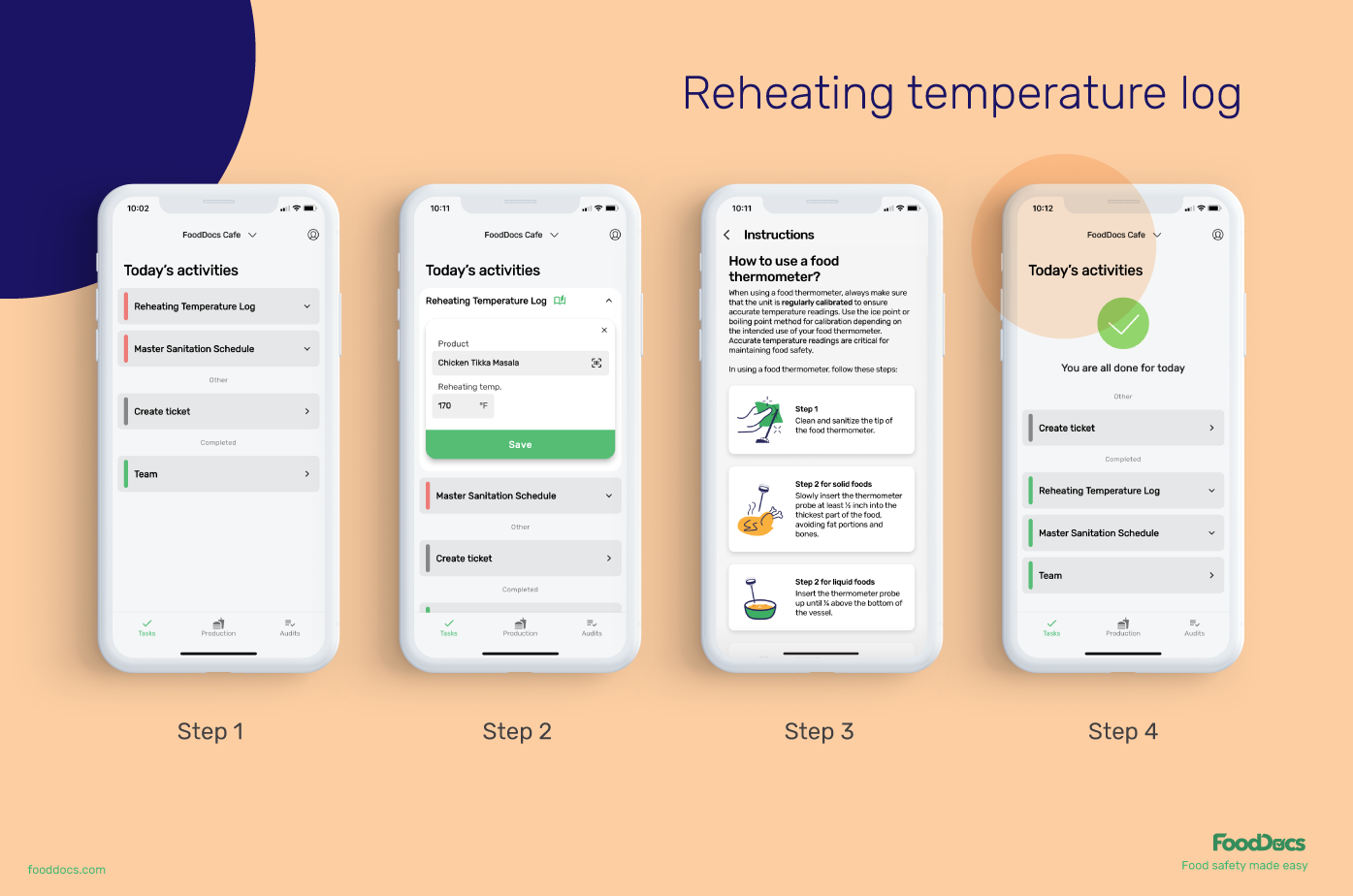
Reheating temperature log with training instructions in FoodDocs' app
How can digital solutions save managers time?
In addition to the many features that our system offers to improve the efficiency of your team, our digital Food Safety Management System can also help managers save time from overseeing their food safety practices:
- Switching to our digital solution from a paper-based system would only require 15 minutes. You can get a comprehensive digital food system even without prior knowledge of how to make one.
- Our digital FSMS software can be fully integrated with IoT sensors (Internet of Things). Our system allows the integration of these equipment sensors to instantly reflect temperature readings on your FoodDocs desktop. You can see a real-time overview of your operations and save significant time from manually supervising your team.
- Store all of your digital food safety documents in cloud-based storage. This secure storage system ensures that you can access and organize everything at any time.
Going digital has never been this easy. As we have mentioned, you do not need a thorough knowledge of how to make a food safety management system to get one when you use our digital solution. Using artificial intelligence and a machine-learning program, our system can provide you with the most important food safety documents for your business.
Become more sustainable and efficient with our digital Food Safety Management System now. You can experience all of our features for free by using our 14-day trial.